 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 CSS Tutorial
CSS Tutorial
 Explanation of five values such as CSS position attribute absolute relative
Explanation of five values such as CSS position attribute absolute relative
Explanation of five values such as CSS position attribute absolute relative
This article mainly introduces the explanation of the five values of CSS position attribute absolute relative. It has a certain reference value. Now I share it with you. Friends in need can refer to it.
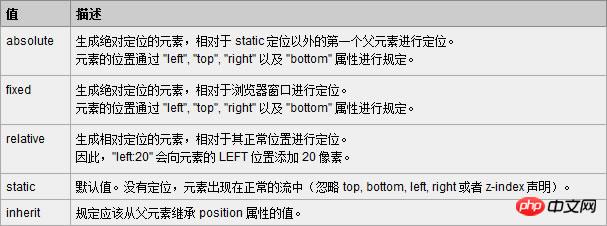
Almost all mainstream All browsers support the position attribute (except "inherit", "inherit" does not support all browsers including IE8 and previous versions of IE, and IE9 and IE10 have not been tested). The following is w3school's explanation of the five values of position. What is needed Friends can refer to
Currently, almost all mainstream browsers support the position attribute (except "inherit", "inherit" does not support all browsers including IE8 and previous versions of IE, and IE9 and IE10 have not been tested yet) , the following is w3school's explanation of the five values of position:
Absolute and relative are the most commonly used, and fixed is also commonly used (IE6 does not support fixed) .
1. Absolute (absolute positioning)
Absolute is an element that generates visual positioning and is separated from the text flow (that is, it no longer occupies a position in the document). Refer to The upper left corner of the browser is positioned via top, right, bottom, left (TRBL for short). You can select a positioned parent object (the combination of relative and absolute will be discussed below) or the body coordinate origin for positioning, or you can perform hierarchical classification through z-index. When the TRBL value is not set, absolute uses the coordinates of the parent object as the starting point. When the TRBL value is set, the upper left corner of the browser is used as the original point. The specific case is as follows:
Copy code
The code is as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>position:absolute定位</title>
<style type="text/css">
html,body,p{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
}
.center{
margin:30px;
border:#999999 solid 10px;
width:400px;
height:300px;
}
.p1{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background:#0099FF;
/*设定TRBL*/
position:absolute;
left:0px;
top:0px;
}
.p2{
width:400px;
height:300px;
font-size:30px;
font-weight:bold;
color:#fff;
background:#FF0000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="center">
<p class="p1"></p>
<p class="p2">position:absolute定位测试</p>
</p>
</body>
</html>
The effect of this code is as follows :
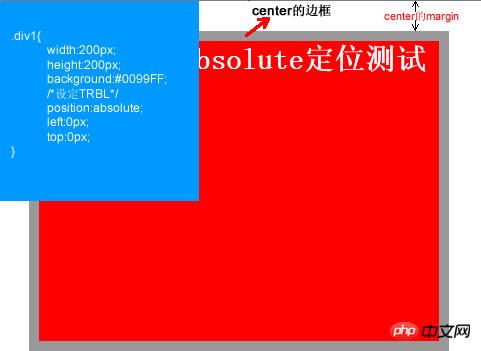
This is the effect after setting TRBL (setting TRBL to the upper left corner of the browser as the origin), when TRBL is not set (TRBL is not set to the parent object The coordinates are the origin), that is, when p1 is changed to the following code
Copy code
The code is as follows:
.p1{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background:#0099FF;
/*没有设定TRBL*/
position:absolute;
}The effect is as follows:

2. Relative (relative positioning)
relative means relative. As the name suggests, it means relative to You can move the element to the position where the element itself should appear in the document. You can use TRBL to move the element's position. In fact, the element still occupies its original position in the document, but it is visually moved relative to its original position. The specific case is as follows:
Copy the code
The code is as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>position:relative定位</title>
<style type="text/css">
html,body,p{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
}
.center{
margin:30px;
border:#999999 solid 10px;
width:400px;
height:300px;
background:#FFFF00;
}
.p1{
width:200px;
height:150px;
background:#0099FF;
position:relative;
top:-20px;
left:0px;
}
.p2{
width:400px;
height:150px;
font-size:30px;
font-weight:bold;
color:#fff;
background:#FF0000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="center">
<p class="p1"></p>
<p class="p2">position:relative定位测试</p>
</p>
</body>
</html>The effect produced by the code is as follows:

