Detailed analysis of Node timer
JavaScript runs in a single thread, and asynchronous operations are particularly important. This article mainly introduces you to the relevant knowledge of Node timer. As long as you use functions other than the engine, you need to interact with the outside to form asynchronous operations. Because there are so many asynchronous operations, JavaScript has to provide a lot of asynchronous syntax.
Node’s asynchronous syntax is more complicated than that of a browser, because it can talk to the kernel, and a special library libuv has to be built to do this. This library is responsible for the execution time of various callback functions. After all, asynchronous tasks must eventually return to the main thread and be queued for execution one by one.
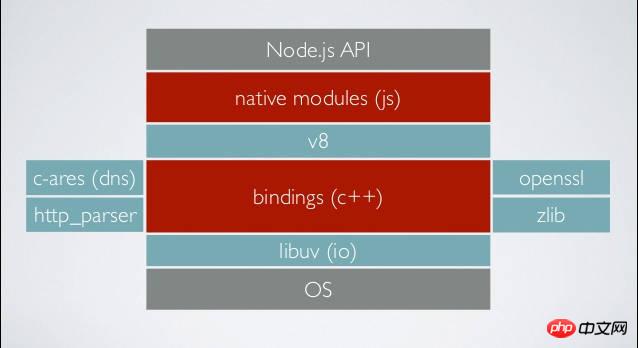
In order to coordinate asynchronous tasks, Node actually provides four timers so that tasks can run at specified times.
setTimeout()
setInterval()
setImmediate()
process.nextTick()
The first two are language standards, and the last two are unique to Node. They are written in similar ways and have similar functions, so it is not easy to distinguish them.
Can you tell me the result of running the following code?
// test.js setTimeout(() => console.log(1)); setImmediate(() => console.log(2)); process.nextTick(() => console.log(3)); Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log(4)); (() => console.log(5))();
The running results are as follows.
$ node test.js
If you can get it right right away, you may not need to read any more. This article explains in detail how Node handles various timers, or more broadly, how the libuv library arranges asynchronous tasks to be executed on the main thread.
1. Synchronous tasks and asynchronous tasks
First of all, synchronous tasks are always executed earlier than asynchronous tasks.
In the previous piece of code, only the last line is a synchronization task, so it is executed earliest.
(() => console.log(5))();
2. This cycle and the second cycle
Asynchronous tasks can be divided into two types.
Add asynchronous tasks in this cycle
Add asynchronous tasks in the second cycle
The so-called "loop" refers to the event loop. This is how the JavaScript engine handles asynchronous tasks, which will be explained in detail later. Just understand here that this cycle must be executed earlier than the second cycle.
Node stipulates that the callback functions of process.nextTick and Promise are appended to this cycle, that is, once the synchronization tasks are completed, they will be executed. The callback functions of setTimeout, setInterval, and setImmediate are added in the second cycle.
This means that the third and fourth lines of the code at the beginning of the article must be executed earlier than the first and second lines.
// 下面两行,次轮循环执行 setTimeout(() => console.log(1)); setImmediate(() => console.log(2)); // 下面两行,本轮循环执行 process.nextTick(() => console.log(3)); Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log(4));
3. process.nextTick()
The name process.nextTick is a bit misleading. It is executed in this cycle and is the fastest among all asynchronous tasks.

#After Node has executed all synchronization tasks, it will then execute the task queue of process.nextTick. So, the following line of code is the second output.
process.nextTick(() => console.log(3));
Basically, if you want an asynchronous task to execute as fast as possible, use process.nextTick.
4. Microtasks
According to the language specifications, the callback function of the Promise object will enter the "microtask" queue in the asynchronous task.
The microtask queue is appended to the process.nextTick queue and also belongs to this cycle. Therefore, the following code always outputs 3 first and then 4.
process.nextTick(() => console.log(3)); Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log(4)); // 3 // 4

Note that the next queue will not be executed until the previous queue is completely emptied.
process.nextTick(() => console.log(1)); Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log(2)); process.nextTick(() => console.log(3)); Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log(4)); // 1 // 3 // 2 // 4
In the above code, all process.nextTick callback functions will be executed earlier than Promise.
At this point, the execution sequence of this cycle is finished.
同步任务 process.nextTick() 微任务
5. The concept of event loop
The following begins to introduce the execution sequence of the second round of loops. This requires understanding what an event loop is.
