How Python uses the xlwt module to operate Excel
Mar 29, 2018 pm 01:15 PMThis article mainly introduces how Python uses the xlwt module to operate Excel. It analyzes common operating techniques such as installing the xlwt module in Python and using the xlwt module to create, set, and save Excel files. Friends in need can refer to it. Next, I hope it can help everyone.
Part is excerpted from the official website documentation.
The module installation is very simple
$ pip install xlwt
Let’s take a simple example first :
#!/usr/bin/python #coding=utf-8 # ============================================================================== # # Filename: demo.py # Description: excel operat # Created: Tue Apr 25 17:10:33 CST 2017 # Author: Yur # # ============================================================================== import xlwt # 创建一个workbook 设置编码 workbook = xlwt.Workbook(encoding = 'utf-8') # 创建一个worksheet worksheet = workbook.add_sheet('My Worksheet') # 写入excel # 参数对应 行, 列, 值 worksheet.write(1,0, label = 'this is test') # 保存 workbook.save('Excel_test.xls')
After running, an Excel_test.xls will be generated in the current directory
Official example:
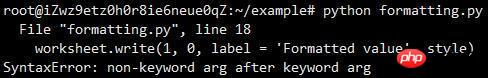
An error occurred when running this example
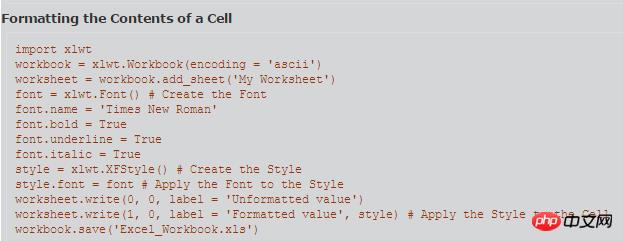
I wrote another one myself:
#!/usr/bin/python #coding=utf-8 # ============================================================================== # # Filename: style.py # Description: style # Created: Thu Apr 27 15:07:53 CST 2017 # Author: Yur # # ============================================================================== import xlwt workbook = xlwt.Workbook(encoding = 'ascii') worksheet = workbook.add_sheet('My Worksheet') style = xlwt.XFStyle() # 初始化样式 font = xlwt.Font() # 为样式创建字体 font.name = 'Times New Roman' font.bold = True # 黑体 font.underline = True # 下划线 font.italic = True # 斜体字 style.font = font # 设定样式 worksheet.write(0, 0, 'Unformatted value') # 不带样式的写入 worksheet.write(1, 0, 'Formatted value', style) # 带样式的写入 workbook.save('formatting.xls') # 保存文件
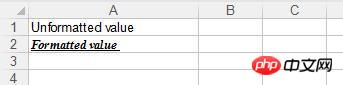
Effect:
Set cell width:
import xlwt workbook = xlwt.Workbook() worksheet = workbook.add_sheet('My Sheet') worksheet.write(0, 0,'My Cell Contents') # 设置单元格宽度 worksheet.col(0).width = 3333 workbook.save('cell_width.xls')
Enter one Date to cell:
import xlwt import datetime workbook = xlwt.Workbook() worksheet = workbook.add_sheet('My Sheet') style = xlwt.XFStyle() style.num_format_str = 'M/D/YY' # Other options: D-MMM-YY, D-MMM, MMM-YY, h:mm, h:mm:ss, h:mm, h:mm:ss, M/D/YY h:mm, mm:ss, [h]:mm:ss, mm:ss.0 worksheet.write(0, 0, datetime.datetime.now(), style) workbook.save('Excel_Workbook.xls')
Add a formula to cell:
##
import xlwt workbook = xlwt.Workbook() worksheet = workbook.add_sheet('My Sheet') worksheet.write(0, 0, 5) # Outputs 5 worksheet.write(0, 1, 2) # Outputs 2 worksheet.write(1, 0, xlwt.Formula('A1*B1')) # Should output "10" (A1[5] * A2[2]) worksheet.write(1, 1, xlwt.Formula('SUM(A1,B1)')) # Should output "7" (A1[5] + A2[2]) workbook.save('Excel_Workbook.xls')
Add a hyperlink to a cell:
import xlwt workbook = xlwt.Workbook() worksheet = workbook.add_sheet('My Sheet') worksheet.write(0, 0, xlwt.Formula('HYPERLINK("http://www.google.com";"Google")')) # Outputs the text "Google" linking to http://www.google.com workbook.save('Excel_Workbook.xls')
Merge columns and rows:
import xlwt workbook = xlwt.Workbook() worksheet = workbook.add_sheet('My Sheet') worksheet.write_merge(0, 0, 0, 3, 'First Merge') # Merges row 0's columns 0 through 3. font = xlwt.Font() # Create Font font.bold = True # Set font to Bold style = xlwt.XFStyle() # Create Style style.font = font # Add Bold Font to Style worksheet.write_merge(1, 2, 0, 3, 'Second Merge', style) # Merges row 1 through 2's columns 0 through 3. workbook.save('Excel_Workbook.xls')
Set the alignment method of cell content:
import xlwt workbook = xlwt.Workbook() worksheet = workbook.add_sheet('My Sheet') alignment = xlwt.Alignment() # Create Alignment alignment.horz = xlwt.Alignment.HORZ_CENTER # May be: HORZ_GENERAL, HORZ_LEFT, HORZ_CENTER, HORZ_RIGHT, HORZ_FILLED, HORZ_JUSTIFIED, HORZ_CENTER_ACROSS_SEL, HORZ_DISTRIBUTED alignment.vert = xlwt.Alignment.VERT_CENTER # May be: VERT_TOP, VERT_CENTER, VERT_BOTTOM, VERT_JUSTIFIED, VERT_DISTRIBUTED style = xlwt.XFStyle() # Create Style style.alignment = alignment # Add Alignment to Style worksheet.write(0, 0, 'Cell Contents', style) workbook.save('Excel_Workbook.xls')
Add a border to the cell :
# Please note: While I was able to find these constants within the source code, on my system (using LibreOffice,) I was only presented with a solid line, varying from thin to thick; no dotted or dashed lines. import xlwt workbook = xlwt.Workbook() worksheet = workbook.add_sheet('My Sheet') borders = xlwt.Borders() # Create Borders borders.left = xlwt.Borders.DASHED DASHED虚线 NO_LINE没有 THIN实线 # May be: NO_LINE, THIN, MEDIUM, DASHED, DOTTED, THICK, DOUBLE, HAIR, MEDIUM_DASHED, THIN_DASH_DOTTED, MEDIUM_DASH_DOTTED, THIN_DASH_DOT_DOTTED, MEDIUM_DASH_DOT_DOTTED, SLANTED_MEDIUM_DASH_DOTTED, or 0x00 through 0x0D. borders.right = xlwt.Borders.DASHED borders.top = xlwt.Borders.DASHED borders.bottom = xlwt.Borders.DASHED borders.left_colour = 0x40 borders.right_colour = 0x40 borders.top_colour = 0x40 borders.bottom_colour = 0x40 style = xlwt.XFStyle() # Create Style style.borders = borders # Add Borders to Style worksheet.write(0, 0, 'Cell Contents', style) workbook.save('Excel_Workbook.xls')
Set the background color for cells:
import xlwt workbook = xlwt.Workbook() worksheet = workbook.add_sheet('My Sheet') pattern = xlwt.Pattern() # Create the Pattern pattern.pattern = xlwt.Pattern.SOLID_PATTERN # May be: NO_PATTERN, SOLID_PATTERN, or 0x00 through 0x12 pattern.pattern_fore_colour = 5 # May be: 8 through 63. 0 = Black, 1 = White, 2 = Red, 3 = Green, 4 = Blue, 5 = Yellow, 6 = Magenta, 7 = Cyan, 16 = Maroon, 17 = Dark Green, 18 = Dark Blue, 19 = Dark Yellow , almost brown), 20 = Dark Magenta, 21 = Teal, 22 = Light Gray, 23 = Dark Gray, the list goes on... style = xlwt.XFStyle() # Create the Pattern style.pattern = pattern # Add Pattern to Style worksheet.write(0, 0, 'Cell Contents', style) workbook.save('Excel_Workbook.xls')
Use Python to operate excel files
Introduction to using Python to operate Excel xlsx files
Python operation Detailed explanation of excel
The above is the detailed content of How Python uses the xlwt module to operate Excel. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot Article

Hot tools Tags

Hot Article

Hot Article Tags

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the advantages and disadvantages of templating?
May 08, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
What are the advantages and disadvantages of templating?
May 08, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
What are the advantages and disadvantages of templating?
 Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
Jul 01, 2024 am 07:22 AM
Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
Jul 01, 2024 am 07:22 AM
Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
 For only $250, Hugging Face's technical director teaches you how to fine-tune Llama 3 step by step
May 06, 2024 pm 03:52 PM
For only $250, Hugging Face's technical director teaches you how to fine-tune Llama 3 step by step
May 06, 2024 pm 03:52 PM
For only $250, Hugging Face's technical director teaches you how to fine-tune Llama 3 step by step
 Share several .NET open source AI and LLM related project frameworks
May 06, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Share several .NET open source AI and LLM related project frameworks
May 06, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Share several .NET open source AI and LLM related project frameworks
 A complete guide to golang function debugging and analysis
May 06, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
A complete guide to golang function debugging and analysis
May 06, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
A complete guide to golang function debugging and analysis










