Progress bar effect that you must learn every day in PyQt5
This article mainly introduces the progress bar effect of PyQt5 in detail, which has certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to it
The progress bar is when we deal with lengthy tasks The controls used. It is animated to let the user know that the task is progressing. The QProgressBar control provides a horizontal or vertical progress bar. Programmers can set the minimum and maximum values of the progress bar. The default value is 0 to 99.
#!/usr/bin/python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ PyQt5 教程 这个例子显示了一个进度条控件。 作者:我的世界你曾经来过 博客:http://blog.csdn.net/weiaitaowang 最后编辑:2016年8月3日 """ import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QProgressBar, QPushButton from PyQt5.QtCore import QBasicTimer class Example(QWidget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.pbar = QProgressBar(self) self.pbar.setGeometry(30, 40, 200, 25) self.btn = QPushButton('开始', self) self.btn.move(40, 80) self.btn.clicked.connect(self.doAction) self.timer = QBasicTimer() self.step = 0 self.setGeometry(300, 300, 280, 170) self.setWindowTitle('进度条') self.show() def timerEvent(self, e): if self.step >= 100: self.timer.stop() self.btn.setText('完成') return self.step = self.step+1 self.pbar.setValue(self.step) def doAction(self, value): if self.timer.isActive(): self.timer.stop() self.btn.setText('开始') else: self.timer.start(100, self) self.btn.setText('停止') if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) ex = Example() sys.exit(app.exec_())
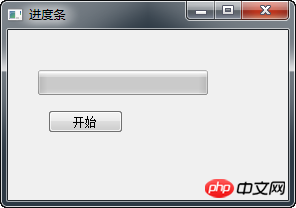
In our example, we have a horizontal progress bar control and a button control. Click the button to start or stop the progress bar.
self.pbar = QProgressBar(self)
Use QProgressBar to create a progress bar
self.timer = QBasicTimer()
To activate the progress bar, we need to use A timer object.
self.timer.start(100, self)
To start the timer event, we need to call its start() method. This method takes two parameters: the timeout and the object of the event that will be received.
def timerEvent(self, e): if self.step >= 100: self.timer.stop() self.btn.setText('完成') return self.step = self.step+1 self.pbar.setValue(self.step)
Every object that inherits from QObject has a timerEvent() event handler. In order for the timer event to apply to the progress bar, we rewrote this event handler.
def doAction(self, value): if self.timer.isActive(): self.timer.stop() self.btn.setText('开始') else: self.timer.start(100, self) self.btn.setText('停止')
Use the doAction() method to start and stop the timer.
After the program is executed


Related recommendations:
PyQt5 must be learned every day QSplitter implements window separation
The tool tip function that PyQt5 must learn every day
The above is the detailed content of Progress bar effect that you must learn every day in PyQt5. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Users encounter rare glitches: Samsung Watch smartwatches suddenly experience white screen issues
Apr 03, 2024 am 08:13 AM
Users encounter rare glitches: Samsung Watch smartwatches suddenly experience white screen issues
Apr 03, 2024 am 08:13 AM
You may have encountered the problem of green lines appearing on the screen of your smartphone. Even if you have never seen it, you must have seen related pictures on the Internet. So, have you ever encountered a situation where the smart watch screen turns white? On April 2, CNMO learned from foreign media that a Reddit user shared a picture on the social platform, showing the screen of the Samsung Watch series smart watches turning white. The user wrote: "I was charging when I left, and when I came back, it was like this. I tried to restart, but the screen was still like this during the restart process." Samsung Watch smart watch screen turned white. The Reddit user did not specify the smart watch. Specific model. However, judging from the picture, it should be Samsung Watch5. Previously, another Reddit user also reported
 How to install pyqt5
Nov 30, 2023 pm 02:05 PM
How to install pyqt5
Nov 30, 2023 pm 02:05 PM
pyqt5 installation steps: 1. Make sure that Python and pip are installed on the computer; 2. Enter the "pip install PyQt5" command in the terminal or command prompt to install PyQt5; 3. After the installation is complete, you can import the PyQt5 module in the Python script and Get started; 4. You can install some specific functions or components by entering the "pip install PyQt5.QtGui" command; 5. If you encounter any problems, you can try to upgrade pip and setuptools.