First of all, some people think that in addition to the main thread, there is a separate event loop thread. That's not the case, there is only one main thread, and the event loop is completed on the main thread.
Secondly, when Node starts executing the script, it will initialize the event loop first, but the event loop has not started yet, and the following things will be completed first.
Synchronous tasks
Issue an asynchronous request
-
Plan the time when the timer takes effect
Execute process.nextTick() and so on
Finally, after all the above things are done, the event loop officially begins.
6. Six stages of event loop
The event loop will be executed infinitely, round after round. Execution will stop only when the callback function queue of the asynchronous task is cleared.
Each round of event loop is divided into six stages. These stages are executed sequentially.
timers
I/O callbacks
idle, prepare
poll
check
close callbacks
Each stage has A first-in, first-out queue of callback functions. Only when the callback function queue of one stage is cleared and all callback functions that should be executed are executed, will the event loop enter the next stage.
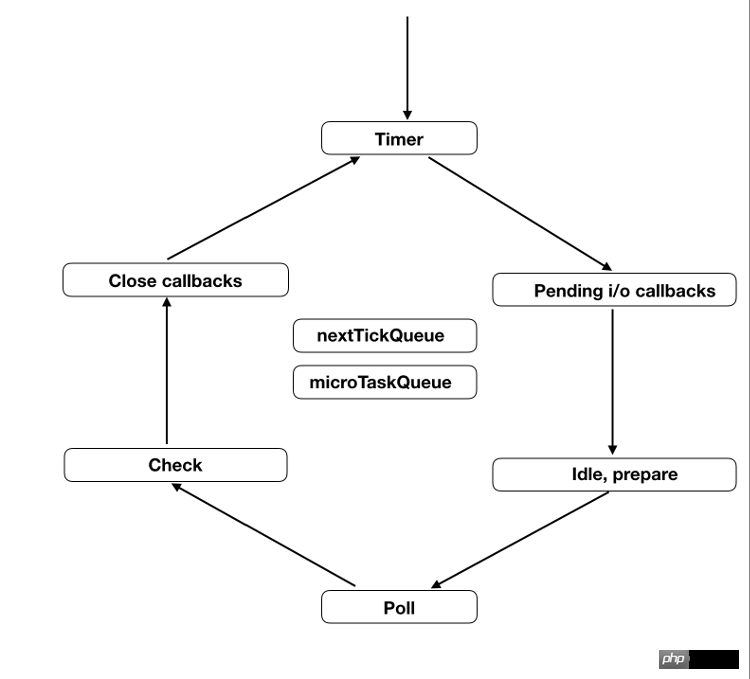
下面简单介绍一下每个阶段的含义,详细介绍可以看官方文档,也可以参考 libuv 的源码解读。
(1)timers
这个是定时器阶段,处理setTimeout()和setInterval()的回调函数。进入这个阶段后,主线程会检查一下当前时间,是否满足定时器的条件。如果满足就执行回调函数,否则就离开这个阶段。
(2)I/O callbacks
除了以下操作的回调函数,其他的回调函数都在这个阶段执行。
setTimeout()和setInterval()的回调函数
setImmediate()的回调函数
用于关闭请求的回调函数,比如socket.on('close', ...)
(3)idle, prepare
该阶段只供 libuv 内部调用,这里可以忽略。
(4)Poll
这个阶段是轮询时间,用于等待还未返回的 I/O 事件,比如服务器的回应、用户移动鼠标等等。
这个阶段的时间会比较长。如果没有其他异步任务要处理(比如到期的定时器),会一直停留在这个阶段,等待 I/O 请求返回结果。
(5)check
该阶段执行setImmediate()的回调函数。
(6)close callbacks
该阶段执行关闭请求的回调函数,比如socket.on('close', ...)。
七、事件循环的示例
下面是来自官方文档的一个示例。
const fs = require('fs');
const timeoutScheduled = Date.now();
// 异步任务一:100ms 后执行的定时器
setTimeout(() => {
const delay = Date.now() - timeoutScheduled;
console.log(`${delay}ms`);
}, 100);
// 异步任务二:至少需要 200ms 的文件读取
fs.readFile('test.js', () => {
const startCallback = Date.now();
while (Date.now() - startCallback < 200) {
// 什么也不做
}
});上面代码有两个异步任务,一个是 100ms 后执行的定时器,一个是至少需要 200ms 的文件读取。请问运行结果是什么?
