A senior programmer's summary of JavaScript arrays
The
data type in JavaScript must be used in our daily development of JavaScript. Array is one of them. In PHP There is almost no difference between arrays and arrays in JavaScript. In this article, let’s take a look at how senior programmers summarize JavaScript arrays
1. The concept of array
1.1 What is an array
An array refers to an ordered list of data.
Each value in the array is called an element of the array.
Each element in the array has a position, which is called the index (subscript, index). The index of the array starts from 0
There are no restrictions on the type of elements in the same array. In other words, Number, String, Boolean, Object objects, etc. can be used in the same array. Any type can be put in at the same time. Even the elements in an array can be another array (constituting a multi-dimensional array).
1.2 Characteristics of arrays in JavaScript
Although every language has data structures such as arrays, JavaScript arrays have Very different.
The array length can be changed dynamically.
Different data types can be stored in the same array.
An ordered collection of data
-
Each array has a length attribute, which represents the number of elements in the array
2. Creation of Arrays
There are two basic ways to create arrays: literal method and Constructor
2.1 Literal method
Array literal: All elements are enclosed in square brackets, and different elements are separated by commas.
//例如: [“a”, 5, “b”]
//创建一个长度为 3 的数组,并初始化了3 个元素:"abc" "b" "d" var colors = ["abc", "b", "d"]; //创建一个长度为 0 的空数组数组。里面一个值都没有 var colors = []; //不要在最后一个元素的后面添加逗号,添加逗号虽然语法没有问题,但是在不同的浏览器可能得到不同的结果 var colors = [5, 6, 7,]; //这样数组的长度可能为 3 也可能为 4。在不同浏览器会得到不同的结果应避免这种创建方式。
2.2 Constructor method
The constructor is used when creating an object. Array constructor type Array()
例如: new Array(数组长度);
//创建一个长度为 0 的空数组
var colors = new Array();
//创建一个长度为 5 的数组。每个数组的元素的默认值是 undefined。
var colors = new Array(5);
//创建一个长度为 3 的数组,并且3个元素分别是 "blue" "red" "green"
var colors = new Array("blue", "red", "green");Note:
When using the constructor to create an array object, do not add after the last element brackets, otherwise an error will be reported. This is wrong: new Array("a", )
If only one Number value is passed in when using the constructor, this value must be >= 0, otherwise an error will be reported.
When using the constructor to create an array object, the new keyword can be omitted. For example: Array(5) This is OK.
3. Access and modify elements in the array
Use the index to access the elements in the array.
If the length of the array is 5, then the index of the array is 0,1,2,3,4
//创建一个长度为 5 的数据 var arr = [10, 20, 60, 5, 7]; alert(arr[0]); //获取下标为 0 的元素, 即:10 alert(arr[2]); //获取下标为 2 的元素, 即:60 arr[1] = 100; //把下标为 1 的元素赋值为100。
4. The length of the array
4.1 Get the length of the array
Every array has an attribute called length, which represents the length of the array (ie: the number of elements).
var arr = [10, 20, 60, 5, 7]; alert(arr.length); //弹出:5
4.2 Modify the length of the array
In general strongly typed languages, the length of the array is fixed, that is: once the array is created successfully, the array cannot be changed. length.
However, JavaScript is a weakly typed dynamic language, and the length of the array can be dynamically changed as needed during the running of the program.
==The array length property is not read-only, but can be modified. ==
1. Directly modify the length of the array to the specified value by setting the length value.
var arr = ["a", 8, "bc"]; //数组的长度为 3 arr.length = 6; // 修改数组的长度为 6 alert(arr.length); //数组的长度已经被修改为了 6 ,所以此处输出6. // 下标为 3, 4, 5 的元素的值为undefined的。 alert(arr[3]); //弹出:undefined的。 arr.length = 2; // 修改数组的长度为 2 ,则下标为 >= 的元素被自动从数组移除。
