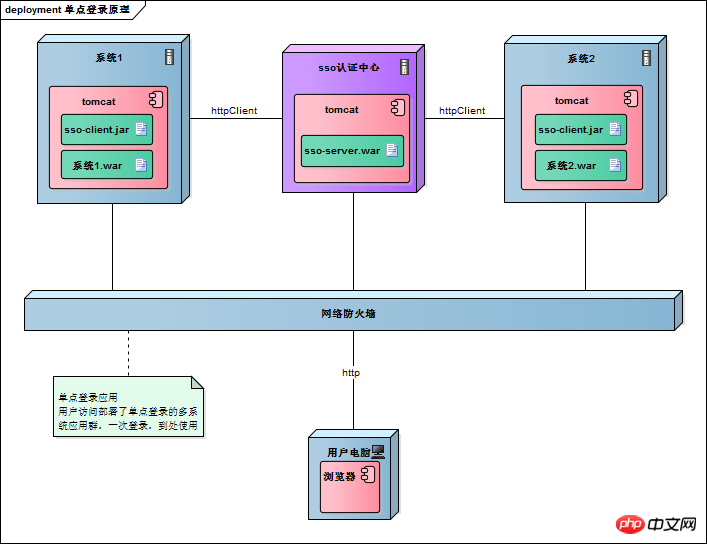
Examples to explain the principle of SSO single sign-on
1. http stateless protocol
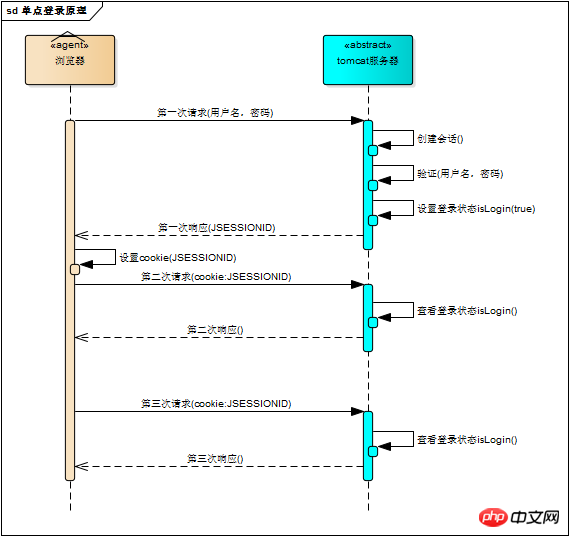
The web application adopts browser/server architecture, and http is used as the communication protocol. HTTP is a stateless protocol. Each request from the browser will be processed independently by the server and will not be associated with previous or subsequent requests. This process is illustrated in the figure below. There is no connection between the three request/response pairs
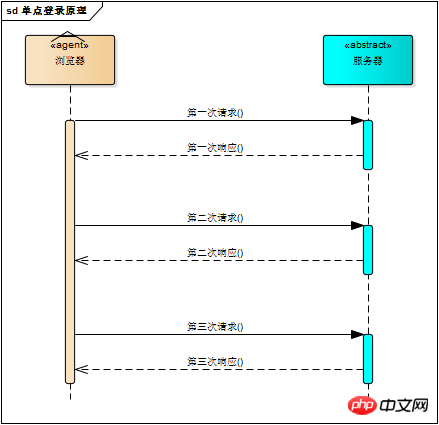
But this also means that any user can access server resources through a browser. If you want to protect certain resources of the server, you must limit browser requests; to limit browser requests, you must Identify browser requests, respond to legitimate requests, and ignore illegal requests; to identify browser requests, you must know the browser request status. Since the http protocol is stateless, let the server and browser jointly maintain a state! This is the session mechanism
2. Session mechanism
The first time the browser requests the server, the server creates a session and sends the session id to the browser as part of the response. The browser stores Session ID, and bring the session ID in the second and third subsequent requests. The server will know if it is the same user by getting the session ID in the request. This process is illustrated in the figure below. Subsequent requests are the same as the first request. An association is generated
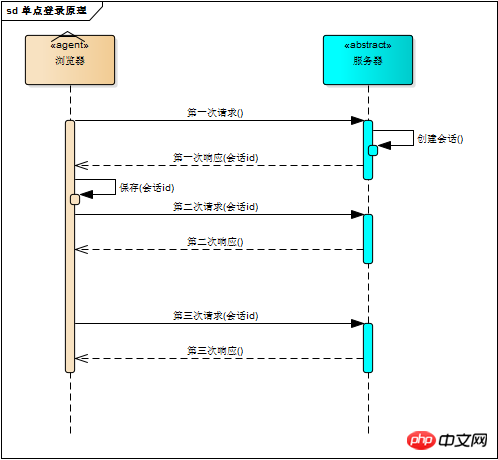
# The server saves the session object in memory, how does the browser save the session id? You may think of two ways
Request parameters
cookie
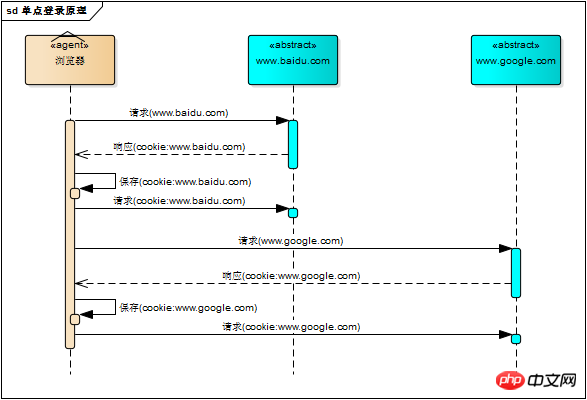
# Use the session id as For each request parameter, when the server receives the request, it can naturally parse the parameters to obtain the session ID, and use this to determine whether it comes from the same session. Obviously, this method is unreliable. Then let the browser maintain the session ID by itself. The browser automatically sends the session ID every time an http request is sent. The cookie mechanism is used to do this. Cookie is a mechanism used by the browser to store a small amount of data. The data is stored in the form of "key/value". When the browser sends an http request, it automatically attaches cookie information
Of course, the tomcat session mechanism also implements cookies. Visit tomcat When running the server, you can see a cookie named "JSESSIONID" in the browser. This is the session ID maintained by the tomcat session mechanism. The request response process using cookies is as shown below
