JSON object use case (with code)
This time I will bring you a JSON object usage case (with code). What are the precautions for using JSON objects? The following is a practical case, let’s take a look.
Previous words
The full name of json (javascript object notation) is javascript object notation. It is a text format for data exchange, and Not a programming language for reading structured data. It was proposed by Douglas Crockford in 2001 with the purpose of replacing the cumbersome and cumbersome XML format. This article will introduce in detail the content of json
Grammar rules
The syntax of JSON can represent the following three types of values
[1] Simple value
Simple values use the same syntax as JavaScript and can represent strings, numeric values, Boolean values, and null in JSON
Strings must be represented by double quotes, single quotes cannot be used. The value must be expressed in decimal, and NaN and Infinity
cannot be used [Note] JSON does not support the special value undefined
//合格的简单值 5 "hello world" true null
//不合格的简单值 +0x1 'hello world' undefined NaN Infinity
[2] Object
The object is used as an A complex data type that represents an ordered set of key-value pairs. The value in each key-value pair can be a simple value or a complex data type value
Compared with JavaScript object literals, json has three differences
1. JSON does not have the concept of variables
2. In JSON, the key name of the object must be placed in double quotes
3. Because JSON is not a javascript statement, there is no semicolon at the end
[Note] Two properties with the same name should not appear in the same object
//合格的对象
{
"name":"huochai",
"age":29,
"school":{
"name":"diankeyuan",
"location":"beijing"
}
}//不合格的对象
{ name: "张三", 'age': 32 }//属性名必须使用双引号
{};//不需要末尾的分号
{ "birthday": new Date('Fri, 26 Aug 2011 07:13:10 GMT'),
"getName": function() {
return this.name;
}
} // 不能使用函数和日期对象[3] Array
Array is also a complex data type, representing a set of ordered values. A list whose values can be accessed by numeric index. The value of the array can also be of any type - simple value, object or array
JSON array also has no variables and semicolons. Combining arrays and objects can form more complex data collections
[Note] A comma cannot be added after the last member of an array or object
JSON object
The reason why JSON is popular is that the JSON data structure can be parsed as Useful javascript objects
ECMAScript5 standardizes the behavior of parsing JSON and defines the global object JSON
[Note] IE7-browser does not support
There are two JSON objects Methods: stringify() and parse(). These two methods are used to serialize JavaScript objects into JSON strings and parse JSON strings into native JavaScript values
stringify()
JSON.stringify () method is used to convert a value into a string. The string should conform to JSON format and can be restored by the JSON.parse() method
By default, the JSON string output by JSON.stringify() does not include any space characters or indentation
var jsonObj = {
"title":"javascript",
"group":{
"name":"jia",
"tel":12345
}
};
//{"title":"javascript","group":{"name":"jia","tel":12345}}
JSON.stringify(jsonObj);Specific conversion
JSON.stringify('abc') // ""abc""
JSON.stringify(1) // "1"
JSON.stringify(false) // "false"
JSON.stringify([]) // "[]"
JSON.stringify({}) // "{}"
