
This time I will show you how to obtain the local peak value of a two-dimensional array in python Get up and take a look. The meaning of the question is roughly to find a local peak in an n*m two-dimensional array. The peak value is required to be greater than the four adjacent elements (outside the array boundary is regarded as negative infinity). For example, if we finally find the peak value A[j][i], then A[j][i] > A[j 1][i ] && A[j][i] > A[j-1][i] && A[j][i] > A[j][i 1] && A[j][i] > A[ j][i-1]. Returns the coordinates and value of this peak.
Of course, the simplest and most direct method is to traverse all array elements to determine whether they are peak values. The time complexity is O(n^2) Then optimize a little more to find the value of each row (column) Maximum value, and then find the peak value of the maximum value column through the dichotomy method (the specific method can be seen inOne-dimensional array
finding the peak value). The time complexity of this algorithm is O(logn)What is discussed here is an algorithm with a complexity of O(n). The algorithm idea is divided into the following steps:1. Find "Tian "Character. Including the four outer edges and the two horizontal and vertical edges in the middle (the green part in the picture), compare their sizes and find the position of the maximum value.
(7 in the picture)
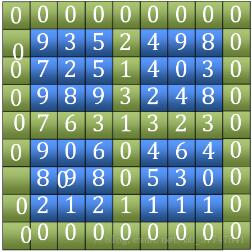
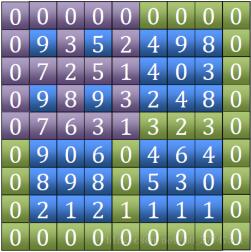
As to why there must be a peak within the range we choose, you can think of it this way, first we have a circle, we It is known that there is at least one element in a circle that is greater than all the elements in this circle. So, is there a maximum value in this circle?
It may be a bit convoluted, but if you think about it more, you should be able to understand it, and you can also use mathematical proof by contradiction to prove it. After we understand the algorithm, the next step is to implement the code. The language I use here is python (I am new to python, so please forgive me for some usages that may not be concise enough). Let’s start with the code:import numpy as np
def max_sit(*n): #返回最大元素的位置
temp = 0
sit = 0
for i in range(len(n)):
if(n[i]>temp):
temp = n[i]
sit = i
return sit
def dp(s1,s2,e1,e2):
m1 = int((e1-s1)/2)+s1 #row
m2 = int((e2-s1)/2)+s2 #col
nub = e1-s1
temp = 0
sit_row = 0
sit_col = 0
for i in range(nub):
t = max_sit(list[s1][s2+i], #第一排
list[m1][s2+i], #中间排
list[e1][s2+i], #最后排
list[s1+i][s2], #第一列
list[s1+i][m2], #中间列
list[s1+i][e2], #最后列
temp)
if(t==6):
pass
elif(t==0):
temp = list[s1][s2+i]
sit_row = s1
sit_col = s2+i
elif(t==1):
temp = list[m1][s2+i]
sit_row = m1
sit_col = s2+i
elif(t==2):
temp = list[e1][s2+i]
sit_row = e1
sit_col = s2+i
elif(t==3):
temp = list[s1+i][s2]
sit_row = s1+i
sit_row = s2
elif(t==4):
temp = list[s1+i][m2]
sit_row = s1+i
sit_col = m2
elif(t==5):
temp = list[s1+i][e2]
sit_row = s1+i
sit_col = m2
t = max_sit(list[sit_row][sit_col], #中
list[sit_row-1][sit_col], #上
list[sit_row+1][sit_col], #下
list[sit_row][sit_col-1], #左
list[sit_row][sit_col+1]) #右
if(t==0):
return [sit_row-1,sit_col-1]
elif(t==1):
sit_row-=1
elif(t==2):
sit_row+=1
elif(t==3):
sit_col-=1
elif(t==4):
sit_col+=1
if(sit_row<m1):