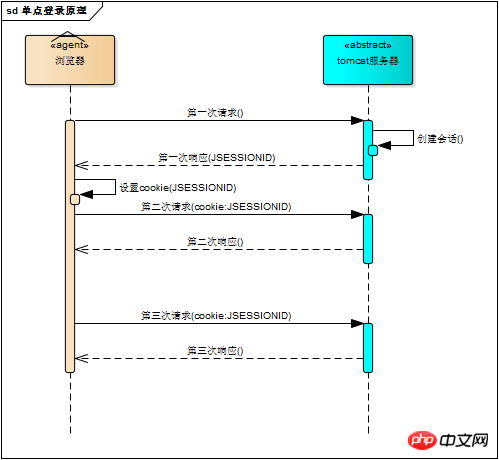
3. Login status
With the session mechanism, the login status is easy to understand. We assume that the first time the browser requests the server, it needs to enter the username and password to verify the identity. The server gets the username and password to the database. If the comparison is correct, it means that the user currently holding this session is a legitimate user, and this session should be marked as "authorized" or "logged in", etc. Since it is the status of the session, it must be saved in the session. In the object, tomcat sets the login status in the session object as follows
|
1 2 |
## HttpSession session = request.getSession();session.setAttribute("isLogin",true); |
| 12 | HttpSession session = request. getSession();session.getAttribute("isLogin"); |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
##public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request; HttpServletResponse res = (HttpServletResponse) response;
HttpSession session = req.getSession(); if(session.getAttribute("isLogin")) { chain.doFilter(request, response) ; return; } //Jump to sso certification center res.sendRedirect("sso-server-url-with-system -url"); } |
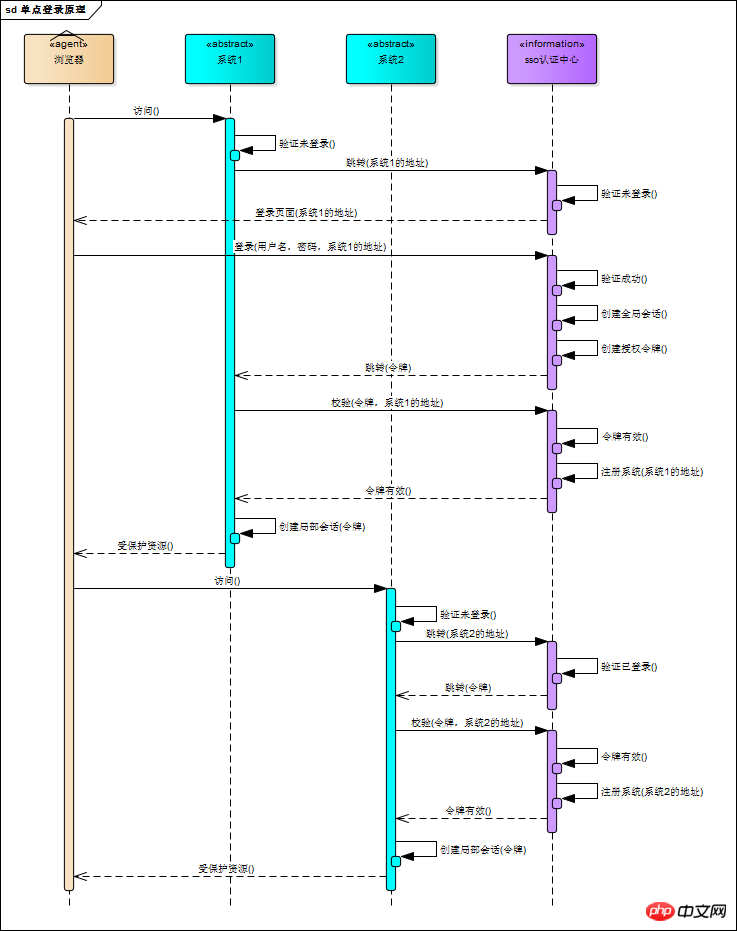
Intercepts requests from sso-client Jump to the non-login request of the sso authentication center and jump to the login page. This process is exactly the same as sso-client
3. sso-server verifies user login information
The user is on the login page Enter the user name and password, request login, the SSO certification center verifies the user information, the verification is successful, and the session status is marked as "Logged in"
| 23456 @RequestMapping("/ login") | public String login(String username, String password, HttpServletRequest req) { this.checkLoginInfo(username, password); req.getSession(). setAttribute("isLogin",true); return"success";} |
##String token = UUID.randomUUID().toString(); |
5. sso-client obtains the token and verifies it |
| ## in doFilter() of LoginFilter.java #3456789 1011 //The request comes with the token parameterString token = req.getParameter("token"); | if (token != null) { // Go to the sso certification center to verify the token booleanverifyResult = this.verify("sso-server-verify-url", token); if(!verifyResult) { res.sendRedirect("sso-server-url"); return; } chain.doFilter(request, response);}