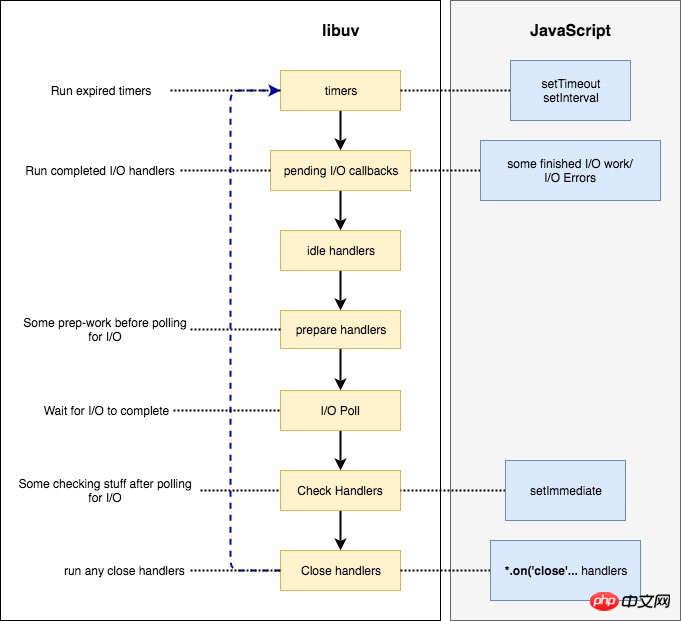
脚本进入第一轮事件循环以后,没有到期的定时器,也没有已经可以执行的 I/O 回调函数,所以会进入 Poll 阶段,等待内核返回文件读取的结果。由于读取小文件一般不会超过 100ms,所以在定时器到期之前,Poll 阶段就会得到结果,因此就会继续往下执行。
第二轮事件循环,依然没有到期的定时器,但是已经有了可以执行的 I/O 回调函数,所以会进入 I/O callbacks 阶段,执行fs.readFile的回调函数。这个回调函数需要 200ms,也就是说,在它执行到一半的时候,100ms 的定时器就会到期。但是,必须等到这个回调函数执行完,才会离开这个阶段。
第三轮事件循环,已经有了到期的定时器,所以会在 timers 阶段执行定时器。最后输出结果大概是200多毫秒。
八、setTimeout 和 setImmediate
由于setTimeout在 timers 阶段执行,而setImmediate在 check 阶段执行。所以,setTimeout会早于setImmediate完成。
setTimeout(() => console.log(1)); setImmediate(() => console.log(2));
上面代码应该先输出1,再输出2,但是实际执行的时候,结果却是不确定,有时还会先输出2,再输出1。
这是因为setTimeout的第二个参数默认为0。但是实际上,Node 做不到0毫秒,最少也需要1毫秒,根据官方文档,第二个参数的取值范围在1毫秒到2147483647毫秒之间。也就是说,setTimeout(f, 0)等同于setTimeout(f, 1)。
实际执行的时候,进入事件循环以后,有可能到了1毫秒,也可能还没到1毫秒,取决于系统当时的状况。如果没到1毫秒,那么 timers 阶段就会跳过,进入 check 阶段,先执行setImmediate的回调函数。
但是,下面的代码一定是先输出2,再输出1。
const fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('test.js', () => {
setTimeout(() => console.log(1));
setImmediate(() => console.log(2));
});上面代码会先进入 I/O callbacks 阶段,然后是 check 阶段,最后才是 timers 阶段。因此,setImmediate才会早于setTimeout执行。
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of Detailed analysis of Node timer. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 A deep dive into the meaning and usage of HTTP status code 460
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:29 PM
A deep dive into the meaning and usage of HTTP status code 460
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:29 PM
In-depth analysis of the role and application scenarios of HTTP status code 460 HTTP status code is a very important part of web development and is used to indicate the communication status between the client and the server. Among them, HTTP status code 460 is a relatively special status code. This article will deeply analyze its role and application scenarios. Definition of HTTP status code 460 The specific definition of HTTP status code 460 is "ClientClosedRequest", which means that the client closes the request. This status code is mainly used to indicate
 iBatis and MyBatis: Comparison and Advantage Analysis
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:53 PM
iBatis and MyBatis: Comparison and Advantage Analysis
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:53 PM
iBatis and MyBatis: Differences and Advantages Analysis Introduction: In Java development, persistence is a common requirement, and iBatis and MyBatis are two widely used persistence frameworks. While they have many similarities, there are also some key differences and advantages. This article will provide readers with a more comprehensive understanding through a detailed analysis of the features, usage, and sample code of these two frameworks. 1. iBatis features: iBatis is an older persistence framework that uses SQL mapping files.
