
This time I will bring you a detailed explanation of the use case of Angular4's router attribute. What are the precautions for using the router attribute of Angular4? . The following is a practical case. Let's take a look.
router, that is, routing, is a relatively important concept in the front-end. The specific address and the corresponding page are associated and separated through the router to achieve the purpose of decoupling. Create a new detail folder in the src/app directory and create a file named gundam-detail.component.import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { Gundam } from '../../model/gundam';
@Component({
template: `
<p *ngIf="selectedGundam">
<span>{{selectedGundam.name}}</span>
<span>{{selectedGundam.type}}</span>
</p>
`
})
export class GundamDetailComponent {
selectedGundam: Gundam;
}Requirements: Click on any item in the gundam list page to jump to the gundam details page.
As an angular component, if you want to use router in the page, you must first declare it in app.module.ts. ps: The previous business has nothing to do with app.module.ts, but this does not mean that it is not important. app.module.ts is equivalent to the mainifist file ofandroid, which coordinates and manages the entire project.
Open app.module.ts:
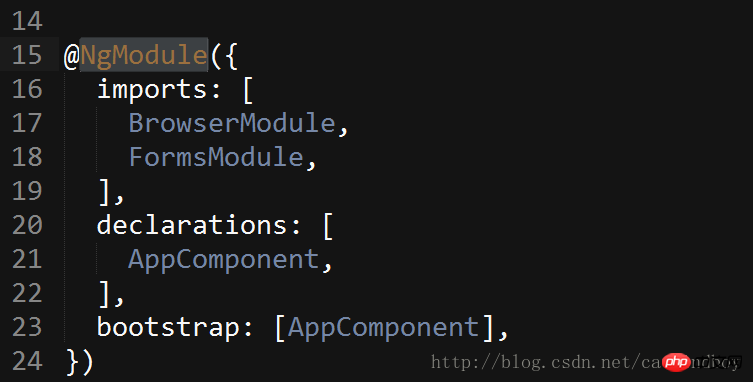
: It can be understood as Android's main launch, which component is entered from when the project starts.
import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router';Because you need to call the forRoot method of RouterModule, RouterModule.forRoot is the basic class used in the project, so you need to write In imports.
imports: [ BrowserModule, FormsModule, RouterModule.forRoot() ],
RouterModule.forRoot accepts two parameters. The first one is the route array to indicate the jump. The second parameter is ignored all year round. I don’t know what its use is.
The route class includes two key attributes: path and component. By accessing the path, you can find the unique component.
Add a route array containing two components, the home page and the details page, in forRoot.
RouterModule.forRoot([
{
path: '',
component: AppComponent
},
{
path: '',
component: GundamDetailComponent
}
])app.module.ts now looks like this:
import {
NgModule
} from '@angular/core';
import {
BrowserModule
} from '@angular/platform-browser';
import {
FormsModule
} from '@angular/forms';
import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import {
AppComponent
} from './component/appcomponent/app.component';
import { GundamDetailComponent } from './component/detail/gundam-detail.component';
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule,
RouterModule.forRoot([
{
path: '',
component: AppComponent
},
{
path: '',
component: GundamDetailComponent
}
])
],
declarations: [
AppComponent,
GundamDetailComponent
],
bootstrap: [AppComponent],
})
export class AppModule {}Both paths are still empty, because there is still one key thing missing, and an error will be reported even if it is written:
 Error: Cannot find primary outlet to load 'AppComponent'
Error: Cannot find primary outlet to load 'AppComponent'
In angular, router is used with the label router-outlet, in other words The router decides which component to display, and the router-outlet decides where to display it.
