 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
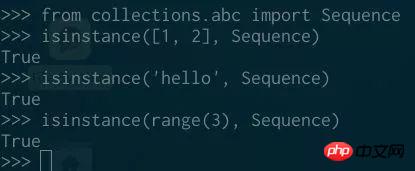
 Discussion on whether the range object in Python is an iterator
Discussion on whether the range object in Python is an iterator
Discussion on whether the range object in Python is an iterator
Iterator (iterator) is a lazy iterable object (lazy iterable). The range function is a lazy iterable object in Python 3. So, is range an iterator? Why.
TLNR: Range objects in Python 3 (xrange objects in Python 2) are lazy, but range objects are not iterators.
Yes , this is very confusing
When talking about iterators (iterators) and iterable objects (iterables) in Python, you are likely to hear someone repeat that range is an iterator. misunderstanding. I think this is a very serious misunderstanding. If you think that range objects are iterators, then your mental model of "how iterators work" is not clear enough. In a sense, ranges and iterators are both "lazy", but they achieve "laziness" in quite different ways.
What is an iterator
In Python, An iterable is anything you can iterate over, and an iterator is what you actually iterate over.
Iter-ables are able to be iterated over. Iter-ators are the agents that perform the iteration.
You can use the iter function to get an iterator from any iterable object:
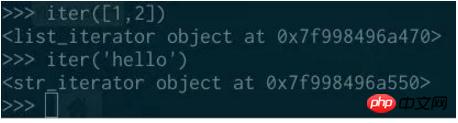
Once you have With an iterator, the only thing you can do with it is get its next element:
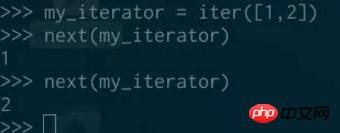
If there is no more If there are too many elements, a stop iteration exception will be thrown:
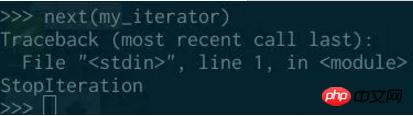
##All iterators are iterable objects , meaning you can get an iterator from an iterator, so you can iterate over an iterator:
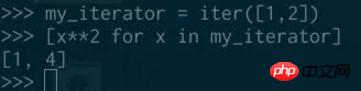
#It should be pointed out that iterators are stateful, after looping through an iterator once, if you try to loop again, it will be empty:
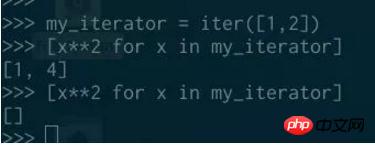
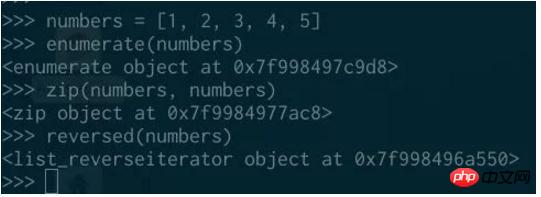
##In Python 3, enumerate, zip, reversed<span style="color: rgb(103, 103, 103);"></span> and some other built-in functions return iterators:
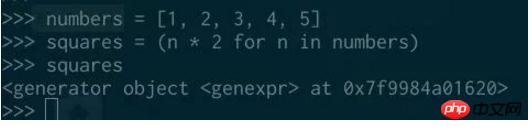
generator (whatever comes from the generator function or a generator expression) is a simple way to create an iterator:
I often say that iterators are lazy A one-time iterable object. "Lazy" because they only count items in a loop, "single-use" because once an element is "consumed" from an iterator, the element is gone forever.