3. The combination of relative and absolute
Floating is often used to layout the page during web design, but There are many uncertain factors caused by floating (for example: IE browser compatibility issues). Relatively speaking, positioning in some layouts will be simpler, faster, and more compatible (used in combination with relative and absolute). The following is an example in a web page (the head part of the web page). The specific code is as follows :
Copy code
The code is as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<style type="text/css">
html,body,p,ul,li,a{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
}
a, a:hover{
color:#000;
border:0;
text-decoration:none;
}
#warp,#head,#main,#foot
{
width: 962px;
}
/*设置居中*/
#warp{
margin: 0 auto;
}
#head{
height:132px;
position:relative;
}
.logo{
position:absolute;
top:17px;
}
.head_pic{
position:absolute;
top:17px;
left:420px;
}
.sc{
position:absolute;
right:5px;
top:12px;
}
.sc a{
padding-left:20px;
color:#666;
}
.nav{
width:960px;
height:42px;
line-height:42px;
position:absolute;
bottom:0px;
background:url(img/nav_bj.jpg) no-repeat center;
}
.nav ul{
float:left;
padding:0 10px;
}
.nav li{
float:left;
background:url(img/li_bj.jpg) no-repeat right center;
padding-right:40px;
padding-left:20px;
text-align:center;
display:inline;
}
.nav li a{
font-size:14px;
font-family:Microsoft YaHei !important;
white-space:nowrap;
}
.nav li a:hover{
color:#FBECB7;
}
</style>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="warp">
<p id="head">
<p class="logo"><img src="img/logo.jpg" /></p>
<p class="head_pic"><img src="img/head_pic.jpg" /></p>
<p class="sc">
<a href=""><img src="img/sc_btn.jpg" /></a>
<a href=""><img src="img/sy_btn.jpg" /></a>
<a href=""><img src="img/kf_btn.jpg" /></a>
</p>
<p class="nav">
<ul>
<li><a href="">首页</a></li>
<li><a href="">关于我们</a></li>
<li><a href="">团队文化</a></li>
<li><a href="">公司动态</a></li>
<li><a href="">资讯参考</a></li>
<li><a href="">业务中心</a></li>
<li><a href="">合作银行</a></li>
<li><a href="">联系我们</a></li>
</ul>
</p>
</p>
<p id="main"></p>
<p id="foot"></p>
</p>
</body>
</html>The effect is as follows:

In the above code, the relative positioning is first set for the head. Then you can see that all the sub-elements inside will be positioned relative to the head instead of relative to the body after setting absolute. This is much simpler and more convenient than using floating, and there is no need to worry about compatibility issues.
The above is the detailed content of Explanation of five values such as CSS position attribute absolute relative. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Flexible application skills of position attribute in H5
Dec 27, 2023 pm 01:05 PM
Flexible application skills of position attribute in H5
Dec 27, 2023 pm 01:05 PM
How to flexibly use the position attribute in H5. In H5 development, the positioning and layout of elements are often involved. At this time, the CSS position property will come into play. The position attribute can control the positioning of elements on the page, including relative positioning, absolute positioning, fixed positioning and sticky positioning. This article will introduce in detail how to flexibly use the position attribute in H5 development.
 CSS layout property optimization tips: position sticky and flexbox
Oct 20, 2023 pm 03:15 PM
CSS layout property optimization tips: position sticky and flexbox
Oct 20, 2023 pm 03:15 PM
CSS layout attribute optimization tips: positionsticky and flexbox In web development, layout is a very important aspect. A good layout structure can improve the user experience and make the page more beautiful and easy to navigate. CSS layout properties are the key to achieving this goal. In this article, I will introduce two commonly used CSS layout property optimization techniques: positionsticky and flexbox, and provide specific code examples. 1. positions
 How to put div at the bottom in html
Mar 02, 2021 pm 05:44 PM
How to put div at the bottom in html
Mar 02, 2021 pm 05:44 PM
How to place a div at the bottom of HTML: 1. Use the position attribute to position the div tag relative to the browser window, with the syntax "div{position:fixed;}"; 2. Set the distance to the bottom to 0 to permanently place the div at At the bottom of the page, the syntax is "div{bottom:0;}".
 How to use position in h5
Dec 26, 2023 pm 01:39 PM
How to use position in h5
Dec 26, 2023 pm 01:39 PM
In H5, you can use the position attribute to control the positioning of elements through CSS: 1. Relative positioning, the syntax is "style="position: relative;"; 2. Absolute positioning, the syntax is "style="position: absolute;" "; 3. Fixed positioning, the syntax is "style="position: fixed;" and so on.
 What attributes does position have?
Oct 10, 2023 am 11:18 AM
What attributes does position have?
Oct 10, 2023 am 11:18 AM
The position attribute values include static, relative, absolute, fixed, sticky, etc. Detailed introduction: 1. static is the default value of the position attribute, which means that the elements are laid out according to the normal document flow without special positioning. The position of the elements is determined by their order in the HTML document and cannot be passed through top, right, and bottom. Adjust with the left attribute; 2. relative is relative positioning and so on.
 How to clear position in css
Oct 07, 2023 pm 12:02 PM
How to clear position in css
Oct 07, 2023 pm 12:02 PM
How to clear position in css: 1. Use the static attribute, which can be set to static to clear the position attribute; 2. Use the inherit attribute to clear the position attribute of the element and inherit the position attribute of the parent element; 3. Use the unset attribute, Restore the attributes to their default values and clear the position attribute of the element; 4. Use the !important rule, which will override other style rules and clear the position attribute, etc.
 Interpretation of CSS cascading properties: z-index and position
Oct 20, 2023 pm 07:19 PM
Interpretation of CSS cascading properties: z-index and position
Oct 20, 2023 pm 07:19 PM
Interpretation of CSS cascading properties: z-index and position In CSS, the design of layout and style is very important. In design, it is often necessary to layer and position elements. Two important CSS properties, z-index and position, can help us achieve these needs. This article will dive into these two properties and provide specific code examples. 1. z-index attribute The z-index attribute is used to define the stacking order of elements in the vertical direction. Stacking of elements
 Usage and effect display of sticky positioning attribute in CSS
Dec 27, 2023 pm 12:08 PM
Usage and effect display of sticky positioning attribute in CSS
Dec 27, 2023 pm 12:08 PM
Application examples of the position attribute in CSS: usage and effects of sticky positioning In front-end development, we often use the position attribute of CSS to control the positioning of elements. Among them, the position attribute has four optional values: static, relative, absolute and fixed. In addition to these common location attributes, there is also a special positioning method, namely sticky positioning. This article will discuss the usage and effects of sticky positioning



