Detailed explanation of mysql data table operation examples
This article mainly shares with you detailed examples of mysql data table operation. I hope it can help you. First, let's take a look at how to create a data table.
Create table
Basic syntax form:
create table [if not exists] table name (field list [, index or constraint list]) [table option list];
- ##Field setting format:
Field name Type [Field attribute 1 Field attribute 2…..]Instructions:
1. You can choose the field name yourself;
2. The type is the data type learned earlier: int, tinyint, float, double, char(6), varchar(25), text, datetime.
3. There can be multiple field attributes (according to specific needs), directly separated by spaces; the main ones are as follows:
- The index is a hidden "data table" automatically maintained within the system. Its function is to greatly speed up data search!
- The data in this hidden data table is automatically sorted, and its search speed is based on this.
1 |
|
索引创建语法:

外键索引:
1 |
|
外键:表中的一个字段不是本表的主键或候选键,而是另一个表的主键或候选键。
候选键或候选键:如果一个表中具有能够唯一标识的一个行的属性,则称为候选键,候选键中任选一个为主键。
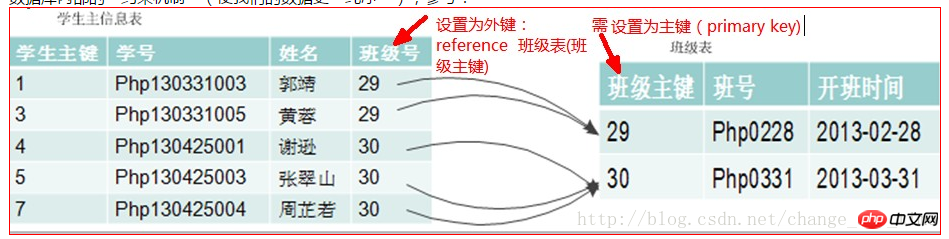
示例: 
注意: 插入xuesheng表中的数据时,banji_id字段的值,就不可以随便插入了,而是必须是banji表中的id字段所已经有的数据值,才可以插入。
全文索引:仅做了解,因为对中文还不够友好
一、概述
MySQL中的全文检索是利用查询关键字和查询列内容之间的相关度进行检索,可以利用全文索引来提高匹配的速度。
二、语法MATCH (col1,col2,...) AGAINST (expr [search_modifier])search_modifier: { IN BOOLEAN MODE | WITH QUERY EXPANSION }
例如:SELECT * FROM tab_name WHERE MATCH (col1,col2) AGAINST (search_word);
这里的table需要是MyISAM类型的表,col1、col2需要是char、varchar或text类型,在查询之前需要在col1和col2上建立一个全文索引。
约束
约束,就是要求数据需要满足什么条件的一种“规定”。
| 约束类型 | 形式 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| 主键约束 | primary key ( 字段名) | 使该设定字段的值可以用于“唯一确定一行数据”,其实就是“主键”的意思。 |
| 唯一约束 | unique key ( 字段名) | 使该设定字段的值具有“唯一性”,自然也是可区分的。 |
| 外键约束 | foreign key ( 字段名) references 其他表名(对应其他表中的字段名) | 使该设定字段的值,必须在其谁定的对应表中的对应字段中已经有该值了。 |
| 非空约束 | not null | 其实就是设定一个字段时写的那个“not null”属性。这个约束只能写在字段属性上 |
| 默认约束 | default XX值 | 其实就是设定一个字段时写的那个“default 默认值”属性,这个约束只能写在字段属性上。 |
| 检查约束 | check(某种判断语句) |
比如:
1 2 3 |
|
其实,主键约束,唯一约束,外键约束,只是“同一件事情的2个不同角度的说法”,他们同时也称为“主键索引”,“唯一索引”,“外键索引”。
表选项列表
表选项就是,创建一个表的时候,对该表的整体设定,主要有如下几个:
1、 charset = 要使用的字符编码,
2、 engine = 要使用的存储引擎(也叫表类型),
3、auto_increment = 设定当前表的自增长字段的初始值,默认是1
4、comment =‘该表的一些说明文字’