2. Dynamically modify the length of the element by assigning a value to the last element.
var arr = [4, 6, 8]; // 给下标为 10 的元素赋值为 100. 由于最初长度为 3 ,这个赋值操作完成后,数组的长度会自动增长为11 arr[10] = 100; alert(arr.length); // 弹出:11 // 没有赋值的元素默认都为 undefined alert(arr[5]); //弹出:undefined alert(arr[20]); //弹出: undefined alert(arr.length); // 长度仍然为11. 上一行代码仅仅去访问元素,而没有赋值操作,则不会引起数组长度的变化
- for loop
- for… in
- for each (ES5 new)
5.1 Use a normal for loop to traverse the array
var arr = [50, 20, 10, 5, 15, 6];
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){ //数组长度多长,就遍历多少次。 循环变量作为数组的下标
console.log(arr[i]);
}12345.2 Use for...in to loop through the array
The for-in statement is a A precise iteration statement that can be used to enumerate the properties of an object and the elements of an array. Example:var arr = [50, 20, 10, 5, 15, 6];
// 每循环一轮,都会把数组的下标赋值给变量index,然后num就拿到了每个元素的下标。
//注意:这里index是元素的下标,不是与元素
//对数组来说,index从从0开始顺序获取下标
for (var index in arr) {
console.log(num); //循环输出: 0 1 2 3 4 5
}
//这里var 关键字也是可以省略的,但是不建议省略。
for(i in arr){
console.log(arr[i]);
}5.3 Use for...each to traverse the array
ES5 adds a new method array.forEach(function) for each array , using this method can automatically help us traverse all the elements in the arrayvar arr = [50, 20, 10, 5, 15, 6];
//调用数组的forEach方法,传入一个匿名函数
//匿名函数接受两个参数: 参数1--迭代遍历的那个元素 参数2:迭代遍历的那个元素的下标
//可以在匿名函数内部书需要的代码
arr.forEach( function(element, index) {
alert(element);
});6. Common array methods
6.1 Conversion Method
toString() conversion method:- Returns a comma-separated string concatenated by the string form of each value in the array
<script type="text/javascript"> var arr = [50, 20, 10, 5, 15, 6]; alert(arr.toString()); // 50,20,10,5,15,6 alert(arr); // 50,20,10,5,15,6 当把一个对象直接给alert,则会调用这个对象的toString方法,然后再输出。 </script>
toString() 方法只能使用逗号连接,而 join() 方法可以使用指定的连接符连接
<script type="text/javascript">
var arr = [50, 20, 10, 5, 15, 6];
alert(arr.join("=")); // 50=20=10=5=15=6
</script>6.2 栈方法
栈:一种数据结构。特点:FILO (先进后出)
向栈中存入元素 称之为 入栈(push)、从栈中移除元素称之为出栈(pop)。先入栈的元素在栈地下,后入栈的元素在栈顶。这两个动作都是对栈顶的元素进行操作。一般栈提供这两个操作足矣。
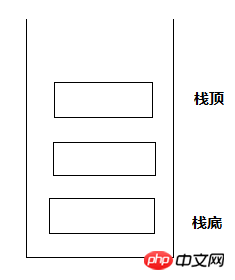
JavaScript中,支持像操作栈一样去操作数组。
<script type="text/javascript">
var arr = ["张三", "李四", "王五"];
//向栈中添加元素(最后添加的元素肯定在栈顶) 数组中的元素:"张三", "李四", "王五", "志玲"
var len = arr.push("志玲"); //push方法返回添加成功后的数组的长度
alert(len); // 弹出:4
arr.push("a", "b"); //也可以向在push方法中传入多个参数,这样每个参数都会添加到数组中。 栈顶元素是 "b"
//pop出栈,一次只能出栈一个元素
var item = arr.pop(); //把栈顶的元素从栈(数组)中移除。并返回移除的这个元素
alert(item); // 弹出:b
</script>说明:
入栈其实就是把新的元素添加到数组的后面
