The most comprehensive solution to cross-domain ajax
When I first started learning JavaScript, I didn’t know what ajax cross-domain was, but I often heard some big guys talking about ajax cross-domain issues across domains. I must have classmates like me. , so let’s take a look today at what exactly ajax cross-domain is, and what are the methods to solve ajax cross-domain!
Preface
Regarding cross-domain, there are N types. This article only focuses on ajax request cross-domain (, ajax cross-domain only belongs to browsing Part of the "same origin policy" of the server, others include Cookie cross-domain, iframe cross-domain, LocalStorage cross-domain, etc. (not introduced here), the content is roughly as follows:
1. What Is ajax cross-domain
##Principle
Performance (sorted out some encounters problems and solutions)
2. How to solve ajax cross-domain
JSONP method
CORS method
Proxy request method
3. How to analyze ajax cross-domain
http packet capture analysis
Some examples
What is ajax cross-domain
The principle of cross-domain ajax
The main reason why ajax has a cross-domain request error problem is because of browsing For the "same origin policy" of the browser, you can refer toBrowser origin policy and its circumvention methods
CORS request principle
CORS is a W3C standard, the full name is "Cross-origin resource sharing" (Cross-origin resource sharing). It allows the browser to issue XMLHttpRequest requests to cross-origin servers, thereby overcoming the limitation that AJAX can only be used from the same origin. Basically all current browsers have implemented the CORS standard. In fact, almost all browser ajax requests are based on the CORS mechanism, but front-end developers may not care about it (so in fact The current CORS solution mainly considers how to implement the background). Regarding CORS, it is highly recommended to readDetailed explanation of CORS for cross-domain resource sharing
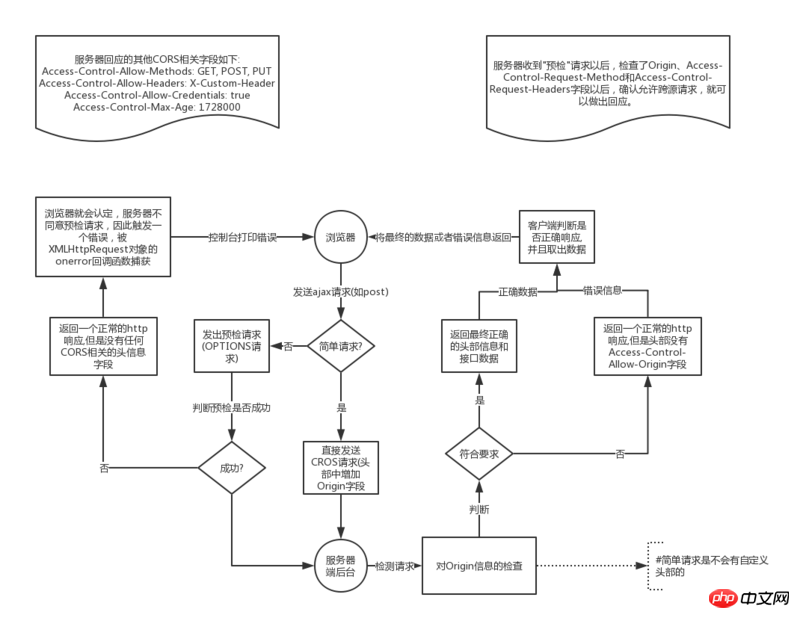
#How to determine whether it is a simple request?Browsers divide CORS requests into two categories: simple requests (simple requests) and non-so-simple requests (not-so-simple requests). As long as the following two conditions are met at the same time, it is a simple request.
1.Request method is one of the following three methods: HEAD, GET, POST
2. HTTP header information Do not exceed the following fields:1. Accept 2. Accept-Language
3. Content-Language
4. Last-Event-ID
5. Content-Type (limited to three values application/x-www-form-urlencoded, multipart/form-data, text/plain)
Whenever different If the above two conditions are met, it is a non-simple request.
