How does H5's FileReader read files distributedly?
This time I will bring you how to distribute H5 FileReaderread files, what are the precautions for FileReader to distribute and read files, the following is a practical case, let’s take a look .
Renderings
Old rules include renderings first
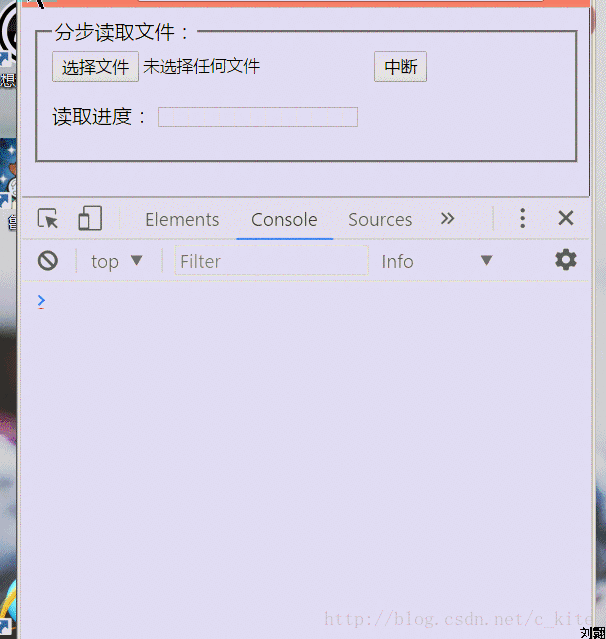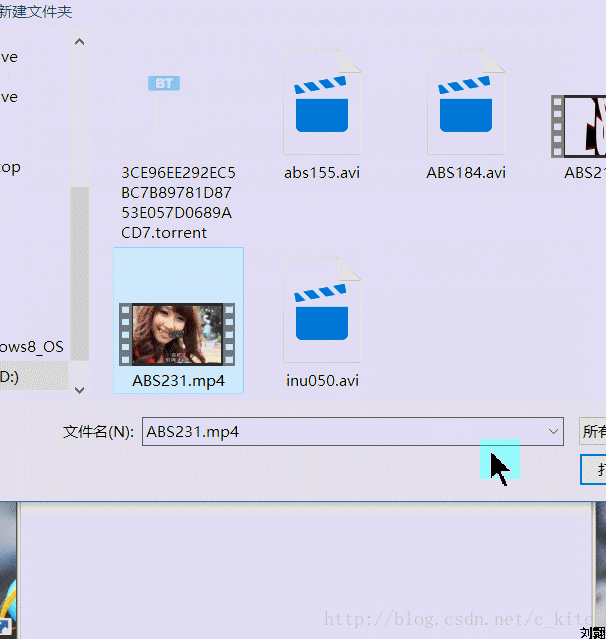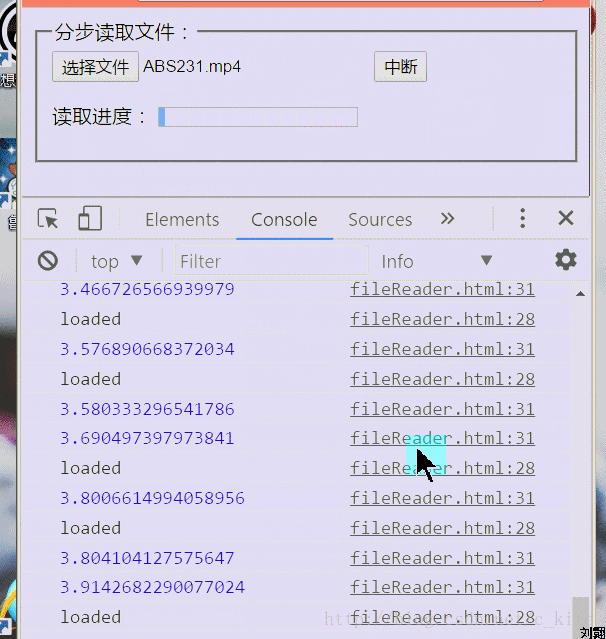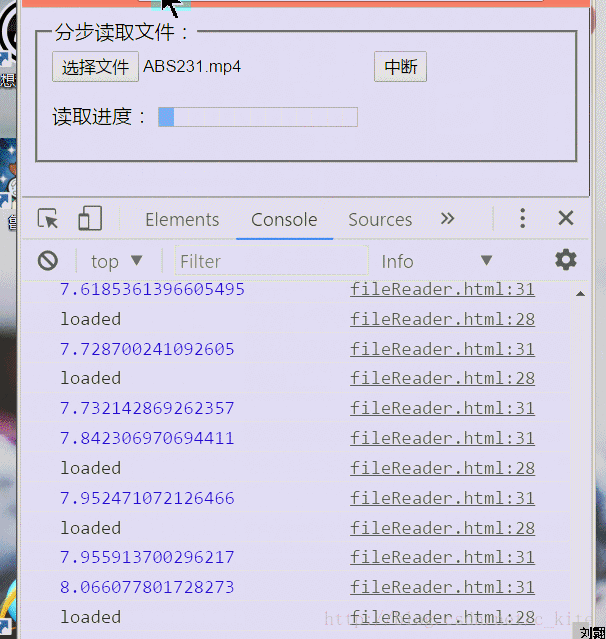
First introduce some methods and events of FileReader in H5
FileReader method
| Name | Function |
|---|---|
| about() | Terminate reading |
| readAsBinaryString(file) | Read the file as binary encoding |
| readAsDataURL( file) | Read the file as DataURL encoding |
| readAsText(file, [encoding]) | Read the file as text |
| readAsArrayBuffer(file) | Read the file as arraybuffer |
FileReader event
| Name | Function |
|---|---|
| onloadstart | Triggered when reading starts |
| onprogress | Reading |
| onloadend | Reading completion triggers, regardless of success or failure |
| onload | Triggered when file reading is successfully completed |
| onabort | Triggered when interrupted |
| onerror | Triggered when an error occurs |
Code
The core idea of reading the file is distributed, dividing the file into chunks for each M to read.