Add the tag
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
to the template in
app.component.ts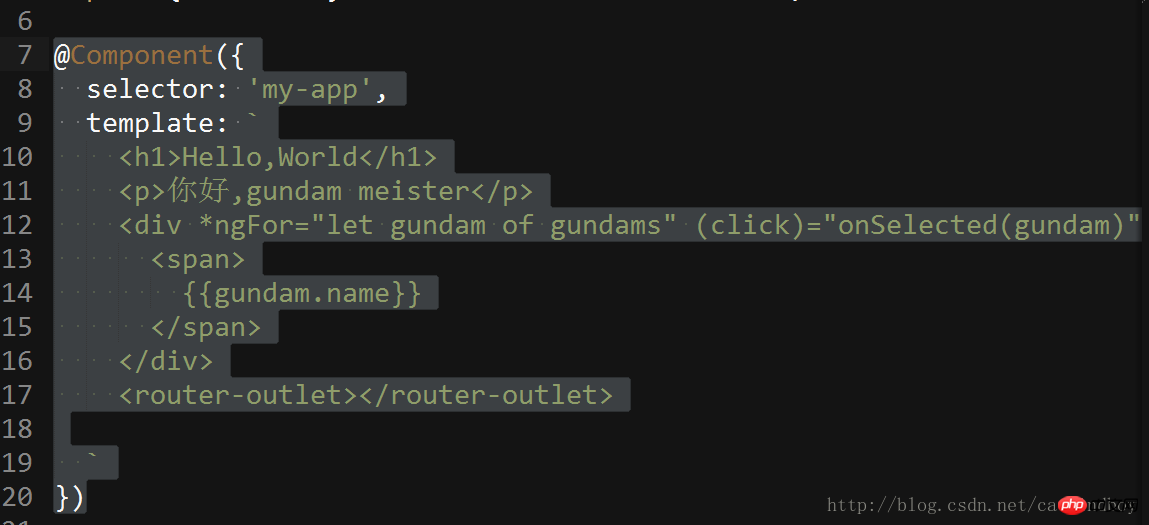 and then 2 homepages are displayed as expected. :
and then 2 homepages are displayed as expected. :
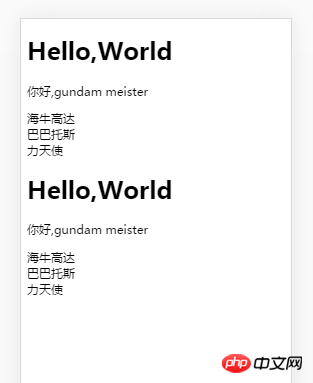
is a component and a page. Angular first entered app.component.ts# from bootstrap. ##The interface is rendered (that is, the part above the router-outlet). I went to find the router again and found that the corresponding router also had components, so I loaded it again.
所以为了正常显示,也要把主页也单独抽出来。所有组件通过app.component.ts里的来进行加载。而app.component.ts作为整个demo的最外层容器可以进行一些公共的操作(典型:后退动作)。
在src下新建host包,新建gundam-host.component.ts文件。
基本上可以把整个app挪过来,删除掉out标签,删掉selector(暂时用不到)。
import {
Component
} from '@angular/core';
import { Gundam } from '../../model/gundam';
import { GUNDAMS } from './../../service/data';
@Component({
template: `
<p *ngFor="let gundam of gundams" (click)="onSelected(gundam)">
<span>
{{gundam.name}}
</span>
</p>
`
})
export class GundamHostComponent {
gundam: Gundam = {
name: '海牛',
type: 'NewType'
};
gundams = GUNDAMS;
selectedGundam: Gundam; // 定义一个selectedGudam作为展示详情的变量
onSelected (gundam: Gundam): void {
this.selectedGundam = gundam; // 通过参数赋值
}
}app.component.ts只保留标签,其他一概去掉。
修改app.module.ts文件,导入gundam-host.component.ts并把GundamHostComponent 增加到组件声明declarations里。
修改route里的path所指向的component,默认进入后显示主页组件:
before

after

path的值为”(空字符串)的表示不需要增加子路径。
修改详情页的路径:
{
path: 'detail',
component: GundamDetailComponent
}在主页里增加跳转连接:
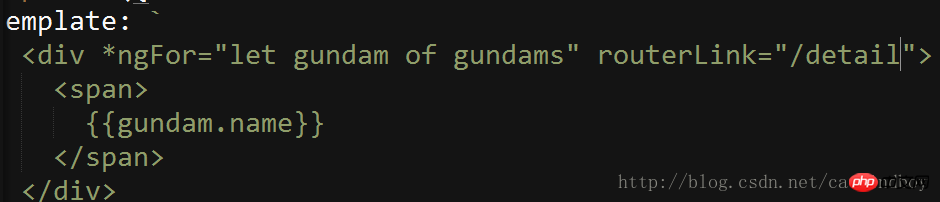
点击跳转(路径已改变)
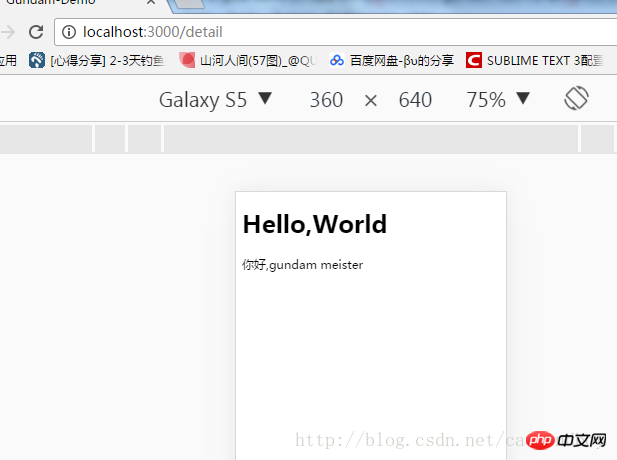
现在点击主页的高达列表的item后,可以跳转到一个空白的详情页。之所以是空白,是因为详情页的值是需要由主页进行传递的。现在主页详情页分家以后,需要通过路由来进行值传递。
传值的方法有很多种,甚至可以传的值也有很多种。
目前我先用最笨的方法:将gundam类转化为一个字符串,将字符串传递到详情页面后再转化为gundam类。
在app.component.ts文件的class里添加函数:
parseGundamToString(gundam: Gundam): string {
return gundam.name + '&' + gundam.type;
} // 将gundam类转化为固定格式的字符串修改app.component.ts文件的template,访问gundam路径时转化传递转化过的gundam字符串
<p *ngFor="let gundam of gundams" routerLink="/detail/name=parseGundamToString(gundam)">
<span>
{{gundam.name}}
</span>
</p>修改详情页的path
{