说明:
1,设定的字符编码是为了跟数据库设定的不一样。如果一样,就不需要设定了:因为其会自动使用数据库级别的设定;
2,engine(存储引擎)在代码层面,就是一个名词:InnoDB, MyIsam, BDB, archive, Memory。默认是InnoDB。
存储引擎
存储引擎是将数据存储到硬盘的“机制”。
不同的存储引擎,其实主要是从2个大的层面来设计存储机制:
尽可能快的速度;
尽可能多的功能;
选择不同的存储引擎,就是上述性能和功能的“权衡”。
大体如下: 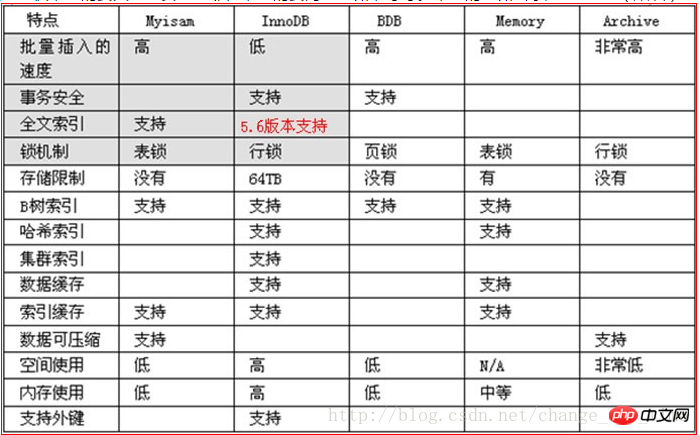
演示: 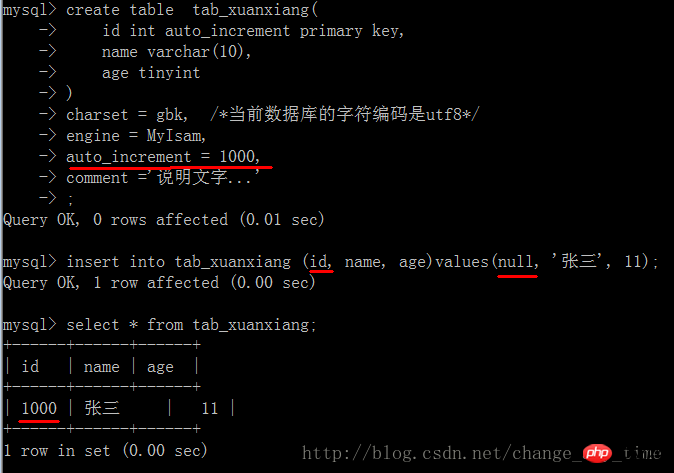
修改表
几点说明:
修改表,是指修改表的结构——正如创建表也是设定表的结构。
创建表能做的事,修改表几乎都能做——但很不推荐去修改表,而是应该在创建表的时候就基本确定表的结构。
大体来说:
1:可以对字段进行:添加,删除,修改;
2:可以对索引进行:添加,删除表的选项,通常“都是修改”,即使不写任何表选项,他们都有其默认值。
常见几个:
| 操作类型 | 表达式 |
|---|---|
| 添加字段 | alter table 表名 add [column] 新字段名 字段类型 [字段属性列表] |
| 修改字段(并可改名) | alter table 表名 change [column] 旧字段名 新字段名 新字段类型 [新字段属性列表] |
| 删除字段 | alter table 表名 drop [column] 字段名 |
| 添加普通索引 | alter table 表名 add key [索引名] (字段名1[,字段名2,…]) |
| 添加唯一索引(约束) | alter table 表名 add unique key (字段名1[,字段名2,…]) |
| 添加主键索引(约束) | alter table 表名 add primary key (字段名1[,字段名2,…]) |
| 修改表名 | alter table 旧表名 rename [to] 新表名 |
| 删除表 | drop table 【if exists】 表名 |
其他表的相关语句:
| 操作类型 | 表达式 |
|---|---|
| 显示当前数据库中的所有表 | show tables |
| 显示某表的结构 | desc 表名; 或:describe 表名 |
| 显示某表的创建语句 | show create table 表名 |
| 重命名表 | rename table 旧表名 to 新表名 |
| 从已有表复制表结构 | create table [if not exists] 新表名 like 原表名 |
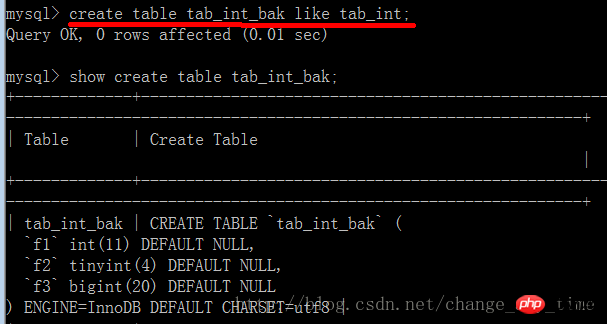
演示复制表结构:
创建表tab_int,显示表创建语句
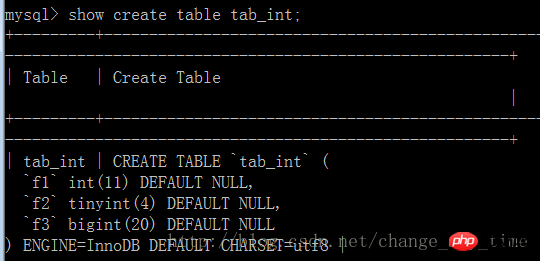
将tab_int复制给tab_int_bak,显示tab_int_bak表创建语句,与tab_int一致

相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of mysql data table operation examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1369
1369
 52
52
 Unable to log in to mysql as root
Apr 08, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
Unable to log in to mysql as root
Apr 08, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
The main reasons why you cannot log in to MySQL as root are permission problems, configuration file errors, password inconsistent, socket file problems, or firewall interception. The solution includes: check whether the bind-address parameter in the configuration file is configured correctly. Check whether the root user permissions have been modified or deleted and reset. Verify that the password is accurate, including case and special characters. Check socket file permission settings and paths. Check that the firewall blocks connections to the MySQL server.