## The verify() method is implemented using httpClient. This is only briefly introduced. httpClient is used in detail. Please refer to the official documentation for the method |
| HttpPost httpPost =new HttpPost(" sso-server-verify-url-with-token");HttpResponse httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpPost); | 6、 sso-server receives and processes the verification token requestAfter the user successfully logs in to the sso authentication center, sso-server creates an authorization token and stores the token. Therefore, sso-server verifies the token. It is to find whether the token exists and whether it has expired. After the token verification is successful, sso-server will register the system that sent the verification request to the sso certification center (meaning to store it) |
7. sso-client verifies the token and successfully creates the partial session
After the token verification is successful, sso- The client marks the current local session as "logged in", modifies LoginFilter.java, and adds a few lines
| if (verifyResult) { session.setAttribute("isLogin",true);} |
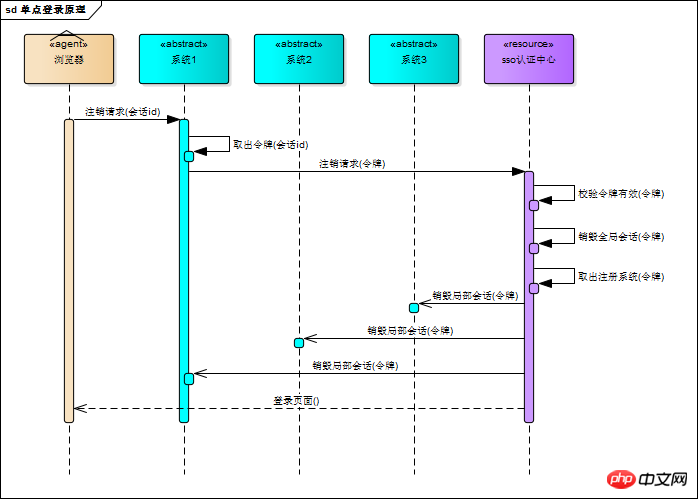
sso-client also needs to bind the current session id to the token, indicating that the login status of this session is related to the token. This relationship can be saved using java hashmap, and the saved data is used to process the data sent by the sso authentication center. Logout request 8, logout processThe user sends a request with the "logout" parameter (logout request) to the subsystem, and the sso-client interceptor intercepts the request and initiates it to the sso authentication center Logout request
The sso certification center also uses the same method to identify that the sso-client request is a logout request (with the "logout" parameter), the sso certification center Log out of global session
|
The above is the detailed content of Examples to explain the principle of SSO single sign-on. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 What should I do if I download other people's wallpapers after logging into another account on wallpaperengine?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
What should I do if I download other people's wallpapers after logging into another account on wallpaperengine?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