Ajax cross-domain performance
To be honest, I compiled an article at first and then used it as a solution, but later I found that it was still Many people still don't know how. We have no choice but to debug it which is time-consuming and labor-intensive. However, even if I analyze it, I will only judge whether it is cross-domain based on the corresponding performance, so this is very important. When making an ajax request, if there is a cross-domain phenomenon and it is not resolved, the following behavior will occur: (Note, it is an ajax request. Please do not say why http requests are OK but ajax is not, because ajax is accompanied by Cross-domain, so just http request ok is not enough)
Note: Please see the title position for specific back-end cross-domain configuration.
The first phenomenon:No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource, and The response had HTTP status code 404
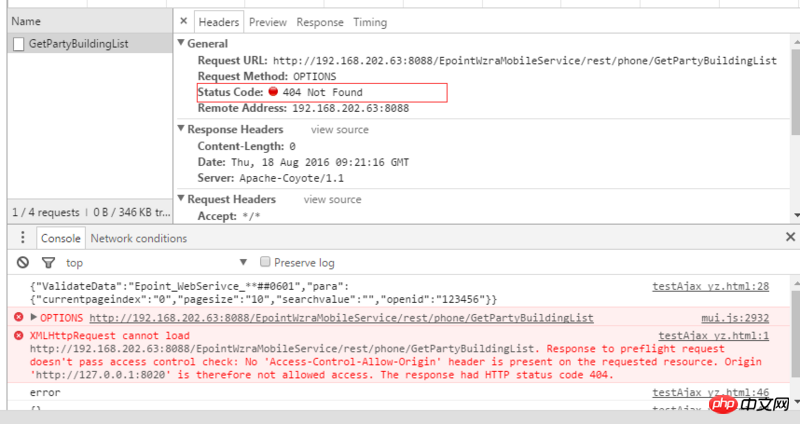
The reasons for this situation are as follows:
1. This ajax request is "Not a simple request", so a preflight request (OPTIONS) will be sent before the request
2. The server-side background interface does not allow OPTIONS requests, resulting in the inability to find the corresponding interface address
Solution: The backend allows options requests
Second phenomenon:No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource, andThe response had HTTP status code 405
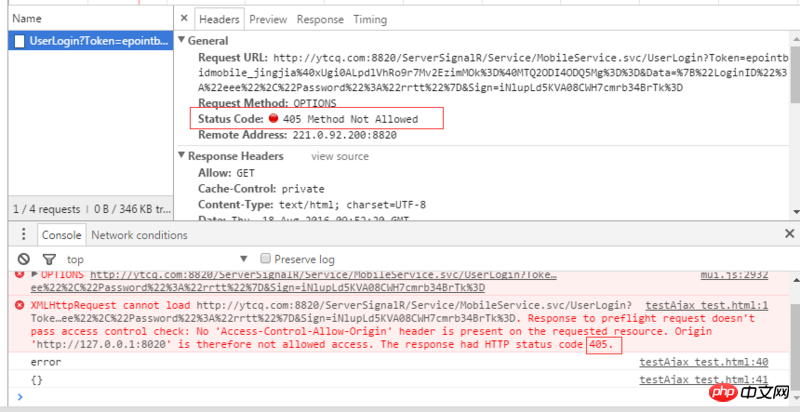
This phenomenon is different from the first one. In this case, the background method allows OPTIONS requests, but some
configuration files (such as security configuration) block OPTIONS requests, which causes this phenomenon.
Solution: Close the corresponding security configuration on the backendThe third phenomenon:No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource , and status 200
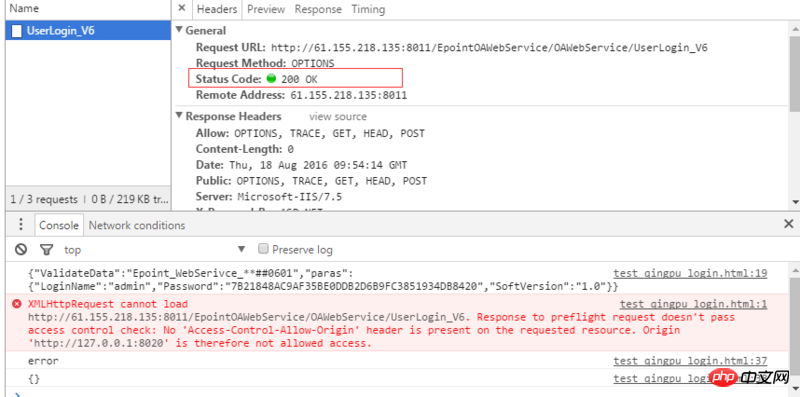
##This phenomenon is different from the first and second , In this case, the server-side background allows OPTIONS requests, and the interface also allows OPTIONS requests, but there is a mismatch when the headers match.