 Kyushu Fengshen Assassin 4S Radiator Review Air-cooled 'Assassin Master' Style
Mar 28, 2024 am 11:11 AM
Kyushu Fengshen Assassin 4S Radiator Review Air-cooled 'Assassin Master' Style
Mar 28, 2024 am 11:11 AM
Speaking of ASSASSIN, I believe players will definitely think of the master assassins in "Assassin's Creed". They are not only skilled, but also have the creed of "devoting themselves to the darkness and serving the light". The ASSASSIN series of flagship air-cooled radiators from the appliance brand DeepCool coincide with each other. Recently, the latest product of this series, ASSASSIN4S, has been launched. "Assassin in Suit, Advanced" brings a new air-cooling experience to advanced players. The appearance is full of details. The Assassin 4S radiator adopts a double tower structure + a single fan built-in design. The outside is covered with a cube-shaped fairing, which has a strong overall sense. It is available in white and black colors to meet different colors. Tie
 Exquisite light and shadow art in spring, Haqu H2 is the cost-effective choice
Apr 17, 2024 pm 05:07 PM
Exquisite light and shadow art in spring, Haqu H2 is the cost-effective choice
Apr 17, 2024 pm 05:07 PM
With the arrival of spring, everything revives and everything is full of vitality and vitality. In this beautiful season, how to add a touch of color to your home life? Haqu H2 projector, with its exquisite design and super cost-effectiveness, has become an indispensable beauty in this spring. This H2 projector is compact yet stylish. Whether placed on the TV cabinet in the living room or next to the bedside table in the bedroom, it can become a beautiful landscape. Its body is made of milky white matte texture. This design not only makes the projector look more advanced, but also increases the comfort of the touch. The beige leather-like material adds a touch of warmth and elegance to the overall appearance. This combination of colors and materials not only conforms to the aesthetic trend of modern homes, but also can be integrated into
 Huntkey MX750P full module power supply review: 750W of concentrated platinum strength
Mar 28, 2024 pm 03:20 PM
Huntkey MX750P full module power supply review: 750W of concentrated platinum strength
Mar 28, 2024 pm 03:20 PM
With its compact size, the ITX platform has attracted many players who pursue the ultimate and unique beauty. With the improvement of manufacturing processes and technological advancements, both Intel's 14th generation Core and RTX40 series graphics cards can exert their strength on the ITX platform, and gamers also There are higher requirements for SFX power supply. Game enthusiast Huntkey has launched a new MX series power supply. In the ITX platform that meets high-performance requirements, the MX750P full-module power supply has a rated power of up to 750W and has passed 80PLUS platinum level certification. Below we bring the evaluation of this power supply. Huntkey MX750P full-module power supply adopts a simple and fashionable design concept. There are two black and white models for players to choose from. Both use matte surface treatment and have a good texture with silver gray and red fonts.
 Colorful Hidden Star P15 24 Review: A hard-core all-round gaming laptop with both good looks and performance
Mar 06, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
Colorful Hidden Star P15 24 Review: A hard-core all-round gaming laptop with both good looks and performance
Mar 06, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
In the current era of rapid technological development, laptops have become an indispensable and important tool in people's daily life and work. For those players who have high performance requirements, a laptop with powerful configuration and excellent performance can meet their hard-core needs. With its excellent performance and stunning design, the Colorful Hidden Star P15 notebook computer has become the leader of the future and can be called a model of hard-core notebooks. Colorful Hidden Star P1524 is equipped with a 13th generation Intel Core i7 processor and RTX4060Laptop GPU. It adopts a more fashionable spaceship design style and has excellent performance in details. Let us first take a look at the features of this notebook. Supreme equipped with Intel Core i7-13620H processing
 Easily understand 4K HD images! This large multi-modal model automatically analyzes the content of web posters, making it very convenient for workers.
Apr 23, 2024 am 08:04 AM
Easily understand 4K HD images! This large multi-modal model automatically analyzes the content of web posters, making it very convenient for workers.
Apr 23, 2024 am 08:04 AM
A large model that can automatically analyze the content of PDFs, web pages, posters, and Excel charts is not too convenient for workers. The InternLM-XComposer2-4KHD (abbreviated as IXC2-4KHD) model proposed by Shanghai AILab, the Chinese University of Hong Kong and other research institutions makes this a reality. Compared with other multi-modal large models that have a resolution limit of no more than 1500x1500, this work increases the maximum input image of multi-modal large models to more than 4K (3840x1600) resolution, and supports any aspect ratio and 336 pixels to 4K Dynamic resolution changes. Three days after its release, the model topped the HuggingFace visual question answering model popularity list. Easy to handle
 Super complete! Python graphical interface framework PyQt5 usage guide!
Apr 13, 2023 am 08:43 AM
Super complete! Python graphical interface framework PyQt5 usage guide!
Apr 13, 2023 am 08:43 AM
Common GUI framework PyQt5: Qt is a cross-platform C++ graphical user interface library. QT was once owned by Nokia and later sold to Digia Oyj, a Finnish software company. PyQt5 is a Python interface based on Digia's Qt5 and consists of a set of Python modules. PyQt5 itself has more than 620 classes and 6000 functions and methods. Can run on multiple platforms, including: Unix, Windows, and Mac OS. Pyside6: Pyside is the Python package officially provided by QT Company. The previous version was Pyside2, which corresponds to QT5. The naming rules of the latest version have been adjusted and changed to Pysid.