When you log in to someone else's steam account on your computer, and that other person's account happens to have wallpaper software, steam will automatically download the wallpapers subscribed to the other person's account after switching back to your own account. Users can solve this problem by turning off steam cloud synchronization. What to do if wallpaperengine downloads other people's wallpapers after logging into another account 1. Log in to your own steam account, find cloud synchronization in settings, and turn off steam cloud synchronization. 2. Log in to someone else's Steam account you logged in before, open the Wallpaper Creative Workshop, find the subscription content, and then cancel all subscriptions. (In case you cannot find the wallpaper in the future, you can collect it first and then cancel the subscription) 3. Switch back to your own steam
 How do I log in to my previous account on Xiaohongshu? What should I do if the original number is lost after it is reconnected?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:41 PM
How do I log in to my previous account on Xiaohongshu? What should I do if the original number is lost after it is reconnected?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:41 PM
With the rapid development of social media, Xiaohongshu has become a popular platform for many young people to share their lives and explore new products. During use, sometimes users may encounter difficulties logging into previous accounts. This article will discuss in detail how to solve the problem of logging into the old account on Xiaohongshu, and how to deal with the possibility of losing the original account after changing the binding. 1. How to log in to Xiaohongshu’s previous account? 1. Retrieve password and log in. If you do not log in to Xiaohongshu for a long time, your account may be recycled by the system. In order to restore access rights, you can try to log in to your account again by retrieving your password. The operation steps are as follows: (1) Open the Xiaohongshu App or official website and click the "Login" button. (2) Select "Retrieve Password". (3) Enter the mobile phone number you used when registering your account
 Discuz background login problem solution revealed
Mar 03, 2024 am 08:57 AM
Discuz background login problem solution revealed
Mar 03, 2024 am 08:57 AM
The solution to the Discuz background login problem is revealed. Specific code examples are needed. With the rapid development of the Internet, website construction has become more and more common, and Discuz, as a commonly used forum website building system, has been favored by many webmasters. However, precisely because of its powerful functions, sometimes we encounter some problems when using Discuz, such as background login problems. Today, we will reveal the solution to the Discuz background login problem and provide specific code examples. We hope to help those in need.
