This article shares with you about some front-end interview questions, hoping to help friends in need
1. Dynamic type language
JavaScript is a kind of dynamic Typed language (dynamically typed language). This means that you don't have to specify a data type when declaring a variable, and the data type will be automatically converted as needed when the script is executed. 1.1 Define variables
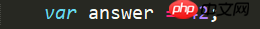 And you can also assign a string value to the same variable, such as
And you can also assign a string value to the same variable, such as
 Because JavaScript is dynamically typed, assignment
Because JavaScript is dynamically typed, assignment
will not prompt an error
. 1.2 Addition operator (+)
In numeric and string expressions involving the addition operator (+), JavaScript will convert the
numeric value into a string
. For example
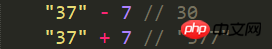
 But when it comes to other operators (Annotation: such as the minus sign '
But when it comes to other operators (Annotation: such as the minus sign '
-
' below), the JavaScript language Does not convert numbers into strings. For example (Annotation: The first example is mathematical operation, the second example is string operation):
 2. Typeof operator
2. Typeof operator
Since variables in JavaScript are
loosely typed
, JavaScript provides an operator to detect the data type of the current variable, which is typeof. By using typeof()
Get the data type of the object
, including the following types: boolean, string, number, undefined, object, function. 2.1 boolean ------------- Boolean value Boolean
 2.2 string --- -------------- String String
2.2 string --- -------------- String String
 #2.3 number ---------- ---- Numeric Number
#2.3 number ---------- ---- Numeric Number
 2.4 undefined ---------- UndefinedUndefined
2.4 undefined ---------- UndefinedUndefined
 2.5 object ---------------- Object or null Object
2.5 object ---------------- Object or null Object
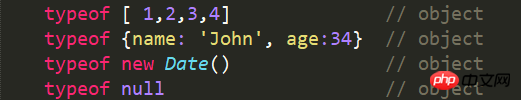 2.6 function --------------- Function Function
2.6 function --------------- Function Function
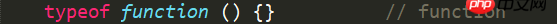 ##Note
##Note
(1) The data type of
NaN
is number
(2) The data type of undefined variable
is undefined
(3) The data type of array
(Array) is object
(4)The data type of date
(Date) is object
(5)## The data type of #null is object
(6) The data type of function (function) is function
3. Convert string to number 3.1 Number() function
3.2 parseInt() function
3.3 parseFloat() function
3.4 Unary addition operator
4. Number() function
4.1 Definition and usage
Number() function converts the value of an object into a number.
4.2 Syntax
Number(object)
Parameters
Description
| |
object
Required. JavaScript object.
|
4.3 Return value
(1) If the parameter is a Date object, Number() returns the number of milliseconds from January 1, 1970 to the present.
(2) If the value of the object cannot be converted to a number , then the Number() function returns NaN.
4.4 Example
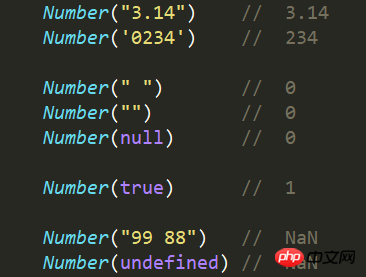
5. parseInt() function
5.1 Definition and usage## The #parseInt() function parses a string and returns an integer.
(1) When the value of parameter radix is 0, or the parameter is not set, parseInt() will determine the base of the number based on string. (2) When ignores the parameter radix, JavaScript defaults the radix of the number as follows:
- If the string starts with "
0x " at the beginning, parseInt() will parse the rest of the string into a hexadecimal integer.
- If string starts with
0, then ECMAScript v3 allows an implementation of parseInt() to parse the following characters into octal or hexadecimal number.
- If string starts with a number from
1 ~ 9, parseInt() will parse it into a decimal integer.
5.2 SyntaxparseInt(string, radix)
##Parameters
| Description |
|
string
| Required. The string to be parsed. |
|
radix
| Optional. Represents the base of the number to be parsed. The value is between 2 ~ 36. |
|
5.3 Tips and Notes
(1) Only the first number in the string will be returned. (2) Spaces at the beginning of and at the end of are allowed. (3) If the first character of the string cannot be converted to a number , then parseInt() will return NaN. (4) Old browsers use octal base by default when the string starts with "0". ECMAScript 5, the default is decimal base.
5.4 Example
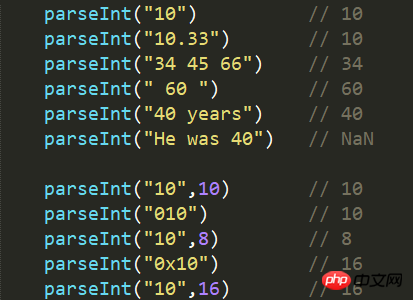 6. parseFloat() function 6. parseFloat() function
6.1 Definition and usage## The #parseFloat() function parses a string and returns a float.
This function specifies whether the first character in the string is a number . If so, the string is parsed until the end of the number is reached, and the number is returned as number rather than as a string. 6.2 Syntax parseFloat(string)
##Parameters
Description
| |
string
Required. The string to be parsed.
|
6.3 Tips and comments
(1) Only the first number is returned in the string.
(2) Spaces at the beginning of and at the end of are allowed.
(3) If the first character of the string cannot be converted to a number , then parseFloat() will return NaN.
6.4 Example
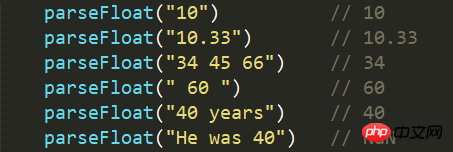
7. Unary addition operator
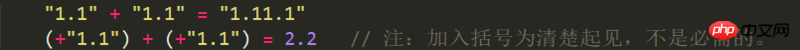
8. Convert numbers to strings
To be continued
##1. Dynamic type languageJavaScript It is a dynamically typed language. This means that you don't have to specify a data type when declaring a variable, and the data type will be automatically converted as needed when the script is executed. 1.1 Define variables
##And you can also assign a character to the same variable String value, such as 
Because JavaScript is dynamically typed, such assignment  will not prompt an error . will not prompt an error .
1.2 Addition operator (+)In numeric and string expressions involving the addition operator (+), JavaScript will convert the numeric value into a string . For example
But when it comes to other operators (Annotation: such as the minus sign ' -' below), the JavaScript language Does not convert numbers into strings. For example (Annotation: The first example is -' below), the JavaScript language Does not convert numbers into strings. For example (Annotation: The first example is mathematical operation, the second example is string operation):
2. Typeof operator Since variables in JavaScript are Since variables in JavaScript are loosely typed, JavaScript provides an operator to detect the data type of the current variable, which is typeof.
By using typeof()Get the data type of the object, including the following types: boolean, string, number, undefined, object, function.
2.1 boolean ------------- Boolean value Boolean
2.2 string --- -------------- String String
#2.3 number ---------- ---- Numeric Number
2.4 undefined ---------- UndefinedUndefined
2.5 object ---------------- Object or null Object
2.6 function --------------- Function Function
##Note 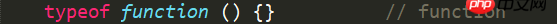 (1) The data type of NaN (1) The data type of NaN is number (2) The data type of undefined variable is undefined (3) The data type of array(Array) is object (4)The data type of date(Date) is object (5)## The data type of #null is object (6) The data type of function (function) is function 3. Convert string to number 3.1 Number() function3.2 parseInt() function
3.3 parseFloat() function
3.4 Unary addition operator
4. Number() function
4.1 Definition and usage
Number() function converts the value of an object into a number.
4.2 Syntax
Number(object)
ParametersDescription
|
object |
Required. JavaScript object.
4.3 Return value
(1) If the parameter is a Date object, Number() returns the number of milliseconds from January 1, 1970 to the present.
(2) If the value of the object cannot be converted to a number , then the Number() function returns NaN.
4.4 Example

