python basic tutorial project five virtual tea party
This article mainly introduces the virtual tea party of python basic tutorial project 5 in detail, which has certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to it
Almost learn and use any kind of When programming languages, there is never a shortage of socket exercises, especially when writing about local area network communication. So this project in the book is just right for practicing socket programming.
The overall idea of this exercise is to first have a chat server. The main functions of this server are to provide client socket connections, store each client’s connection session, process the messages sent by each connection, and parse the client. sent data. That's it. As for the client, you don't need to write code, just use the system's telnet tool.
I think with the above analysis, there is nothing much to say about the rest of this program, except of course the two classes that encapsulate sockets.
I tried this by using the socket class in python and wrote a simple communication program. However, for some reason, accidents always occurred during communication. This simple code is as follows:
server.py
import socket
mysocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
mysocket.bind(('',8888))
mysocket.listen(5)
while True:
connection,addr = mysocket.accept()
revStr = connection.recv(1024)
connection.send('Server:' + revStr)
connection.close()clinet.py
import socket
import time
clientsocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
clientsocket.connect(('',8888))
while True:
time.sleep(2)
clientsocket.send('hello the5fire')
print clientsocket.recv(1024)
clientsocket.close()The reason why this program went wrong was not investigated in detail, because python provides two encapsulated classes to complete the socket communication process: async_chat in asynchat and dispatcher in asyncore and asyncore itself. The former class is used to handle each session between the client and the server, and the latter class is mainly used to provide socket connection services. And each socket connection is hosted by the former (async_chat) for processing.
Look at the code:
from asyncore import dispatcher
from asynchat import async_chat
import socket, asyncore
PORT = 5005
NAME = 'TestChat'
class EndSession(Exception):pass
class CommandHandler:
def unknown(self, session, cmd):
session.push('Unknown command: %s\r\n' % cmd)
def handle(self, session, line):
if not line.strip(): return
parts = line.split(' ',1)
cmd = parts[0]
try: line = parts[1].strip()
except IndexError: line = ''
meth = getattr(self, 'do_'+cmd, None)
try:
meth(session, line)
except TypeError:
self.unknown(session,cmd)
class Room(CommandHandler):
def __init__(self, server):
self.server = server
self.sessions = []
def add(self, session):
self.sessions.append(session)
def remove(self, session):
self.sessions.remove(session)
def broadcast(self, line):
for session in self.sessions:
session.push(line)
def do_logout(self, session, line):
raise EndSession
class LoginRoom(Room):
def add(self,session):
Room.add(self,session)
self.broadcast('Welcome to %s\r\n' % self.server.name)
def unknown(self, session, cmd):
session.push('Please log in \nUse "login"\r\n')
def do_login(self, session, line):
name = line.strip()
if not name:
session.push('Please enter a name\r\n')
elif name in self.server.users:
session.push('The name "%s" is taken.\r\n' % name)
sessoin.push('Please try again.\r\n')
else:
session.name = name
session.enter(self.server.main_room)
class ChatRoom(Room):
def add(self, session):
self.broadcast(session.name + ' has entered the room.\r\n')
self.server.users[session.name] = session
Room.add(self, session)
def remove(self, session):
Room.remove(self, session)
self.broadcast(session.name + ' has left the room.\r\n')
def do_say(self, session, line):
self.broadcast(session.name + ': ' + line + '\r\n')
def do_look(self, session, line):
session.push('The following are in this room:\r\n')
for other in self.sessions:
session.push(other.name + '\r\n')
def do_who(self, session, line):
session.push('The following are logged in:\r\n')
for name in self.server.users:
session.push(name + '\r\n')
class LogoutRoom(Room):
def add(self, session):
try: del self.server.users[session.name]
except KeyError: pass
class ChatSession(async_chat):
def __init__(self, server, sock):
async_chat.__init__(self,sock)
self.server = server
self.set_terminator('\r\n')
self.data = []
self.name = None
self.enter(LoginRoom(server))
def enter(self, room):
try:
cur = self.room
except AttributeError:
pass
else: cur.remove(self)
self.room = room
room.add(self)
def collect_incoming_data(self, data):
self.data.append(data)
def found_terminator(self):
line = ''.join(self.data)
self.data = []
try: self.room.handle(self, line)
except EndSession:
self.handle_close()
def handle_close(self):
async_chat.handle_close(self)
self.enter(LogoutRoom(self.server))
class ChatServer(dispatcher):
def __init__(self, port, name):
dispatcher.__init__(self)
self.create_socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
self.bind(('',port))
self.listen(5)
self.name = name
self.users = {}
self.main_room = ChatRoom(self)
def handle_accept(self):
conn, addr = self.accept()
ChatSession(self,conn)
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = ChatServer(PORT, NAME)
try: asyncore.loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt: printThe whole program is divided into the three parts I mentioned at the beginning :
Provides the client's socket connection: ChatServer class.
