Detailed explanation of Django's cookie usage
This time I will bring you a detailed explanation of Django's cookie usage, and what are the notes of Django's cookie usage. The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
This article mainly introduces you to the relevant information about the basic use of cookies in Django. The article introduces it in detail through sample code, which has certain reference learning value for everyone's study or work. Friends who need it, please come and study together.
Various service systems based on the Internet have emerged. To establish a commercial site or a personal site with relatively complete functions, it is often necessary to record some information about visitors; forums as a One of the products of the development of the Internet, the Internet It plays an increasingly important role in the Internet and is one of the main places for users to obtain, communicate, and transmit information. Forums often need to record some basic information of visitors (such as identification numbers, passwords, and user information on the Web). patterns of shopping on the site or the number of times a user visits the site). It is currently recognized that some basic information of visitors is recorded through Cookie and Session technologies.
Let’s take a look at the basic use of cookies in Django. Without further ado, let’s take a look at the detailed introduction.
1. Brief description
(1)Set Cookies
response.set_cookie("cookie_key","value")(2)Get Cookies
value = request.COOKIES["cookie_key"]
(3)Delete Cookies
response.delete_cookie("cookie_key",path="/",domain=name)(4)Detect Cookies
if "cookie_name" in request.COOKIES :
(5)response.set_cookie() Pass some optional parameters Description
2.Example
2.1 Setting Cookies
login_user = models.User.objects.get(username=username, password=password) # 这里用的mongodb进行的数据存储
# print(login_user["username"])
# 帐号和密码正确,cookie保存登录状态
# 获取相应对象
response = redirect(reverse("blog:index"))
# 设置cookie
response.set_cookie("blog_username", login_user["username"], 604800) #过期时间单位是s (这里设置为7天)
response.set_cookie("blog_password", login_user["password"], 604800)2.2 Detect and obtain Cookies
def index(request):
# 检测cookies是否存在
if "blog_username" in request.COOKIES:
# 获取cookies
login_username = request.COOKIES.get("blog_username")
login_password = request.COOKIES.get("blog_password")
# 获取登录用户信息
login_user = models.User.objects.get(username=login_username, password=login_password)
# 返回登录成功后页面
return render(request, "blog/index.html", {"login_user": login_user})
else:
# 进入未登录状态的主页
return render(request, "blog/index.html")2.3 Delete Cookies
# 注销登录视图函数
def logout(request):
response = redirect(reverse("blog:index"))
response.delete_cookie("blog_username")
response.delete_cookie("blog_password")
return responseI believe you have mastered the method after reading the case in this article. For more exciting information, please pay attention to other related articles on the php Chinese website!
Recommended reading:
Add the loading effect before the vue image is loaded
##vue changes the status of the currently selected item
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Django's cookie usage. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Django vs. Flask: A comparative analysis of Python web frameworks
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Django vs. Flask: A comparative analysis of Python web frameworks
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Django and Flask are both leaders in Python Web frameworks, and they both have their own advantages and applicable scenarios. This article will conduct a comparative analysis of these two frameworks and provide specific code examples. Development Introduction Django is a full-featured Web framework, its main purpose is to quickly develop complex Web applications. Django provides many built-in functions, such as ORM (Object Relational Mapping), forms, authentication, management backend, etc. These features allow Django to handle large
 Django Framework Pros and Cons: Everything You Need to Know
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Django Framework Pros and Cons: Everything You Need to Know
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Django is a complete development framework that covers all aspects of the web development life cycle. Currently, this framework is one of the most popular web frameworks worldwide. If you plan to use Django to build your own web applications, then you need to understand the advantages and disadvantages of the Django framework. Here's everything you need to know, including specific code examples. Django advantages: 1. Rapid development-Djang can quickly develop web applications. It provides a rich library and internal
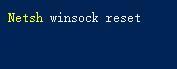 What should I do if win11 cannot use ie11 browser? (win11 cannot use IE browser)
Feb 10, 2024 am 10:30 AM
What should I do if win11 cannot use ie11 browser? (win11 cannot use IE browser)
Feb 10, 2024 am 10:30 AM
More and more users are starting to upgrade the win11 system. Since each user has different usage habits, many users are still using the ie11 browser. So what should I do if the win11 system cannot use the ie browser? Does windows11 still support ie11? Let’s take a look at the solution. Solution to the problem that win11 cannot use the ie11 browser 1. First, right-click the start menu and select "Command Prompt (Administrator)" to open it. 2. After opening, directly enter "Netshwinsockreset" and press Enter to confirm. 3. After confirmation, enter "netshadvfirewallreset&rdqu
 How to upgrade Django version: steps and considerations
Jan 19, 2024 am 10:16 AM
How to upgrade Django version: steps and considerations
Jan 19, 2024 am 10:16 AM
How to upgrade Django version: steps and considerations, specific code examples required Introduction: Django is a powerful Python Web framework that is continuously updated and upgraded to provide better performance and more features. However, for developers using older versions of Django, upgrading Django may face some challenges. This article will introduce the steps and precautions on how to upgrade the Django version, and provide specific code examples. 1. Back up project files before upgrading Djan
 Detailed explanation of where browser cookies are stored
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:15 AM
Detailed explanation of where browser cookies are stored
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:15 AM
With the popularity of the Internet, we use browsers to surf the Internet have become a way of life. In the daily use of browsers, we often encounter situations where we need to enter account passwords, such as online shopping, social networking, emails, etc. This information needs to be recorded by the browser so that it does not need to be entered again the next time you visit. This is when cookies come in handy. What are cookies? Cookie refers to a small data file sent by the server to the user's browser and stored locally. It contains user behavior of some websites.
 Is Django front-end or back-end? check it out!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:37 AM
Is Django front-end or back-end? check it out!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:37 AM
Django is a web application framework written in Python that emphasizes rapid development and clean methods. Although Django is a web framework, to answer the question whether Django is a front-end or a back-end, you need to have a deep understanding of the concepts of front-end and back-end. The front end refers to the interface that users directly interact with, and the back end refers to server-side programs. They interact with data through the HTTP protocol. When the front-end and back-end are separated, the front-end and back-end programs can be developed independently to implement business logic and interactive effects respectively, and data exchange.
 How to use the Django framework to create a project in PyCharm
Feb 19, 2024 am 08:56 AM
How to use the Django framework to create a project in PyCharm
Feb 19, 2024 am 08:56 AM
Tips on how to create projects using the Django framework in PyCharm, requiring specific code examples. Django is a powerful Python Web framework that provides a series of tools and functions for quickly developing Web applications. PyCharm is an integrated development environment (IDE) developed in Python, which provides a series of convenient functions and tools to increase development efficiency. Combining Django and PyCharm makes it faster and more convenient to create projects
 Frequently Asked Questions and Solutions about Cookie Settings
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:08 AM
Frequently Asked Questions and Solutions about Cookie Settings
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:08 AM
Common problems and solutions for cookie settings, specific code examples are required. With the development of the Internet, cookies, as one of the most common conventional technologies, have been widely used in websites and applications. Cookie, simply put, is a data file stored on the user's computer that can be used to store the user's information on the website, including login name, shopping cart contents, website preferences, etc. Cookies are an essential tool for developers, but at the same time, cookie settings are often encountered