 Detailed explanation of Oracle error 3114: How to solve it quickly
Mar 08, 2024 pm 02:42 PM
Detailed explanation of Oracle error 3114: How to solve it quickly
Mar 08, 2024 pm 02:42 PM
Detailed explanation of Oracle error 3114: How to solve it quickly, specific code examples are needed. During the development and management of Oracle database, we often encounter various errors, among which error 3114 is a relatively common problem. Error 3114 usually indicates a problem with the database connection, which may be caused by network failure, database service stop, or incorrect connection string settings. This article will explain in detail the cause of error 3114 and how to quickly solve this problem, and attach the specific code
 Analysis of new features of Win11: How to skip logging in to Microsoft account
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:24 PM
Analysis of new features of Win11: How to skip logging in to Microsoft account
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:24 PM
Analysis of new features of Win11: How to skip logging in to a Microsoft account. With the release of Windows 11, many users have found that it brings more convenience and new features. However, some users may not like having their system tied to a Microsoft account and wish to skip this step. This article will introduce some methods to help users skip logging in to a Microsoft account in Windows 11 and achieve a more private and autonomous experience. First, let’s understand why some users are reluctant to log in to their Microsoft account. On the one hand, some users worry that they
 Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Detailed explanation and installation guide for PiNetwork nodes This article will introduce the PiNetwork ecosystem in detail - Pi nodes, a key role in the PiNetwork ecosystem, and provide complete steps for installation and configuration. After the launch of the PiNetwork blockchain test network, Pi nodes have become an important part of many pioneers actively participating in the testing, preparing for the upcoming main network release. If you don’t know PiNetwork yet, please refer to what is Picoin? What is the price for listing? Pi usage, mining and security analysis. What is PiNetwork? The PiNetwork project started in 2019 and owns its exclusive cryptocurrency Pi Coin. The project aims to create a one that everyone can participate
 Analysis of the meaning and usage of midpoint in PHP
Mar 27, 2024 pm 08:57 PM
Analysis of the meaning and usage of midpoint in PHP
Mar 27, 2024 pm 08:57 PM
[Analysis of the meaning and usage of midpoint in PHP] In PHP, midpoint (.) is a commonly used operator used to connect two strings or properties or methods of objects. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into the meaning and usage of midpoints in PHP, illustrating them with concrete code examples. 1. Connect string midpoint operator. The most common usage in PHP is to connect two strings. By placing . between two strings, you can splice them together to form a new string. $string1=&qu
 Apache2 cannot correctly parse PHP files
Mar 08, 2024 am 11:09 AM
Apache2 cannot correctly parse PHP files
Mar 08, 2024 am 11:09 AM
Due to space limitations, the following is a brief article: Apache2 is a commonly used web server software, and PHP is a widely used server-side scripting language. In the process of building a website, sometimes you encounter the problem that Apache2 cannot correctly parse the PHP file, causing the PHP code to fail to execute. This problem is usually caused by Apache2 not configuring the PHP module correctly, or the PHP module being incompatible with the version of Apache2. There are generally two ways to solve this problem, one is
 Parsing Wormhole NTT: an open framework for any Token
Mar 05, 2024 pm 12:46 PM
Parsing Wormhole NTT: an open framework for any Token
Mar 05, 2024 pm 12:46 PM
Wormhole is a leader in blockchain interoperability, focused on creating resilient, future-proof decentralized systems that prioritize ownership, control, and permissionless innovation. The foundation of this vision is a commitment to technical expertise, ethical principles, and community alignment to redefine the interoperability landscape with simplicity, clarity, and a broad suite of multi-chain solutions. With the rise of zero-knowledge proofs, scaling solutions, and feature-rich token standards, blockchains are becoming more powerful and interoperability is becoming increasingly important. In this innovative application environment, novel governance systems and practical capabilities bring unprecedented opportunities to assets across the network. Protocol builders are now grappling with how to operate in this emerging multi-chain