What is range
The range object in Python 3 (Python 2) can be looped like any other iterable object:
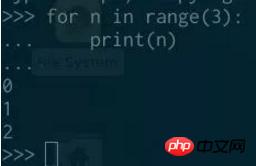
Because range is an iterable object, So you can get an iterator from it:
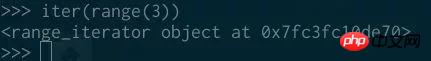
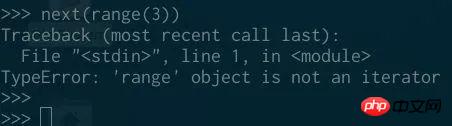
But the range object itself is not an iterator, we cannot call it on the range object next:
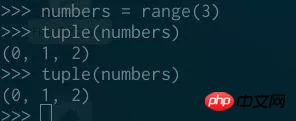
Unlike iterators, we can iterate over a range object without "consuming" it:
If we do this using an iterator, we won’t get any elements the second time through the loop:
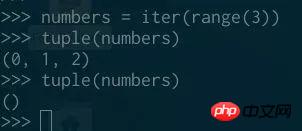
Zongshang, and <span style="color: rgb(103, 103, 103);">zip</span>, <span style="color: rgb(103, 103, 103);">enumerate</span>, or <span style="color: rgb(103, 103, 103);">generator</span> objects are different, and the range object is not an iterator.
So, what exactly is range?
The range object is in a certain It is "lazy" in the sense that it does not generate every number it contains when it is created. Instead, it returns these numbers to us when we need them in the loop.
The following is a range object and a generator (a kind of iterator):
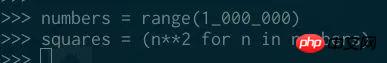
##Unlike generators, range objects have length:
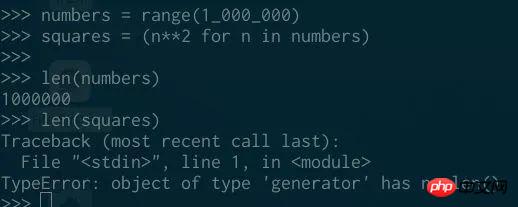
and can be indexed:
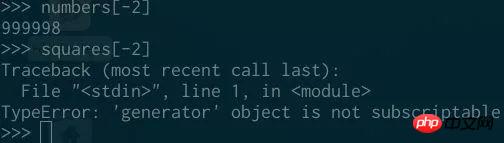
Unlike iterators, you can ask them whether they contain an element without changing their state:
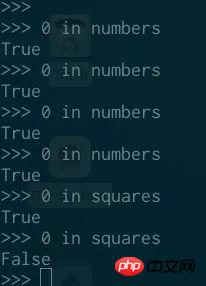
#If you want a description of range objects, you can call them <span style="color: rgb(103, 103, 103);">Lazy Sequences</span>, range is a sequence (such as list, tuple and string), but it does not contain any content in memory, but answers the question through calculation.
#Why this distinction is important
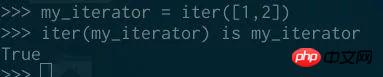
If I tell you that an object is an iterator, you will know that when you call the iter function on this object, you will always get the same object (by definition):
Make sure you can call the next function on this object, because the next function can be called on all iterators:
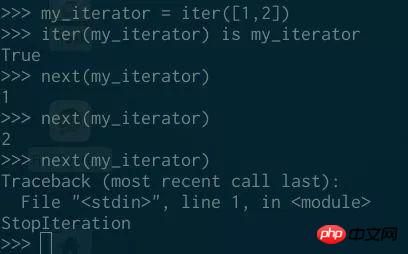
And you will know that when iterating over it, the elements will be consumed from the iterator, sometimes this feature can come in handy Usage (handling iterators in a special way):
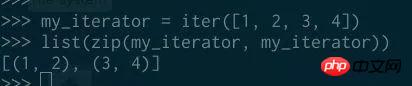
So although it seems that "lazy iterable object" and " The difference between "iterator" is subtle, but these terms do mean different things. While "lazy iterable object" is a very general term with no specific meaning, the word "iterator" means an object with very specific behavior.
Summary
If you know you can loop over an object, it is an iterable (iterable ).
