HTTP protocol front-end common sense
This article shares with you some common sense issues about the front-end of the http protocol. Friends who are interested can take a look
http

Introduction: http transfers data based on tcp/ip communication
Notes
http is no connection: every time The connection only processes one request. After the server processes the request and receives a response from the client, it disconnects;
http media is independent: as long as the client and server know How to handle data types, any data can be transmitted using http;
http stateless: Stateless means that the protocol has no memory ability for transaction processing;
Message structure
1.http client request includes: request line, request header, blank line and request data
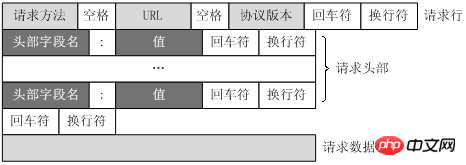
2.http response: status line, message header, blank line, response body
http request method
http1.0: get, post and head
http1.1 adds five new request methods: delete, put, connect, tarce and options
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| get | Initiate a request to a specific resource |
| post | Submit data to the specified resource for data processing. The data is included in the request body. The post request may be used to create new resources and modify existing resources. |
| head | is similar to the get request, except that there is no Return body, used to obtain meta-information contained in the response message header |
| put | Upload the latest content to the specified resource |
| delete | Request the server to delete the specified resource |
| trace | Echo the request received by the server, mainly used for testing or diagnosis |
| connect | http1.1 is reserved for proxy servers that can change connections to pipelines |
| options | Returns the http method supported by the server for specific resources, which is used to send a '*' request to the server to test the functionality of the server |
Introduction to the meaning of common header fields
Headers and methods work together to determine what the client and server can do
General header
Headers that can be used by both the client and the server
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection | Allow The client and server specify options related to the request/response connection |
| Date | Provides a date and time stamp to indicate when the message was created |
| MIME-Version | Gives the MIME version sent to the end |
| Trailer | If the message transmission uses In chunked transfer encoding mode, you can use this header to list the set of headers located in the trailer part of the message |
| Transfer-Encoding | to tell the receiving end In order to ensure reliable transmission of the message, what encoding method is used for the message |
| Update | gives that the sender may want to "upgrade" to use a new version or protocol |
| Via | Display the intermediate nodes (agents, gateways) that the message passes through |
Request header
Special to the request message, providing some additional information to the server, such as what kind of data type the client hopes to receive
Requested Informational Header
##Client-IpProvide the IP address of the machine running the clientFromProvide the email address of the client userHostGives the address and port number of the server receiving the requestRefererProvides the URL of the document containing the current request URLUA-colorProvide information about the display color of the client monitorUA-CPUgiven Client CPU type and manufacturerUA-DispProvides information about client display capabilities##UA -OSUA-PixelsUser-AgentAccept header| Header | Description |
|---|---|
| Provides the operating system and version running on the client machine | |
| Provides the pixel information of the client display | |
| Inform the server of the name of the application sending the request |
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Tells the server which media types it can send | |
| Tell the server which character sets can be sent | |
| Tell Which encoding methods the server can send | |
| Tell the server which languages it can send | |
| Tell the server which extended transfer encodings can be used |
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Allows the client to list the server behavior required by the request | |
| If the entity tag matches the document's current entity tag, get the document | |
| unless The resource has been modified after a specified date, otherwise the request will be restricted | |
| If the entity tag does not match the current entity of the document, Just get the document | |
| Allow conditional request for a certain range of the document | |
| Restrict this request unless the resource has not been modified after a specified date | |
| If the server supports range requests, Request the specified range of resources |
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Contains the data provided by the client to the server in order to authenticate itself | |
| The client uses it to send a token to the server--it is not a real security header, it does imply security functions | |
Response headers
The response message has its own set of headers to provide information to the client
Informative headers of the response
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
| Description | |
|---|---|
| For this resource, the data types acceptable to the server | |
| The server checks other header lists, which may cause the response to change; that is to say, this is a header list, and the server will select the most appropriate resource version based on the contents of these headers and send it to the client |
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Challenge list from proxy to client | |
| Not a true security header, but implicit security Function; you can set a security token on the client to mark the client through the server | |
| Similar to Set-Cookie | |
| Challenge list from server to client |
Content header
##HeaderDescriptionContent-BaseThe base URL used when parsing relative URLs in the bodyContent-EncondingArbitrary encoding method performed on the subjectContent-LanguageThe most appropriate natural language to use when understanding the subjectContent-LengthThe length or size of the bodyContent-LocationThe location of the resource entityContent-MD5The MD5 checksum of the subjectContent-RangeThe range of resources represented by this entity in the entire resource Content-TypeThe object type of this topicEntity cache header| Expires | |
| Last- Modified | |
100-199
- : Informational status code
200-299: Success status code
When the client sends a request, these requests are usually successful.