e1 = m1
else:
s1 = m1
if(sit_col<m2):
e2 = m2
else:
s2 = m2
return dp(s1,s2,e1,e2)
f = open("demo.txt","r")
list = f.read()
list = list.split("\n") #对行进行切片
list = ["0 "*len(list)]+list+["0 "*len(list)] #加上下的围墙
for i in range(len(list)): #对列进行切片
list[i] = list[i].split()
list[i] = ["0"]+list[i]+["0"] #加左右的围墙
list = np.array(list).astype(np.int32)
row_n = len(list)
col_n = len(list[0])
ans_sit = dp(0,0,row_n-1,col_n-1)
print("找到峰值点位于:",ans_sit)
print("该峰值点大小为:",list[ans_sit[0]+1,ans_sit[1]+1])
f.close()string
. The specific conversion process can be seen in my previous blog -Converting a string to a two-dimensional array in python . (It should be noted that if the list after splitting in windows environment does not have an empty tail, there is no need to add the sentence list.pop()). Some changes are that I added a "0" wall around the two-dimensional array. Adding a wall eliminates the need to consider boundary issues when we judge peak values. max_sit(*n) function is used to find the position of the maximum value among multiple values and return its position. Python's built-in max function can only return the maximum value, so you still need to write it yourself, *n means Indefinite length parameters, because I need to use this function when comparing Tian and Ten (judging peak values)
def max_sit(*n): #返回最大元素的位置 temp = 0 sit = 0 for i in range(len(n)): if(n[i]>temp): temp = n[i] sit = i return sit
def dp(s1,s2,e1,e2): m1 = int((e1-s1)/2)+s1 #row m2 = int((e2-s1)/2)+s2 #col
for i in range(nub): t = max_sit(list[s1][s2+i], #第一排 list[m1][s2+i], #中间排 list[e1][s2+i], #最后排 list[s1+i][s2], #第一列 list[s1+i][m2], #中间列 list[s1+i][e2], #最后列 temp) if(t==6): pass elif(t==0): temp = list[s1][s2+i] sit_row = s1 sit_col = s2+i elif(t==1): temp = list[m1][s2+i] sit_row = m1 sit_col = s2+i elif(t==2): temp = list[e1][s2+i] sit_row = e1 sit_col = s2+i elif(t==3): temp = list[s1+i][s2] sit_row = s1+i sit_row = s2 elif(t==4): temp = list[s1+i][m2] sit_row = s1+i sit_row = m2 elif(t==5): temp = list[s1+i][e2] sit_row = s1+i sit_row = m2
t = max_sit(list[sit_row][sit_col], #中 list[sit_row-1][sit_col], #上 list[sit_row+1][sit_col], #下 list[sit_row][sit_col-1], #左 list[sit_row][sit_col+1]) #右 if(t==0): return [sit_row-1,sit_col-1] elif(t==1): sit_row-=1 elif(t==2): sit_row+=1 elif(t==3): sit_col-=1 elif(t==4): sit_col+=1
if(sit_row<m1): e1 = m1 else: s1 = m1 if(sit_col<m2): e2 = m2 else: s2 = m2 return dp(s1,s2,e1,e2)
大体的思路就是从中间位置起找相邻4个点中最大的点,继续把该点来找相邻最大点,最后一定会找到一个峰值点,有兴趣的可以看一下,上代码:
#!/usr/bin/python3
def dp(n):
temp = (str[n],str[n-9],str[n-1],str[n+1],str[n+9]) #中 上 左 右 下
sit = temp.index(max(temp))
if(sit==0):
return str[n]
elif(sit==1):
return dp(n-9)
elif(sit==2):
return dp(n-1)
elif(sit==3):
return dp(n+1)
else:
return dp(n+9)
f = open("/home/nancy/桌面/demo.txt","r")
list = f.read()
list = list.replace(" ","").split() #转换为列表
row = len(list)
col = len(list[0])
str="0"*(col+3)
for x in list: #加围墙 二维变一维
str+=x+"00"
str+="0"*(col+1)
mid = int(len(str)/2)
print(str,mid)
p = dp(mid)
print (p)
f.close()相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of How to obtain the local peak value of a two-dimensional array in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




