Notification bar script startup tool written in Python
这次给大家带来Python编写的通知栏脚本启动工具,Python编写通知栏脚本启动工具的注意事项有哪些,下面就是实战案例,一起来看一下。
首先
安装PyQt5
pip3 install PyQt5
然后创建目录
新建一个文件夹用于存放项目
文件夹示例结构如下:
/main #主文件夹 名字自定义├─main.pyw #主启动程序├─conf.py #用于自定义菜单配置├─/icons #用于存放图标 文件夹└─/scripts #用于存放脚本 文件夹 可以省略
.pyw后缀的文件是指窗体应用程序默认是Python环境变量目录下的pythonw.exe文件如果打开方式是控制台程序,需要手动指定打开方式
关于图标可以前往http://www.iconfont.cn/下载
2.代码
2.1.我们来创建个通知栏显示:
################ main.pyw ################from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QDialog, QSystemTrayIcon, QMenu ,QAction,QApplication
from PyQt5.QtGui import QIcon
import sysclass main(QDialog):
def init(self): super().init() self.loadMenu() self.initUI() def loadMenu(self):
menuItems = [] # 菜单列表
menuItems.append({"text": "启动", "icon": "./icons/set.png", "event": self.show, "hot": "D"})
menuItems.append({"text": "退出", "icon": "./icons/close.png", "event": self.close, "hot": "Q"}) self.trayIconMenu = QMenu(self)# 创建菜单
#遍历绑定 显示的文字、图标、热键和点击事件
#热键可能是无效的 我这里只是为了显示效果而已
for i in menuItems:
tmp = QAction(QIcon(i["icon"]), i["text"],self, triggered=i["event"])
tmp.setShortcut(self.tr(i["hot"])) self.trayIconMenu.addAction(tmp)
def initUI(self): self.trayIcon = QSystemTrayIcon(self) # <===创建通知栏托盘图标
self.trayIcon.setIcon(QIcon("./icons/menu2.png"))#<===设置托盘图标
self.trayIcon.setContextMenu(self.trayIconMenu)#<===创建右键连接菜单
self.trayIcon.show()#<====显示托盘
self.setWindowIcon(QIcon("./icons/menu2.png")) #<===设置窗体图标
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 180, 300) # <===设置窗体打开位置与宽高
self.setWindowTitle('窗体标题') # self.show()#<====显示窗体
# self.hide()#<====隐藏窗体
# 默认不显示窗体
# 重写窗体关闭事件,让其点击关闭时隐藏
def closeEvent(self, event): if self.trayIcon.isVisible(): self.trayIcon.hide()if name == 'main':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = main()
sys.exit(app.exec_())效果:
2.2.如果通知栏显示成功后接下来的配置就十分简单了,只是绑定显示与事件就行了
################ conf.pyw ################import osimport timedef PrScrn():#调用 dll示例
time.sleep(0.5)
os.popen('rundll32 .\\script\\截图\\PrScrn.dll PrScrn')def Open360Wifi():#打开应用程序示例
os.popen('"C:\\Program Files (x86)\\360\\360AP\\360AP.exe" /menufree')def OpenRegedit():#调用 命令示例
os.popen('regedit')def Ifconfig():
os.system('''ipconfig & pause''')
menuItems=[ #.....示例....
{"text":"截图","icon":"./icons/cut.png","event":PrScrn,"hot":"Alt+P"},
{"text":"360Wifi","icon":"./icons/wifi.png","event":Open360Wifi,"hot":"Alt+W"},
{"text":"注册表","icon":"./icons/regedit.png","event":OpenRegedit,"hot":"Alt+R"},
{"text":"ifconfig","icon":"./icons/ip.png","event":Ifconfig,"hot":"Alt+R"}
]2.3.读取配置并显示
读取十分简单:
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QDialog, QSystemTrayIcon, QMenu ,QAction,QApplicationfrom PyQt5.QtGui import QIconimport sysimport conf#<====导入confclass main(QDialog):
def init(self):
super().init()
self.loadMenu()
self.initUI() def loadMenu(self):
menuItems =conf.menuItems #<=====菜单列表
#....略
#....略if name == 'main':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = main()
sys.exit(app.exec_())2.4.将窗体利用起来
我这里就举个简单的例子:
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QDialog, QAction, QApplication, QListWidget, QVBoxLayout, QSystemTrayIcon, QMenu, QListWidgetItem
from PyQt5.QtGui import QIcon
import sys
import confclass main(QDialog):
def init(self): super().init() self.loadMenu() self.initUI() #省略.....