| Meaning | ||
|---|---|---|
300-399: Redirect status code
Redirect status code or tell the client to use an alternative location. Access the resource they are interested in, or provide an alternative response instead of the resource's content. If the resource has been moved, a redirect status code and an optional Location header can be sent to inform the client that the resource has been moved and where it can be found now
| Status Code | Reason Phrase | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | OK | There is no problem with the request, the body part of the entity contains the requested resource |
| 201 | Created | Used to create an object request for the server (such as PUT). The entity part of the response should contain various URLs that reference the resources created. The Location header contains the most specific reference. The server must send In this state, the previously created object |
| 202 | Accepted | The request has been accepted, but the server has not performed any operations on it. There is no guarantee that the server will complete the request, it just means that when the request is accepted, it appears to be valid. The server SHOULD include a description of the status of the request in the body of the entity, and perhaps an estimate of when the request will complete (or include a pointer to where this information can be obtained) |
| 203 | Non-Authoritative Information | The information contained in the entity header does not come from the source server, but from a copy of the resource. This situation occurs if the intermediate node has a copy of the resource, but cannot or does not verify the metainformation (header) related to the resource it sends |
| 204 | No Content | The response message contains several headers and a status line, but there is no entity body. Mainly used to update the browser without converting it to a new document (such as refreshing an expression page) |
| 205 | Reset Content | Another code mainly for browsers. Responsible for telling the browser to clear all html tags in the current page |
| 206 | Partail Content | Successfully execute a part or range request. We will see later that the client can obtain part or range of documents through some special headers - this status code indicates that the range request is successful The response must include Content-Range, Date and ETag or Content-Location header |
400-499: Client error status code
Sometimes the client will send a message that the server cannot handle Something, such as a malformed request message, or most commonly a non-existent URL
| Status code | Reason phrase | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
500-599: Server error status code
Sometimes the client sends a request and the server itself On error
| Status code | Reason phrase | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Status code | Reason phrase | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
Edit this page on github
blogger’s personal blog
Reference: http protocol[http authoritative guide]
Process of using http protocol
What is the difference between HTTP protocol and TCP protocol
The above is the detailed content of HTTP protocol front-end common sense. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 What does http status code 520 mean?
Oct 13, 2023 pm 03:11 PM
What does http status code 520 mean?
Oct 13, 2023 pm 03:11 PM
HTTP status code 520 means that the server encountered an unknown error while processing the request and cannot provide more specific information. Used to indicate that an unknown error occurred when the server was processing the request, which may be caused by server configuration problems, network problems, or other unknown reasons. This is usually caused by server configuration issues, network issues, server overload, or coding errors. If you encounter a status code 520 error, it is best to contact the website administrator or technical support team for more information and assistance.
 What is http status code 403?
Oct 07, 2023 pm 02:04 PM
What is http status code 403?