For example, the origin header check does not match, for example, some headers are missing. Support (such as the common X-Requested-With header), and then the server will return the response to the front-end. After the front-end detects this, it will trigger XHR.onerror, causing the front-end console to report an error
Solution: The backend adds corresponding header support
Fourth phenomenon:
heade contains multiple values '*,*'
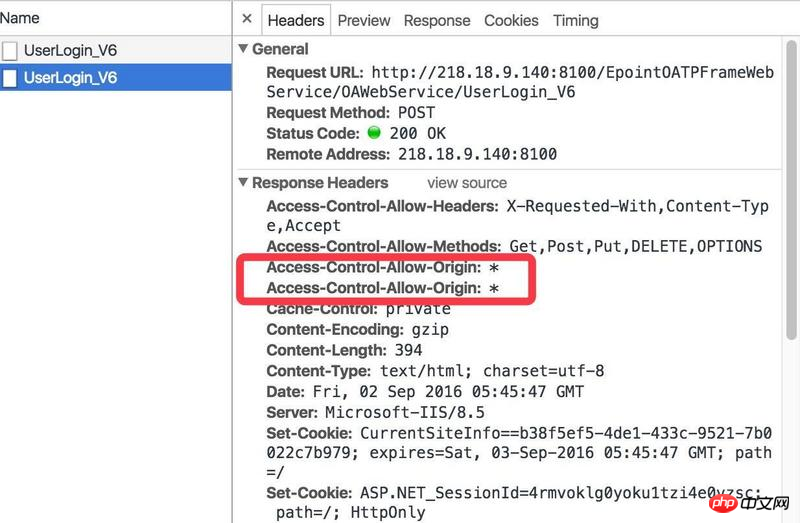
##The phenomenon is that the http header information of the background response has two Access-Control-Allow-Origin:*
To be honest, this kind of problem occurs The main reason is that people who perform cross-domain configuration do not understand the principle, resulting in repeated configurations, such as: 1. Commonly seen in the .net background (usually origin is configured once in web.config, and then again in the code Manually added an origin (for example, the code manually sets the return *)) 2. Commonly used in the .net background (set Origin:* in IIS and the project's webconfig at the same time)Solution (one-to-one correspondence):
1. It is recommended to delete the * manually added in the code and only use the ones in the project configuration 2 , it is recommended to delete the configuration under IIS*, and only use the configuration in the project configuration How to solve ajax cross-domainGeneral Ajax cross-domain solution is solved through JSONP or CORS, as follows: (Note that JSONP is almost no longer used, so just understand JSONP)
jsonp is a relatively old solution to solve cross-domain problems (not recommended in practice). Here is a brief introduction (if you want to use JSONP in actual projects, you will generally use JQ and other class libraries that encapsulate JSONP to make ajax requests)
Implementation principleThe reason why JSONP can be used to solve cross-domain problems The main reason for this solution is that <script> scripts have cross-domain capabilities, and JSONP takes advantage of this to achieve it. The specific principle is shown in the figure</script>
Implementation process
The implementation steps of JSONP are roughly as follows (refer to the article in the source)
1. The client web page requests JSON from the server by adding a <script> element Data, this approach is not restricted by the same-origin policy</script>
function addScriptTag(src) {
var script = document.createElement('script');
script.setAttribute("type","text/javascript");
script.src = src;
document.body.appendChild(script);
}
window.onload = function () {
addScriptTag('http://example.com/ip?callback=foo');
}
function foo(data) {
console.log('response data: ' + JSON.stringify(data));
};When requesting, the interface address is used as the src of the built script tag. In this way, when the script tag is built, the final src is returned by the interface Content
2. The corresponding interface on the server side adds a function wrapping layer outside the return parameter
foo({
"test": "testData"
});3. Since the script requested by the

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to solve the 403 error encountered by jQuery AJAX request
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:07 AM
How to solve the 403 error encountered by jQuery AJAX request
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:07 AM
Title: Methods and code examples to resolve 403 errors in jQuery AJAX requests. The 403 error refers to a request that the server prohibits access to a resource. This error usually occurs because the request lacks permissions or is rejected by the server. When making jQueryAJAX requests, you sometimes encounter this situation. This article will introduce how to solve this problem and provide code examples. Solution: Check permissions: First ensure that the requested URL address is correct and verify that you have sufficient permissions to access the resource.