JSON.stringify([1, "false", false])// '[1,"false",false]'
JSON.stringify({ name: "张三" })// '{"name":"张三"}'The stringify() method converts regular expressions and mathematical objects into the string form of empty objects
JSON.stringify(/foo/) // "{}"
JSON.stringify(Math) // "{}"The stringify() method converts date objects and wrapper objects into strings
JSON.stringify(new Boolean(true)) //"true"
JSON.stringify(new String('123')) //""123""
JSON.stringify(new Number(1)) //"1"
JSON.stringify(new Date()) //""2016-09-20T02:26:38.294Z""If the member of the object is undefined or a function, this member will be omitted
If the member of the array is undefined or a function, Then these values are converted to null
JSON.stringify({
a: function(){},
b: undefined,
c: [ function(){}, undefined ]
});
// "{"c":[null,null]}"The JSON.stringify() method will ignore the non-traversable properties of the object
var obj = {};
Object.defineProperties(obj, {
'foo': {
value: 1,
enumerable: true
},
'bar': {
value: 2,
enumerable: false
}
});
JSON.stringify(obj); // {"foo":1}]Parameters
JSON.stringify In addition to the JavaScript object to be serialized, () can also receive two other parameters, which are used to specify different ways to serialize the JavaScript object. The first parameter is a filter, which can be an array or a function; the second parameter is an option, indicating whether to retain indentation in the JSON string
[Array Filter]
When the second parameter of the stringify() method is an array, it is equivalent to implementing the function of a filter
【1】过滤器只对对象的第一层属性有效
var jsonObj = {
"title":"javascript",
"group":{
"a":1
}
};
//{"group":{"a":1}}
console.log(JSON.stringify(jsonObj,["group","a"]))【2】过滤器对数组无效
var jsonObj =[1,2]; JSON.stringify(jsonObj,["0"])//"[1,2]"
【函数参数】
stringify()方法的第二个参数也可以是一个函数。传入的函数接收两个参数,属性(键)名和属性值
JSON.stringify({a:1,b:2}, function(key, value){
if (typeof value === "number") {
value = 2 * value;
}
return value;
})
// "{"a":2,"b":4}"属性名只能是字符串,而在值并非键值对儿结构的值时,键名可以是空字符串
这个函数参数会递归处理所有的键
下面代码中,对象o一共会被f函数处理三次。第一次键名为空,键值是整个对象o;第二次键名为a,键值是{b:1};第三次键名为b,键值为1
JSON.stringify({a: {b: 1}}, function (key, value) {
console.log("["+ key +"]:" + value);
return value;
})
// []:[object Object]
// [a]:[object Object]
// [b]:1
// '{"a":{"b":1}}'函数返回的值就是相应键的值。如果函数返回了undefined或没有返回值,那么相应的属性会被忽略
JSON.stringify({ a: "abc", b: 123 }, function (key, value) {
if (typeof(value) === "string") {
return undefined;
}
return value;
})
// '{"b": 123}'【缩进】
stringify()方法还可以接受第三个参数,用于增加返回的JSON字符串的可读性
如果是数字,表示每个属性前面添加的空格(最多不超过10个)
如果是字符串(不超过10个字符),则该字符串会添加在每行前面
/*"{
"p1": 1,
"p2": 2
}"*/
JSON.stringify({ p1: 1, p2: 2 }, null, 2);
//"{"p1":1,"p2":2}"
JSON.stringify({ p1: 1, p2: 2 }, null, 0);
/*"{
|-"p1": 1,
|-"p2": 2
}"*/
JSON.stringify({ p1:1, p2:2 }, null, '|-');
toJSON()有时候,JSON.stringify()还是不能满足对某些对象进行自定义序列化的需求。在这些情况下, 可以通过对象上调用toJSON()方法,返回其自身的JSON数据格式
JSON.stringify({
toJSON: function () {
return "Cool"
}
})
// ""Cool""var o = {
foo: 'foo',
toJSON: function() {
return 'bar';
}
};
JSON.stringify({x: o});// '{"x":"bar"}'如果toJSON()方法返回undefined,此时如果包含它的对象嵌入在另一个对象中,会导致该对象的值变成null。而如果包含它的对象是顶级对象,结果就是undefined
JSON.stringify({
toJSON: function () {
return undefined
}
})
//undefinedDate对象部署了一个自己的toJSON方法,自动将Date对象转换成日期字符串
JSON.stringify(new Date("2016-08-29"))
// "2016-08-29T00:00:00.000Z"toJSON方法的一个应用是,可以将正则对象自动转为字符串