 How to log in to Kuaishou PC version - How to log in to Kuaishou PC version
Mar 04, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
How to log in to Kuaishou PC version - How to log in to Kuaishou PC version
Mar 04, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
Recently, some friends have asked me how to log in to the Kuaishou computer version. Here is the login method for the Kuaishou computer version. Friends who need it can come and learn more. Step 1: First, search Kuaishou official website on Baidu on your computer’s browser. Step 2: Select the first item in the search results list. Step 3: After entering the main page of Kuaishou official website, click on the video option. Step 4: Click on the user avatar in the upper right corner. Step 5: Click the QR code to log in in the pop-up login menu. Step 6: Then open Kuaishou on your phone and click on the icon in the upper left corner. Step 7: Click on the QR code logo. Step 8: After clicking the scan icon in the upper right corner of the My QR code interface, scan the QR code on your computer. Step 9: Finally log in to the computer version of Kuaishou
 Analysis of the function and principle of nohup
Mar 25, 2024 pm 03:24 PM
Analysis of the function and principle of nohup
Mar 25, 2024 pm 03:24 PM
Analysis of the role and principle of nohup In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, nohup is a commonly used command that is used to run commands in the background. Even if the user exits the current session or closes the terminal window, the command can still continue to be executed. In this article, we will analyze the function and principle of the nohup command in detail. 1. The role of nohup: Running commands in the background: Through the nohup command, we can let long-running commands continue to execute in the background without being affected by the user exiting the terminal session. This needs to be run
 How to log in to two devices on Quark
Feb 23, 2024 pm 10:55 PM
How to log in to two devices on Quark
Feb 23, 2024 pm 10:55 PM
How to log in to two devices with Quark? Quark Browser supports logging into two devices at the same time, but most friends don’t know how to log in to two devices with Quark Browser. Next, the editor brings users Quark to log in to two devices. Method graphic tutorials, interested users come and take a look! Quark Browser usage tutorial Quark how to log in to two devices 1. First open the Quark Browser APP and click [Quark Network Disk] on the main page; 2. Then enter the Quark Network Disk interface and select the [My Backup] service function; 3. Finally, select [Switch Device] to log in to two new devices.
 How to enter Baidu Netdisk web version? Baidu Netdisk web version login entrance
Mar 13, 2024 pm 04:58 PM
How to enter Baidu Netdisk web version? Baidu Netdisk web version login entrance
Mar 13, 2024 pm 04:58 PM
Baidu Netdisk can not only store various software resources, but also share them with others. It supports multi-terminal synchronization. If your computer does not have a client downloaded, you can choose to enter the web version. So how to log in to Baidu Netdisk web version? Let’s take a look at the detailed introduction. Baidu Netdisk web version login entrance: https://pan.baidu.com (copy the link to open in the browser) Software introduction 1. Sharing Provides file sharing function, users can organize files and share them with friends in need. 2. Cloud: It does not take up too much memory. Most files are saved in the cloud, effectively saving computer space. 3. Photo album: Supports the cloud photo album function, import photos to the cloud disk, and then organize them for everyone to view.
 How to log in if Xiaohongshu only remembers the account? I just remember how to retrieve my account?
Mar 23, 2024 pm 05:31 PM
How to log in if Xiaohongshu only remembers the account? I just remember how to retrieve my account?
Mar 23, 2024 pm 05:31 PM
Xiaohongshu has now been integrated into the daily lives of many people, and its rich content and convenient operation methods make users enjoy it. Sometimes, we may forget the account password. It is really annoying to only remember the account but not be able to log in. 1. How to log in if Xiaohongshu only remembers the account? When we forget our password, we can log in to Xiaohongshu through the verification code on our mobile phone. The specific operations are as follows: 1. Open the Xiaohongshu App or the web version of Xiaohongshu; 2. Click the "Login" button and select "Account and Password Login"; 3. Click the "Forgot your password?" button; 4. Enter your account number. Click "Next"; 5. The system will send a verification code to your mobile phone, enter the verification code and click "OK"; 6. Set a new password and confirm. You can also use a third-party account (such as