出栈其实就是把数组中的最后一个元素从数组中移除
6.2队列方法
队列也是一种数据结构。 特点:FIFO(先进先出)
JavaScript中,对数组的操作也提供了模拟队列的方法。
向队列头部添加元素(unshift)、从队列头部移除元素(shift)
向队列尾部添加元素、从队列尾部移除元素
注意:对队列尾部的操作没有提供新的方法,使用push和pop可以完成相应的操作。
<script type="text/javascript">
//把arr当做队列对待,那么 队列头部元素就是 "张三", 队尾元素就是 "王五"
var arr = ["张三", "李四", "王五"];
var firstItem = arr.shift(); //把队首元素从队列中移除,并返回移除的这个元素
alert(firstItem); //张三
alert(arr); // 李四, 王五
var len = arr.unshift("志玲"); //向队列头部添加元素,并返回添加成功后队列(数组)的长度
alert("数组长度:" + len); // 数组长度:3
alert(arr); // 志玲, 李四, 王五
arr.unshift("a", "b");
alert(arr); // a, b, 志玲, 李四, 王五
</script>6.3 数组中元素的倒置
<script type="text/javascript">
var arr = ["张三", "李四", "王五"];
alert("数组倒置前:" + arr);
//对数组元素进行倒置。
arr.reverse();
alert("数组倒置后:" + arr);
</script>注意:
==倒置操作是对原数组本身做了操作,返回的也是原数组对象,并不是一个新创建的数组。==
6.4 查找指定元素在数组中的索引
indexOf(item): 从前面开始向后查找 item 第一次出现的位置
lastIndexOf(item): 从尾部开始向前查找 item 第一次出现的位置
如果找不到元素,则返回 -1
<script type="text/javascript">
var arr = ["张三", "张三", "李四", "王五", "张三", "李四", "王五"];
alert(arr.indexOf("张三")); // 0
alert(arr.lastIndexOf("张三")); // 4
</script>indexOf(item, fromBack): 从第二个参数的位置开向后始查找 item 第一次出现的位置
lastIndexOf(item, fromForward): 从第二个参数的位置开始向前查找 item 第一次出现的位置
<script type="text/javascript">
var arr = ["张三", "张三", "李四", "王五", "张三", "李四", "王五"];
alert(arr.indexOf("张三", 2)); // 4
alert(arr.lastIndexOf("张三", 3)); // 1
</script>6.4 获取新的数组
arr.contact(arrayX,arrayX,……,arrayX)
该方法用于连接两个或多个数组。至少传入一个参数,参数可以是数组也可以是元素。
==注意:该方法是返回的一个新的数组,原数组没有做任何改变==
<script type="text/javascript">
var arr1 = ["a", "b", "c"];
//把参数数组与arr1连接起来,并返回连接后的新数组
var newArr = arr1.concat(["c", "d"]);
//新数组的长度是 5
alert(newArr.length);
//原数组的长度还是 3 。原数组中的元素没有做任何变化
alert(arr1.length);
//把两个元素和一个数组与原数组arr1连接起来,并返回新的数组
var newArr2 = arr1.concat("e", "f", ["g", "h"]);
//新数组长度为:7
alert(newArr2.length);
</script>arr.slice(start,end) : 截取数组,并返回截取到的新数组
start:必须。从原数组中的start位置开始截取==(包括下标为start的元素)==。 如果是负数表示从尾部开始截取: -1表示最后一个元素
end: 可选。截取到指定位置==(不包括下标为end的元素)==。如果没指定,则指的是截取到最后一个元素
end要大于start,否则截取不到元素
==注意:该方法是返回的一个新的数组,原数组没有做任何改变==
<script type="text/javascript">
var arr1 = ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"];
// 从下标为0的位置开始截取,截取到下标2,但是不包括下标为2的元素. 原数组没有任何的变化
var newArr = arr1.slice(0, 2);
alert(newArr);// a, b
alert(arr1.slice(1, 4)); // b,c,d
//从下标为2的元素开始截取,一直到最后一个元素
alert(arr1.slice(2)); //c,d,e,f
//从倒数第5个元素,截取到倒数第2个
alert(arr1.slice(-5, -2)); // b c d
</script>arr.splice(index,howmany,item1,…..,itemX) 方法向/从数组中添加/删除元素,然后==返回被删除的元素组成的数组。==
必需。整数,规定添加/删除元素的位置,使用负数可从数组结尾处规定位置。
必需。要删除的元素数量。如果设置为 0,则不会删除元素。 如果添加元素这里应该是0