If you know that the object you are looping over is calculated while looping, then this is a lazy iterable object (lazy iterable).
If you know you can pass something to the next function, it is an iterator (which is the most common lazy iterable object).
If you can loop multiple times without "exhausting" it, it's not an iterator. If you can't pass something to the next function, then it's not an iterator. Python 3's range objects are not iterators. If you are instructing someone about range objects, please do not use the word "iterator". This is very confusing and may lead others to start abusing the word "iterator"
Related recommendations:
Detailed description of iterators
Understanding of iterable objects and iterator objects in Python
The above is the detailed content of Discussion on whether the range object in Python is an iterator. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to use Debian Apache logs to improve website performance
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use Debian Apache logs to improve website performance
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
This article will explain how to improve website performance by analyzing Apache logs under the Debian system. 1. Log Analysis Basics Apache log records the detailed information of all HTTP requests, including IP address, timestamp, request URL, HTTP method and response code. In Debian systems, these logs are usually located in the /var/log/apache2/access.log and /var/log/apache2/error.log directories. Understanding the log structure is the first step in effective analysis. 2. Log analysis tool You can use a variety of tools to analyze Apache logs: Command line tools: grep, awk, sed and other command line tools.
 Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in gaming and GUI development. 1) Game development uses Pygame, providing drawing, audio and other functions, which are suitable for creating 2D games. 2) GUI development can choose Tkinter or PyQt. Tkinter is simple and easy to use, PyQt has rich functions and is suitable for professional development.
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
The readdir function in the Debian system is a system call used to read directory contents and is often used in C programming. This article will explain how to integrate readdir with other tools to enhance its functionality. Method 1: Combining C language program and pipeline First, write a C program to call the readdir function and output the result: #include#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char*argv[]){DIR*dir;structdirent*entry;if(argc!=2){
 The role of Debian Sniffer in DDoS attack detection
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
The role of Debian Sniffer in DDoS attack detection
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
This article discusses the DDoS attack detection method. Although no direct application case of "DebianSniffer" was found, the following methods can be used for DDoS attack detection: Effective DDoS attack detection technology: Detection based on traffic analysis: identifying DDoS attacks by monitoring abnormal patterns of network traffic, such as sudden traffic growth, surge in connections on specific ports, etc. This can be achieved using a variety of tools, including but not limited to professional network monitoring systems and custom scripts. For example, Python scripts combined with pyshark and colorama libraries can monitor network traffic in real time and issue alerts. Detection based on statistical analysis: By analyzing statistical characteristics of network traffic, such as data
 Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
To maximize the efficiency of learning Python in a limited time, you can use Python's datetime, time, and schedule modules. 1. The datetime module is used to record and plan learning time. 2. The time module helps to set study and rest time. 3. The schedule module automatically arranges weekly learning tasks.
 Nginx SSL Certificate Update Debian Tutorial
Apr 13, 2025 am 07:21 AM
Nginx SSL Certificate Update Debian Tutorial
Apr 13, 2025 am 07:21 AM
This article will guide you on how to update your NginxSSL certificate on your Debian system. Step 1: Install Certbot First, make sure your system has certbot and python3-certbot-nginx packages installed. If not installed, please execute the following command: sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstallcertbotpython3-certbot-nginx Step 2: Obtain and configure the certificate Use the certbot command to obtain the Let'sEncrypt certificate and configure Nginx: sudocertbot--nginx Follow the prompts to select
 How to configure HTTPS server in Debian OpenSSL
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:03 AM
How to configure HTTPS server in Debian OpenSSL
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:03 AM
Configuring an HTTPS server on a Debian system involves several steps, including installing the necessary software, generating an SSL certificate, and configuring a web server (such as Apache or Nginx) to use an SSL certificate. Here is a basic guide, assuming you are using an ApacheWeb server. 1. Install the necessary software First, make sure your system is up to date and install Apache and OpenSSL: sudoaptupdatesudoaptupgradesudoaptinsta