RegExp.prototype.toJSON =RegExp.prototype.toString; JSON.stringify(/foo/)// ""/foo/""
toJSON()可以作为函数过滤器的补充,因此理解序列化的内部顺序十分重要。假设把一个对象传入JSON.stringify(),序列化该对象的顺序如下
1、如果存在toJSON()方法而且能通过它取得有效的值,则调用该方法。否则,按默认顺序执行序列化
2、如果提供了第二个参数,应用这个函数过滤器。传入函数过滤器的值是第一步返回的值
3、对第二步返回的每个值进行相应的序列化
4、如果提供了第三个参数,执行相应的格式化
parse()
JSON.parse方法用于将JSON字符串转化成对象
JSON.parse('{}') // {}
JSON.parse('true') // true
JSON.parse('"foo"') // "foo"
JSON.parse('[1, 5, "false"]') // [1, 5, "false"]
JSON.parse('null') // null
var o = JSON.parse('{"name": "张三"}');
o.name // 张三如果传入的字符串不是有效的JSON格式,JSON.parse方法将报错
//Uncaught SyntaxError: Unexpected token u in JSON at position 0(…)JSON.parse("'String'")
//Uncaught SyntaxError: Unexpected token u in JSON at position 0(…)JSON.parse("undefined") JSON.parse()方法也可以接收一个函数参数,在每个键值对儿上调用,这个函数被称为还原函数(reviver)。该函数接收两个参数,一个键和一个值,返回一个值
如果还原函数返回undefined,则表示要从结果中删除相应的键;如果返回其他值,则将该值插入到结果中
var o = JSON.parse('{"a":1,"b":2}', function(key, value) {
if (key === ''){
return value;
}
if (key === 'a') {
return value + 10;
}
});
o.a // 11
o.b // undefinef在将日期字符串转换为Date对象时,经常要用到还原函数
var book = {
"title": "javascript",
"date": new Date(2016,9,1)
}
var jsonStr = JSON.stringify(book);
//'{"title":"javascript","date":"2016-09-30T16:00:00.000Z"}''
console.log(jsonStr)
var bookCopy = JSON.parse(jsonStr,function(key,value){
if(key == 'date'){
return new Date(value);
}
return value;
})
console.log(bookCopy.date.getFullYear());//2016eval()
实际上,eval()类似于JSON.parse()方法,可以将json字符串转换为json对象
eval('(' + '{"a":1}'+')').a;//1
JSON.parse('{"a":1}').a;//1但是,eval()可以执行不符合JSON格式的代码,有可能会包含恶意代码
eval('(' + '{"a":alert(1)}'+')').a;//弹出1
JSON.parse('{"a":alert(1)}').a;//报错相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of JSON object use case (with code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 GE universal remote codes program on any device
Mar 02, 2024 pm 01:58 PM
GE universal remote codes program on any device
Mar 02, 2024 pm 01:58 PM
If you need to program any device remotely, this article will help you. We will share the top GE universal remote codes for programming any device. What is a GE remote control? GEUniversalRemote is a remote control that can be used to control multiple devices such as smart TVs, LG, Vizio, Sony, Blu-ray, DVD, DVR, Roku, AppleTV, streaming media players and more. GEUniversal remote controls come in various models with different features and functions. GEUniversalRemote can control up to four devices. Top Universal Remote Codes to Program on Any Device GE remotes come with a set of codes that allow them to work with different devices. you may
 Performance optimization tips for converting PHP arrays to JSON
May 04, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Performance optimization tips for converting PHP arrays to JSON
May 04, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Performance optimization methods for converting PHP arrays to JSON include: using JSON extensions and the json_encode() function; adding the JSON_UNESCAPED_UNICODE option to avoid character escaping; using buffers to improve loop encoding performance; caching JSON encoding results; and considering using a third-party JSON encoding library.
 How do annotations in the Jackson library control JSON serialization and deserialization?
May 06, 2024 pm 10:09 PM
How do annotations in the Jackson library control JSON serialization and deserialization?