def loadList(self):
lv = QListWidget() for i in range(len(conf.menuItems)):
itm = conf.menuItems[i] if not 'icon' in itm.keys():
itm["icon"] = None if not 'event' in itm.keys():
itm["event"] = self.show if not 'hot' in itm.keys():
itm["hot"] = 'None'
qlv = QListWidgetItem(QIcon(itm["icon"]), self.tr(itm["text"]+" ("+itm["hot"]+")"))
qlv.event = itm["event"]
# qlv.clicked.connect(self.close)
lv.insertItem(i + 1, qlv)
lv.itemDoubleClicked.connect(self.dbclickItem) self.layout.addWidget(lv) def dbclickItem(self, item):
item.event() #省略.....
#省略.....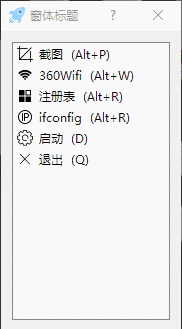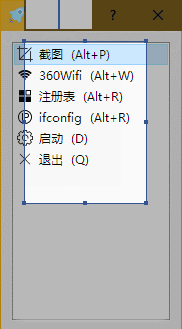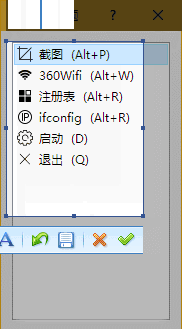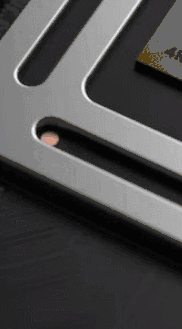
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
相关阅读:
The above is the detailed content of Notification bar script startup tool written in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
You can learn basic programming concepts and skills of Python within 2 hours. 1. Learn variables and data types, 2. Master control flow (conditional statements and loops), 3. Understand the definition and use of functions, 4. Quickly get started with Python programming through simple examples and code snippets.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
The steps to start a Redis server include: Install Redis according to the operating system. Start the Redis service via redis-server (Linux/macOS) or redis-server.exe (Windows). Use the redis-cli ping (Linux/macOS) or redis-cli.exe ping (Windows) command to check the service status. Use a Redis client, such as redis-cli, Python, or Node.js, to access the server.
 How to read data from redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
How to read data from redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
To read data from Redis, you can follow these steps: 1. Connect to the Redis server; 2. Use get(key) to get the value of the key; 3. If you need string values, decode the binary value; 4. Use exists(key) to check whether the key exists; 5. Use mget(keys) to get multiple values; 6. Use type(key) to get the data type; 7. Redis has other read commands, such as: getting all keys in a matching pattern, using cursors to iterate the keys, and sorting the key values.
 Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python is suitable for data science, web development and automation tasks, while C is suitable for system programming, game development and embedded systems. Python is known for its simplicity and powerful ecosystem, while C is known for its high performance and underlying control capabilities.
 What types of files are composed of oracle databases?
Apr 11, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
What types of files are composed of oracle databases?
Apr 11, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
Oracle database file structure includes: data file: storing actual data. Control file: Record database structure information. Redo log files: record transaction operations to ensure data consistency. Parameter file: Contains database running parameters to optimize performance. Archive log file: Backup redo log file for disaster recovery.
 How to find keys with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
How to find keys with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
There are several ways to find keys in Redis: Use the SCAN command to iterate over all keys by pattern or condition. Use GUI tools such as Redis Explorer to visualize the database and filter keys by name or schema. Write external scripts to query keys using the Redis client library. Subscribe to keyspace notifications to receive alerts when key changes.
 How to obtain redis login permission
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
How to obtain redis login permission
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
To obtain Redis login permission, you need to perform the following steps: 1. Create a username and password; 2. Allow remote connections; 3. Restart the Redis server; 4. Connect using the Redis CLI or programming language.