可选。向数组添加的新项目。
==注意:这个方法会对原数组做出修改。==
删除元素
<script type="text/javascript">
var arr1 = ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"];
//因为第2个参数不为0,所以表示删除元素:从小标为1的位置开始删除,共删除2个元素。(2个中包括下标为1的元素)
var deleted = arr1.splice(1, 2); //返回值为删除的元素组成的数组
//原数组
alert(arr1); // a,d,e,f
alert(deleted); // b,c
</script>添加元素
<script type="text/javascript">
var arr1 = ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"];
//因为第2参数为0,所以表示添加元素:从下标为1的位置插入元素。其余的元素会自动向后移动
var v = arr1.splice(1, 0, "m", "n"); // 因为是添加元素,所以返回的数组长度为 0
alert(v.length); // 0
alert(arr1); // a,m,n,b,c,d,e,f
</script>七、 数组排序
JavaScript中,所有的数组对象都提供了一个排序函数。
arr.sort(sortby) 方法用于对数组的元素进行排序。
sortby 可选。规定排序顺序。必须是函数。
不传入参数的时候,是默认的升序排列。但是做升序排列的时候,是把每个元素转换成string之后,按照编码表中的顺序排序的。
<script type="text/javascript">
var arr1 = ["a", "ab", "fca", "cd", "eb", "f"];
arr1.sort(); //默认情况按照编码表中的顺序排列
alert(arr1); // a, ab, cd, eb, f, fca
var arr2 = [10, 8, 6, 20, 30, 15];
arr2.sort();
console.alert(arr2); // 10,15,20,30,6,8</script>从上面可以看出来,当数组中的元素是Number的时候,按照编码表排序并不太符合我们的预期,我们更想按照数字的大小排序。这时,我们可以传递一个 “比较函数”。
<script type="text/javascript">
/*
sort方法进行排序的时候,会调用这个函数,来确定谁大谁小,从而来确定他们的位置。
排序函数的规则:
1、比较函数必须具有两个参数 num1, num2
2、若返回值 > 0, 则认为num1 > num2, 排序的时候num1在num2之后
3、若返回值 == 0,则认为num1== num2,排序的时候两个数的顺序就保持不变
4、若返回值 < 0, 则认为num < num2, 排序的时候num1在num2之前。
总结:
1、若num1 > num2 返回 正数, num1 < num2 返回 负数,则是升序
2、若num1 > num2 返回 负数, num1 < num2 返回 正数,则是降序
*/
function sortNumber (num1, num2) {
//升序
if(num1 > num2){
return 1;
}else if(num1 == num2){
return 0;
}else {
return -1;
}
}
var arr2 = [10, 8, 6, 20, 30, 15];
arr2.sort(sortNumber);
console.log(arr2.toString());
</script>纯数字的数组,还有一种更简洁的排序函数。
//升序函数
function sortAsc(num1, num2){
return num1 - num2; //num1 > num2 就返回正数
}
// 降序函数
function sortDesc(num1, num2){
return num2 - num1; //num1 > num2 就返回负数
}八、 数组检测
如何检测一个对象是不是一个Array。
使用instanceof运算符。
使用Array.isArray(arr) 方法。
8.1 instanceof运算符
JavaScript中instanceof运算符会返回一个 Boolean 值,指出对象是否是特定构造函数的一个实例。
var arr = []; alert(arr instanceof Array); //true12
8.2 Array.isArray(arr) 方法
Array.isArray(arr) , 如果arr是数组,则返回true,否则返回false
var arr = [];
alert(Array.isArray(arr)); //true
alert(Array.isArray("abc")); // false九、 二维数组
如果数组中的元素存储的是数组,则就构成了二维数组。
//数组中的每个元素都是数组,则就是一个二维数组
var towDimArr = [
[4, 5],
[7, 8],
[50, 9, 10],
[5]
];
alert(towDimArr.length); //数组的长度为 4
//使用嵌套循环来遍历二维数组。
for (var i = 0; i < towDimArr.length; i++) {
for (var j = 0; j < towDimArr[i].length; j++) {
alert(towDimArr[i][j]);
}
}详细的讲述了JavaScript中数组,大家可以详细的阅读一下哦!