May 06, 2024 pm 10:09 PM
Annotations in the Jackson library control JSON serialization and deserialization: Serialization: @JsonIgnore: Ignore the property @JsonProperty: Specify the name @JsonGetter: Use the get method @JsonSetter: Use the set method Deserialization: @JsonIgnoreProperties: Ignore the property @ JsonProperty: Specify name @JsonCreator: Use constructor @JsonDeserialize: Custom logic
 How to use Copilot to generate code
Mar 23, 2024 am 10:41 AM
How to use Copilot to generate code
Mar 23, 2024 am 10:41 AM
As a programmer, I get excited about tools that simplify the coding experience. With the help of artificial intelligence tools, we can generate demo code and make necessary modifications as per the requirement. The newly introduced Copilot tool in Visual Studio Code allows us to create AI-generated code with natural language chat interactions. By explaining functionality, we can better understand the meaning of existing code. How to use Copilot to generate code? To get started, we first need to get the latest PowerPlatformTools extension. To achieve this, you need to go to the extension page, search for "PowerPlatformTool" and click the Install button
 Create and run Linux ".a" files
Mar 20, 2024 pm 04:46 PM
Create and run Linux ".a" files
Mar 20, 2024 pm 04:46 PM
Working with files in the Linux operating system requires the use of various commands and techniques that enable developers to efficiently create and execute files, code, programs, scripts, and other things. In the Linux environment, files with the extension ".a" have great importance as static libraries. These libraries play an important role in software development, allowing developers to efficiently manage and share common functionality across multiple programs. For effective software development in a Linux environment, it is crucial to understand how to create and run ".a" files. This article will introduce how to comprehensively install and configure the Linux ".a" file. Let's explore the definition, purpose, structure, and methods of creating and executing the Linux ".a" file. What is L
 Tsinghua University and Zhipu AI open source GLM-4: launching a new revolution in natural language processing
Jun 12, 2024 pm 08:38 PM
Tsinghua University and Zhipu AI open source GLM-4: launching a new revolution in natural language processing
Jun 12, 2024 pm 08:38 PM
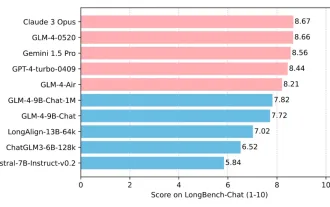
Since the launch of ChatGLM-6B on March 14, 2023, the GLM series models have received widespread attention and recognition. Especially after ChatGLM3-6B was open sourced, developers are full of expectations for the fourth-generation model launched by Zhipu AI. This expectation has finally been fully satisfied with the release of GLM-4-9B. The birth of GLM-4-9B In order to give small models (10B and below) more powerful capabilities, the GLM technical team launched this new fourth-generation GLM series open source model: GLM-4-9B after nearly half a year of exploration. This model greatly compresses the model size while ensuring accuracy, and has faster inference speed and higher efficiency. The GLM technical team’s exploration has not
 Create Agent in one sentence! Robin Li: The era is coming when everyone is a developer
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:28 PM
Create Agent in one sentence! Robin Li: The era is coming when everyone is a developer
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:28 PM
The big model subverts everything, and finally got to the head of this editor. It is also an Agent that was created in just one sentence. Like this, give him an article, and in less than 1 second, fresh title suggestions will come out. Compared to me, this efficiency can only be said to be as fast as lightning and as slow as a sloth... What's even more incredible is that creating this Agent really only takes a few minutes. Prompt belongs to Aunt Jiang: And if you also want to experience this subversive feeling, now, based on the new Wenxin intelligent agent platform launched by Baidu, everyone can create their own intelligent assistant for free. You can use search engines, smart hardware platforms, speech recognition, maps, cars and other Baidu mobile ecological channels to let more people use your creativity! Robin Li himself
 In-depth understanding of PHP: Implementation method of converting JSON Unicode to Chinese
Mar 05, 2024 pm 02:48 PM
In-depth understanding of PHP: Implementation method of converting JSON Unicode to Chinese
Mar 05, 2024 pm 02:48 PM
In-depth understanding of PHP: Implementation method of converting JSONUnicode to Chinese During development, we often encounter situations where we need to process JSON data, and Unicode encoding in JSON will cause us some problems in some scenarios, especially when Unicode needs to be converted When encoding is converted to Chinese characters. In PHP, there are some methods that can help us achieve this conversion process. A common method will be introduced below and specific code examples will be provided. First, let us first understand the Un in JSON