path: 'detail/:gundam',
component: GundamDetailComponent
}/:gundam 是一个占位符,又是参数说明。表示传递过来的参数属性是gundam。
这样在detail文件中,就可以从url的连接中拿到传递过来的高达字符串。
获得这个字符串的时机,应该是在在detail页面初始化的时候。Angular提供了所谓的的“钩子”(hook),用来标示component的活动周期—其实也就是是类似于Android里onStart或者onCreate一样的方法。
在gundam-detail.component.ts的中添加OnInit钩子,或者说接口:
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';在class后面加implements关键词和OnInit来实现该接口:
export class GundamDetailComponent implements OnInit {
selectedGundam: Gundam ;
ngOnInit(): void {
}
}剩下的事情,就是读取连接上传来的参数就可以了。
读取连接上传递的参数还是要用到router里的几个类,所以需要在detail里导入。
import { ActivatedRoute, Params } from '@angular/router';导入完成后,通过在构造器里注入的方式进行调用:
(有关注入,现在暂时没有说到)
constructor(
private route: ActivatedRoute){}angular会自动创建ActivatedRoute的实例。
先在ngOnInit里输出看看params是什么
this.route.params.switchMap((params: Params) => console.log(params))
ps:switchMap是angular官方给的拿取url参数的方法,也是需要预先导入才可以使用:
import 'rxjs/add/operator/switchMap';
ps2: 有关箭头函数
(params: Params) => this.gundamStr = params['gundam']
是一个箭头函数,等同于
function(params){
this.gundamStr = params['gundam']
}其中params是switchMap的返回值,返回的即是通过路由连接传递过来的参数所在的类。
ps3: 箭头函数真的是整个ES6里最恶心的东西,之一。
控制台中 输出:
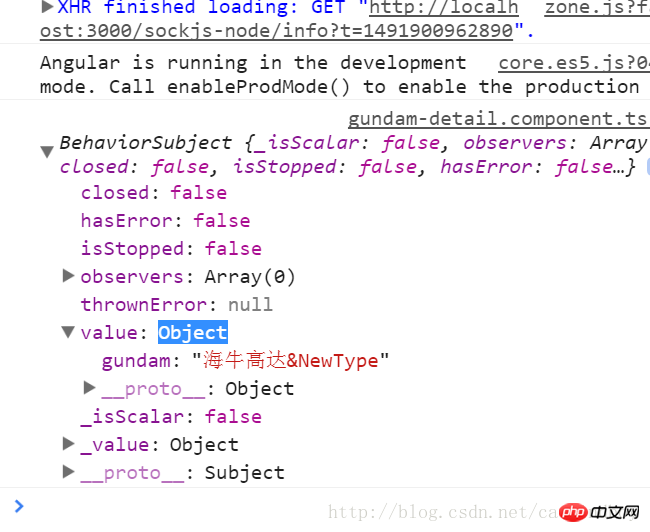
传递过来的参数,是一个gundam类格式化输出的字符串,所以还要在detail里补充一个反格式化字符串到gundam类的函数。
parseStringToGundam(str: string): Gundam {
const temp = str.split('&');
const tempGundam: Gundam = {
name: temp[0],
type: temp[1]
};
return tempGundam;
}最终,获得detail的初始化是这个样子的
ngOnInit(): void {
this.route.params // 通过注入的方式拿到route里的参数params
.switchMap((params: Params) => this.gundamStr = params['gundam']) // 通过参数拿到gundam字符串并付给detail里的一个临时变量
.subscribe(() => this.selectedGundam = this.parseStringToGundam(this.gundamStr)); // 通过反格式化函数解析临时变量并返回给作为显示的model
}移动web页面间传值确实没有什么太好的方法,angular和react都是如此。以前我们的做法是短的参数直接挂连接传走,长的大的或者object的参数就先保存本地,然后第二个页面再从本地读取。
但是像android那样扔一个intent里直接就过去了的方式,确实没有。
回首页:
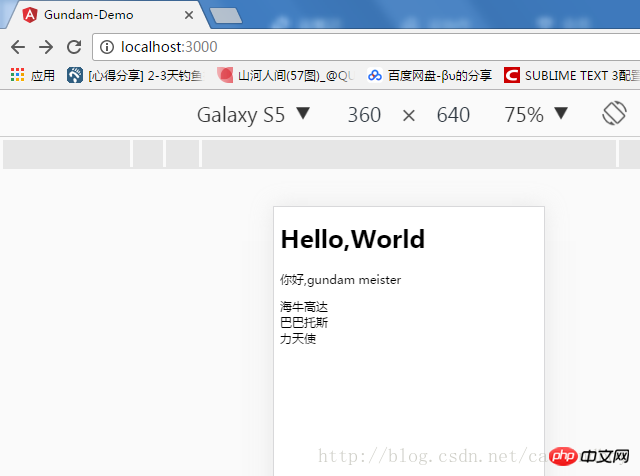
点击一个列表:
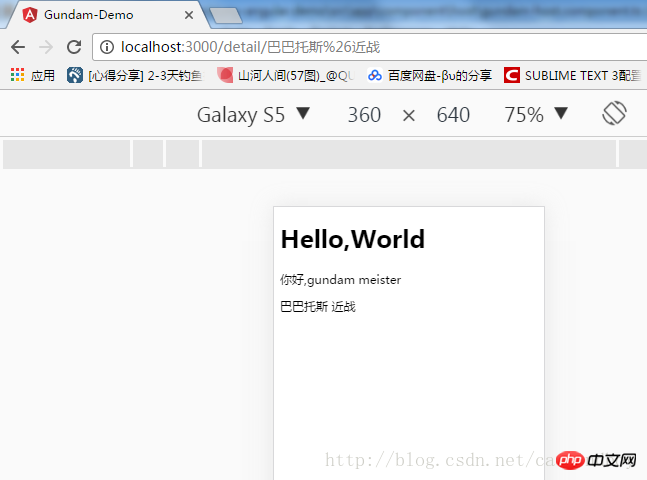
包结构:
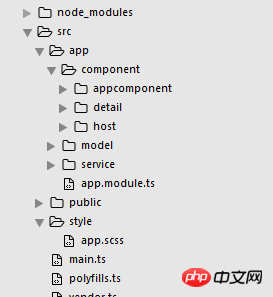
总的来说,业务被分开了,结构干净多了。虽然现在还体现不出来,但是写到后来就觉得心花怒放,磨刀不误砍柴工功啊。
作为router,也可以分离的。
目前我的项目里只有2个页面,如果多起来-比如20来个,那么app.module.ts又会变的乱七八糟。
所以要把router也给扔出去。