Oct 07, 2023 pm 02:04 PM
HTTP status code 403 means that the server rejected the client's request. The solution to http status code 403 is: 1. Check the authentication credentials. If the server requires authentication, ensure that the correct credentials are provided; 2. Check the IP address restrictions. If the server has restricted the IP address, ensure that the client's IP address is restricted. Whitelisted or not blacklisted; 3. Check the file permission settings. If the 403 status code is related to the permission settings of the file or directory, ensure that the client has sufficient permissions to access these files or directories, etc.
 Understand common application scenarios of web page redirection and understand the HTTP 301 status code
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:41 PM
Understand common application scenarios of web page redirection and understand the HTTP 301 status code
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:41 PM
Understand the meaning of HTTP 301 status code: common application scenarios of web page redirection. With the rapid development of the Internet, people's requirements for web page interaction are becoming higher and higher. In the field of web design, web page redirection is a common and important technology, implemented through the HTTP 301 status code. This article will explore the meaning of HTTP 301 status code and common application scenarios in web page redirection. HTTP301 status code refers to permanent redirect (PermanentRedirect). When the server receives the client's
 How to use Nginx Proxy Manager to implement automatic jump from HTTP to HTTPS
Sep 26, 2023 am 11:19 AM
How to use Nginx Proxy Manager to implement automatic jump from HTTP to HTTPS
Sep 26, 2023 am 11:19 AM
How to use NginxProxyManager to implement automatic jump from HTTP to HTTPS. With the development of the Internet, more and more websites are beginning to use the HTTPS protocol to encrypt data transmission to improve data security and user privacy protection. Since the HTTPS protocol requires the support of an SSL certificate, certain technical support is required when deploying the HTTPS protocol. Nginx is a powerful and commonly used HTTP server and reverse proxy server, and NginxProxy
 Quick Application: Practical Development Case Analysis of PHP Asynchronous HTTP Download of Multiple Files
Sep 12, 2023 pm 01:15 PM
Quick Application: Practical Development Case Analysis of PHP Asynchronous HTTP Download of Multiple Files
Sep 12, 2023 pm 01:15 PM
Quick Application: Practical Development Case Analysis of PHP Asynchronous HTTP Download of Multiple Files With the development of the Internet, the file download function has become one of the basic needs of many websites and applications. For scenarios where multiple files need to be downloaded at the same time, the traditional synchronous download method is often inefficient and time-consuming. For this reason, using PHP to download multiple files asynchronously over HTTP has become an increasingly common solution. This article will analyze in detail how to use PHP asynchronous HTTP through an actual development case.
 Common network communication and security problems and solutions in C#
Oct 09, 2023 pm 09:21 PM
Common network communication and security problems and solutions in C#
Oct 09, 2023 pm 09:21 PM
Common network communication and security problems and solutions in C# In today's Internet era, network communication has become an indispensable part of software development. In C#, we usually encounter some network communication problems, such as data transmission security, network connection stability, etc. This article will discuss in detail common network communication and security issues in C# and provide corresponding solutions and code examples. 1. Network communication problems Network connection interruption: During the network communication process, the network connection may be interrupted, which may cause
 HTTP 200 OK: Understand the meaning and purpose of a successful response
Dec 26, 2023 am 10:25 AM
HTTP 200 OK: Understand the meaning and purpose of a successful response
Dec 26, 2023 am 10:25 AM
HTTP Status Code 200: Explore the Meaning and Purpose of Successful Responses HTTP status codes are numeric codes used to indicate the status of a server's response. Among them, status code 200 indicates that the request has been successfully processed by the server. This article will explore the specific meaning and use of HTTP status code 200. First, let us understand the classification of HTTP status codes. Status codes are divided into five categories, namely 1xx, 2xx, 3xx, 4xx and 5xx. Among them, 2xx indicates a successful response. And 200 is the most common status code in 2xx
 http request 415 error solution
Nov 14, 2023 am 10:49 AM
http request 415 error solution
Nov 14, 2023 am 10:49 AM
Solution: 1. Check the Content-Type in the request header; 2. Check the data format in the request body; 3. Use the appropriate encoding format; 4. Use the appropriate request method; 5. Check the server-side support.