 How to solve jQuery AJAX request 403 error
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
How to solve jQuery AJAX request 403 error
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
jQuery is a popular JavaScript library used to simplify client-side development. AJAX is a technology that sends asynchronous requests and interacts with the server without reloading the entire web page. However, when using jQuery to make AJAX requests, you sometimes encounter 403 errors. 403 errors are usually server-denied access errors, possibly due to security policy or permission issues. In this article, we will discuss how to resolve jQueryAJAX request encountering 403 error
 How to get variables from PHP method using Ajax?
Mar 09, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
How to get variables from PHP method using Ajax?
Mar 09, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Using Ajax to obtain variables from PHP methods is a common scenario in web development. Through Ajax, the page can be dynamically obtained without refreshing the data. In this article, we will introduce how to use Ajax to get variables from PHP methods, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to write a PHP file to handle the Ajax request and return the required variables. Here is sample code for a simple PHP file getData.php:
 How to solve the problem of jQuery AJAX error 403?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
How to solve the problem of jQuery AJAX error 403?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
How to solve the problem of jQueryAJAX error 403? When developing web applications, jQuery is often used to send asynchronous requests. However, sometimes you may encounter error code 403 when using jQueryAJAX, indicating that access is forbidden by the server. This is usually caused by server-side security settings, but there are ways to work around it. This article will introduce how to solve the problem of jQueryAJAX error 403 and provide specific code examples. 1. to make
 PHP vs. Ajax: Solutions for creating dynamically loaded content
Jun 06, 2024 pm 01:12 PM
PHP vs. Ajax: Solutions for creating dynamically loaded content
Jun 06, 2024 pm 01:12 PM
Ajax (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) allows adding dynamic content without reloading the page. Using PHP and Ajax, you can dynamically load a product list: HTML creates a page with a container element, and the Ajax request adds the data to that element after loading it. JavaScript uses Ajax to send a request to the server through XMLHttpRequest to obtain product data in JSON format from the server. PHP uses MySQL to query product data from the database and encode it into JSON format. JavaScript parses the JSON data and displays it in the page container. Clicking the button triggers an Ajax request to load the product list.
 PHP and Ajax: Building an autocomplete suggestion engine
Jun 02, 2024 pm 08:39 PM
PHP and Ajax: Building an autocomplete suggestion engine
Jun 02, 2024 pm 08:39 PM
Build an autocomplete suggestion engine using PHP and Ajax: Server-side script: handles Ajax requests and returns suggestions (autocomplete.php). Client script: Send Ajax request and display suggestions (autocomplete.js). Practical case: Include script in HTML page and specify search-input element identifier.
 Asynchronous data exchange using Ajax functions
Jan 26, 2024 am 09:41 AM
Asynchronous data exchange using Ajax functions
Jan 26, 2024 am 09:41 AM
How to use Ajax functions to achieve asynchronous data interaction With the development of the Internet and Web technology, data interaction between the front end and the back end has become very important. Traditional data interaction methods, such as page refresh and form submission, can no longer meet user needs. Ajax (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) has become an important tool for asynchronous data interaction. Ajax enables the web to use JavaScript and the XMLHttpRequest object
 What are the ajax versions?
Nov 22, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
What are the ajax versions?
Nov 22, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
Ajax is not a specific version, but a technology that uses a collection of technologies to asynchronously load and update web page content. Ajax does not have a specific version number, but there are some variations or extensions of ajax: 1. jQuery AJAX; 2. Axios; 3. Fetch API; 4. JSONP; 5. XMLHttpRequest Level 2; 6. WebSockets; 7. Server-Sent Events; 8, GraphQL, etc.