5. parseInt() function
5.1 Definition and usage## The #parseInt() function parses a string and returns an integer.
(1) When the value of parameter radix is 0, or the parameter is not set, parseInt() will determine the base of the number based on string. (2) When ignores the parameter radix, JavaScript defaults the radix of the number as follows:
- If the string starts with "
0x " at the beginning, parseInt() will parse the rest of the string into a hexadecimal integer.
- If string starts with
0, then ECMAScript v3 allows an implementation of parseInt() to parse the following characters into octal or hexadecimal number.
- If string starts with a number from
1 ~ 9, parseInt() will parse it into a decimal integer.
5.2 SyntaxparseInt(string, radix)
##Parameters
| Description |
|
string
| Required. The string to be parsed. |
|
radix
| Optional. Represents the base of the number to be parsed. The value is between 2 ~ 36. |
|
5.3 Tips and Notes
(1) Only the first number in the string will be returned. (2) Spaces at the beginning of and at the end of are allowed. (3) If the first character of the string cannot be converted to a number , then parseInt() will return NaN. (4) Old browsers use octal base by default when the string starts with "0". ECMAScript 5, the default is decimal base.
5.4 Example
 6. parseFloat() function 6. parseFloat() function
6.1 Definition and usage## The #parseFloat() function parses a string and returns a float.
This function specifies whether the first character in the string is a number . If so, the string is parsed until the end of the number is reached, and the number is returned as number rather than as a string. 6.2 Syntax parseFloat(string)
##Parameters
Description
| |
string
Required. The string to be parsed.
|
6.3 提示和注释
(1)字符串中只返回第一个数字。
(2)开头和结尾的空格是允许的。
(3)如果字符串的第一个字符不能被转换为数字,那么 parseFloat() 会返回 NaN。
6.4 实例

七、单目加法运算符
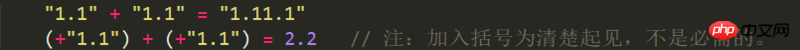
八、数字转换为字符串
未完待续
相关推荐:
2018前端面试常见算法题
前端面试题小结
|
|
|
|
The above is the detailed content of Front-end interview questions - JavaScript data type conversion - JavaScript ING. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

 And you can also assign a string value to the same variable, such as
And you can also assign a string value to the same variable, such as  Because JavaScript is dynamically typed, assignment
Because JavaScript is dynamically typed, assignment  But when it comes to other operators (Annotation: such as the minus sign '
But when it comes to other operators (Annotation: such as the minus sign ' 2. Typeof operator
2. Typeof operator 2.2 string --- -------------- String String
2.2 string --- -------------- String String #2.3 number ---------- ---- Numeric Number
#2.3 number ---------- ---- Numeric Number 2.4 undefined ---------- UndefinedUndefined
2.4 undefined ---------- UndefinedUndefined 2.5 object ---------------- Object or null Object
2.5 object ---------------- Object or null Object 2.6 function --------------- Function Function
2.6 function --------------- Function Function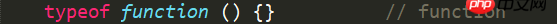 ##Note
##Note 