Store the connection session of each client and process the messages sent by each connection: ChatSession class. The function of this class is very simple. It accepts data and determines whether there is a terminator. If the found_terminator method is called, .
Parse the data sent by the client: it is the remaining room-related classes. These classes are used to process the strings and commands sent by the client, and they are all inherited from CommandHandler.
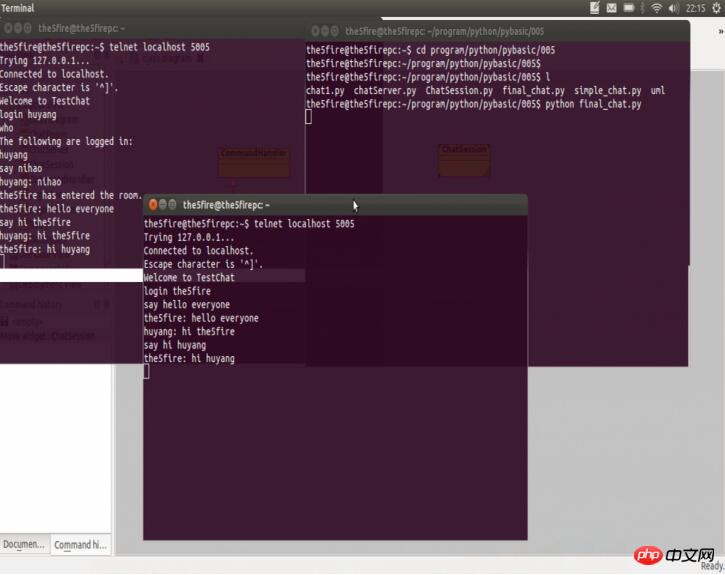
Final screenshot:
Related recommendations:
Python Basic Tutorial Project Three of All XML
Python Basic Tutorial Project 2: Good Pictures
Python Basic Tutorial Project 4: News Aggregation
The above is the detailed content of python basic tutorial project five virtual tea party. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 Is there a free XML to PDF tool for mobile phones?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Is there a free XML to PDF tool for mobile phones?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
There is no simple and direct free XML to PDF tool on mobile. The required data visualization process involves complex data understanding and rendering, and most of the so-called "free" tools on the market have poor experience. It is recommended to use computer-side tools or use cloud services, or develop apps yourself to obtain more reliable conversion effects.
 Does XML modification require programming?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
Does XML modification require programming?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
Modifying XML content requires programming, because it requires accurate finding of the target nodes to add, delete, modify and check. The programming language has corresponding libraries to process XML and provides APIs to perform safe, efficient and controllable operations like operating databases.
 Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML formatting tools can type code according to rules to improve readability and understanding. When selecting a tool, pay attention to customization capabilities, handling of special circumstances, performance and ease of use. Commonly used tool types include online tools, IDE plug-ins, and command-line tools.
 How to beautify the XML format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
How to beautify the XML format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
XML beautification is essentially improving its readability, including reasonable indentation, line breaks and tag organization. The principle is to traverse the XML tree, add indentation according to the level, and handle empty tags and tags containing text. Python's xml.etree.ElementTree library provides a convenient pretty_xml() function that can implement the above beautification process.
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.