 mysql whether to change table lock table
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:06 PM
mysql whether to change table lock table
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:06 PM
When MySQL modifys table structure, metadata locks are usually used, which may cause the table to be locked. To reduce the impact of locks, the following measures can be taken: 1. Keep tables available with online DDL; 2. Perform complex modifications in batches; 3. Operate during small or off-peak periods; 4. Use PT-OSC tools to achieve finer control.
 RDS MySQL integration with Redshift zero ETL
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:06 PM
RDS MySQL integration with Redshift zero ETL
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:06 PM
Data Integration Simplification: AmazonRDSMySQL and Redshift's zero ETL integration Efficient data integration is at the heart of a data-driven organization. Traditional ETL (extract, convert, load) processes are complex and time-consuming, especially when integrating databases (such as AmazonRDSMySQL) with data warehouses (such as Redshift). However, AWS provides zero ETL integration solutions that have completely changed this situation, providing a simplified, near-real-time solution for data migration from RDSMySQL to Redshift. This article will dive into RDSMySQL zero ETL integration with Redshift, explaining how it works and the advantages it brings to data engineers and developers.
 Can mysql handle multiple connections
Apr 08, 2025 pm 03:51 PM
Can mysql handle multiple connections
Apr 08, 2025 pm 03:51 PM
MySQL can handle multiple concurrent connections and use multi-threading/multi-processing to assign independent execution environments to each client request to ensure that they are not disturbed. However, the number of concurrent connections is affected by system resources, MySQL configuration, query performance, storage engine and network environment. Optimization requires consideration of many factors such as code level (writing efficient SQL), configuration level (adjusting max_connections), hardware level (improving server configuration).
 Query optimization in MySQL is essential for improving database performance, especially when dealing with large data sets
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Query optimization in MySQL is essential for improving database performance, especially when dealing with large data sets
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
1. Use the correct index to speed up data retrieval by reducing the amount of data scanned select*frommployeeswherelast_name='smith'; if you look up a column of a table multiple times, create an index for that column. If you or your app needs data from multiple columns according to the criteria, create a composite index 2. Avoid select * only those required columns, if you select all unwanted columns, this will only consume more server memory and cause the server to slow down at high load or frequency times For example, your table contains columns such as created_at and updated_at and timestamps, and then avoid selecting * because they do not require inefficient query se
 The relationship between mysql user and database
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
The relationship between mysql user and database
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
In MySQL database, the relationship between the user and the database is defined by permissions and tables. The user has a username and password to access the database. Permissions are granted through the GRANT command, while the table is created by the CREATE TABLE command. To establish a relationship between a user and a database, you need to create a database, create a user, and then grant permissions.
 Can mysql run on android
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:03 PM
Can mysql run on android
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:03 PM
MySQL cannot run directly on Android, but it can be implemented indirectly by using the following methods: using the lightweight database SQLite, which is built on the Android system, does not require a separate server, and has a small resource usage, which is very suitable for mobile device applications. Remotely connect to the MySQL server and connect to the MySQL database on the remote server through the network for data reading and writing, but there are disadvantages such as strong network dependencies, security issues and server costs.
 Do mysql need to pay
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
Do mysql need to pay
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
MySQL has a free community version and a paid enterprise version. The community version can be used and modified for free, but the support is limited and is suitable for applications with low stability requirements and strong technical capabilities. The Enterprise Edition provides comprehensive commercial support for applications that require a stable, reliable, high-performance database and willing to pay for support. Factors considered when choosing a version include application criticality, budgeting, and technical skills. There is no perfect option, only the most suitable option, and you need to choose carefully according to the specific situation.