HTML part
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<fieldset>
<legend>分步读取文件:</legend>
<input type="file" id="File">
<input type="button" value="中断" id="Abort">
<p>
<lable>读取进度:</lable>
<progress id="Progress" value="0" max="100"></progress>
</p>
</fieldset>
</form>
<script src="./loadFile.js"></script>
<script>
var progress = document.getElementById('Progress');//进度条
var events = {
load: function () {
console.log('loaded');
},
progress: function (percent) {
console.log(percent);
progress.value = percent;
},
success: function () {
console.log('success');
}
};
var loader;
// 选择好要上传的文件后触发onchange事件
document.getElementById('File').onchange = function (e) {
var file = this.files[0];
console.log(file)
//loadFile.js
loader = new FileLoader(file, events);
};
document.getElementById('Abort').onclick = function () {
loader.abort();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>loadFile.js part
/*
* 文件读取模块
* file 文件对象
* events 事件回掉对象 包含 success , load, progress
*/
var FileLoader = function (file, events) {
this.reader = new FileReader();
this.file = file;
this.loaded = 0;
this.total = file.size;
//每次读取1M
this.step = 1024 * 1024;
this.events = events || {};
//读取第一块
this.readBlob(0);
this.bindEvent();
}
FileLoader.prototype = {
bindEvent: function (events) {
var _this = this,
reader = this.reader;
reader.onload = function (e) {
_this.onLoad();
};
reader.onprogress = function (e) {
_this.onProgress(e.loaded);
};
// start 、abort、error 回调暂时不加
},
// progress 事件回掉
onProgress: function (loaded) {
var percent,
handler = this.events.progress;//进度条
this.loaded += loaded;
percent = (this.loaded / this.total) * 100;
handler && handler(percent);
},
// 读取结束(每一次执行read结束时调用,并非整体)
onLoad: function () {
var handler = this.events.load;
// 应该在这里发送读取的数据
handler && handler(this.reader.result);
// 如果未读取完毕继续读取
if (this.loaded < this.total) {
this.readBlob(this.loaded);
} else {
// 读取完毕
this.loaded = this.total;
// 如果有success回掉则执行
this.events.success && this.events.success();
}
},
// 读取文件内容
readBlob: function (start) {
var blob,
file = this.file;
// 如果支持 slice 方法,那么分步读取,不支持的话一次读取
if (file.slice) {
blob = file.slice(start, start + this.step);
} else {
blob = file;
}
this.reader.readAsText(blob);
},
// 中止读取
abort: function () {
var reader = this.reader;
if(reader) {
reader.abort();
}
}
}I believe you have mastered the method after reading the case in this article. For more exciting information, please pay attention to php Chinese website Other related articles!
Recommended reading:
Summary of various incorrect usages of H5
How Canvas makes a 3D dynamic Chart
The above is the detailed content of How does H5's FileReader read files distributedly?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to Table Border in HTML. Here we discuss multiple ways for defining table-border with examples of the Table Border in HTML.
 HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Guide to HTML margin-left. Here we discuss a brief overview on HTML margin-left and its Examples along with its Code Implementation.
 Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
This is a guide to Nested Table in HTML. Here we discuss how to create a table within the table along with the respective examples.
 HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Table Layout. Here we discuss the Values of HTML Table Layout along with the examples and outputs n detail.
 HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Input Placeholder. Here we discuss the Examples of HTML Input Placeholder along with the codes and outputs.
 HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Guide to the HTML Ordered List. Here we also discuss introduction of HTML Ordered list and types along with their example respectively
 Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Guide to Moving Text in HTML. Here we discuss an introduction, how marquee tag work with syntax and examples to implement.
 HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to HTML onclick Button. Here we discuss their introduction, working, examples and onclick Event in various events respectively.