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of A senior programmer's summary of JavaScript arrays. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1384
1384
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 Recommended: Excellent JS open source face detection and recognition project
Apr 03, 2024 am 11:55 AM
Recommended: Excellent JS open source face detection and recognition project
Apr 03, 2024 am 11:55 AM
Face detection and recognition technology is already a relatively mature and widely used technology. Currently, the most widely used Internet application language is JS. Implementing face detection and recognition on the Web front-end has advantages and disadvantages compared to back-end face recognition. Advantages include reducing network interaction and real-time recognition, which greatly shortens user waiting time and improves user experience; disadvantages include: being limited by model size, the accuracy is also limited. How to use js to implement face detection on the web? In order to implement face recognition on the Web, you need to be familiar with related programming languages and technologies, such as JavaScript, HTML, CSS, WebRTC, etc. At the same time, you also need to master relevant computer vision and artificial intelligence technologies. It is worth noting that due to the design of the Web side
 Essential tools for stock analysis: Learn the steps to draw candle charts with PHP and JS
Dec 17, 2023 pm 06:55 PM
Essential tools for stock analysis: Learn the steps to draw candle charts with PHP and JS
Dec 17, 2023 pm 06:55 PM
Essential tools for stock analysis: Learn the steps to draw candle charts in PHP and JS. Specific code examples are required. With the rapid development of the Internet and technology, stock trading has become one of the important ways for many investors. Stock analysis is an important part of investor decision-making, and candle charts are widely used in technical analysis. Learning how to draw candle charts using PHP and JS will provide investors with more intuitive information to help them make better decisions. A candlestick chart is a technical chart that displays stock prices in the form of candlesticks. It shows the stock price
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 Which AI programmer is the best? Explore the potential of Devin, Tongyi Lingma and SWE-agent
Apr 07, 2024 am 09:10 AM
Which AI programmer is the best? Explore the potential of Devin, Tongyi Lingma and SWE-agent
Apr 07, 2024 am 09:10 AM
On March 3, 2022, less than a month after the birth of the world's first AI programmer Devin, the NLP team of Princeton University developed an open source AI programmer SWE-agent. It leverages the GPT-4 model to automatically resolve issues in GitHub repositories. SWE-agent's performance on the SWE-bench test set is similar to Devin, taking an average of 93 seconds and solving 12.29% of the problems. By interacting with a dedicated terminal, SWE-agent can open and search file contents, use automatic syntax checking, edit specific lines, and write and execute tests. (Note: The above content is a slight adjustment of the original content, but the key information in the original text is retained and does not exceed the specified word limit.) SWE-A
 Revealing the appeal of C language: Uncovering the potential of programmers
Feb 24, 2024 pm 11:21 PM
Revealing the appeal of C language: Uncovering the potential of programmers
Feb 24, 2024 pm 11:21 PM
The Charm of Learning C Language: Unlocking the Potential of Programmers With the continuous development of technology, computer programming has become a field that has attracted much attention. Among many programming languages, C language has always been loved by programmers. Its simplicity, efficiency and wide application make learning C language the first step for many people to enter the field of programming. This article will discuss the charm of learning C language and how to unlock the potential of programmers by learning C language. First of all, the charm of learning C language lies in its simplicity. Compared with other programming languages, C language
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 PHP and JS Development Tips: Master the Method of Drawing Stock Candle Charts
Dec 18, 2023 pm 03:39 PM
PHP and JS Development Tips: Master the Method of Drawing Stock Candle Charts
Dec 18, 2023 pm 03:39 PM
With the rapid development of Internet finance, stock investment has become the choice of more and more people. In stock trading, candle charts are a commonly used technical analysis method. It can show the changing trend of stock prices and help investors make more accurate decisions. This article will introduce the development skills of PHP and JS, lead readers to understand how to draw stock candle charts, and provide specific code examples. 1. Understanding Stock Candle Charts Before introducing how to draw stock candle charts, we first need to understand what a candle chart is. Candlestick charts were developed by the Japanese