新建一个文件app-routing.module.ts,然后把footRoot平移过来(带上引用)。
在app-routing.module.ts文件里,也需要ngModul。个人理解ngModul就相当于一个基类指示器,导出class后以便被其他类引用。
import {
NgModule
} from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { GundamDetailComponent } from './component/detail/gundam-detail.component';
import { GundamHostComponent } from './component/host/gundam-host.component';
@NgModule({
imports: [
RouterModule.forRoot([
{
path: '',
component: GundamHostComponent
},
{
path: 'detail/:id',
component: GundamDetailComponent
}
])
],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule {
}然后既然已经有了这个类,可以导入到app.module.ts里使用使得整个文件看起来清爽一些。
import {
NgModule
} from '@angular/core';
import {
BrowserModule
} from '@angular/platform-browser';
import {
FormsModule
} from '@angular/forms';
import {
AppComponent
} from './component/appcomponent/app.component';
import { GundamDetailComponent } from './component/detail/gundam-detail.component';
import { GundamHostComponent } from './component/host/gundam-host.component';
import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module';
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule,
AppRoutingModule // 调用路由
],
declarations: [
AppComponent,
GundamDetailComponent,
GundamHostComponent
],
bootstrap: [AppComponent],
})
export class AppModule {}当然,官方文档又进行了进一步简化。
既然forRoot是一个Route数组,那么数组也可以单独抽出来,当然进一步抽取也可以放到另一个文件里。
import {
NgModule
} from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Route } from '@angular/router';
import { GundamDetailComponent } from './component/detail/gundam-detail.component';
import { GundamHostComponent } from './component/host/gundam-host.component';
const routes: Route[] = [
{
path: '',
component: GundamHostComponent
},
{
path: 'detail/:gundam',
component: GundamDetailComponent
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [
RouterModule.forRoot(routes)
],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule {
}我个人比较偷懒,就先抽取到这一步。
现在连主页面和详情页面都被分开了,项目的耦合度又进一步降低。
再接再厉,我们继续把业务逻辑给也分离出来。
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the use case of router attribute in Angular4. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




