Detailed explanation of the steps to use jsx syntax of vue component
This time I will bring you a detailed explanation of the steps for using the jsx syntax of the vue component. What are the precautions for using the jsx syntax of the vue component. The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
Configuration
Requires the babel plug-in
Installation
npm install\ babel-plugin-syntax-jsx\ babel-plugin-transform-vue-jsx\ babel-helper-vue-jsx-merge-props\ babel-preset-env\ --save-dev
.babelrc configuration
Add transform-vue-jsx in plugins
{
"presets": ["env"],
"plugins": ["transform-vue-jsx"]
}Basic example
Before escaping
<p id="foo">{this.text}</p>Translation After
h('p', {
attrs: {
id: 'foo'
}
}, [this.text])Note: The h function is the $createElement method of the vue instance. It must exist in the scope of jsx and must be the first one in the rendering function. Parameters are passed in, such as:
render (h) { // <-- h 函数必须在作用域内
return <p id="foo">bar</p>
}Automatically inject h function
Starting from 3.4.0, methods declared using ES2015 syntax and# In the ##getter accessor (except when using the function keyword or arrow function), babel will automatically inject h (const h = this.$createElement) function, so the (h) parameter can be omitted.
Vue.component('jsx-example', {
render () { // h 会自动注入
return <p id="foo">bar</p>
},
myMethod: function () { // h 不会注入
return <p id="foo">bar</p>
},
someOtherMethod: () => { // h 不会注入
return <p id="foo">bar</p>
}
})
@Component
class App extends Vue {
get computed () { // h 会自动注入
return <p id="foo">bar</p>
}
}Comparison between Vue JSX and React JSX
First of all, the vnode format of Vue2.0 is different from react,createElement The second parameter of the function is a data object, which accepts a nested object. Each nested object will have a corresponding module for processing.
render (h) {
return h('p', {
// 组件props
props: {
msg: 'hi'
},
// 原生HTML属性
attrs: {
id: 'foo'
},
// DOM props
domProps: {
innerHTML: 'bar'
},
// 事件是嵌套在`on`下面的,所以将不支持修饰符,如:`v-on:keyup.enter`,只能在代码中手动判断keyCode
on: {
click: this.clickHandler
},
// For components only. Allows you to listen to
// native events, rather than events emitted from
// the component using vm.$emit.
nativeOn: {
click: this.nativeClickHandler
},
// class is a special module, same API as `v-bind:class`
class: {
foo: true,
bar: false
},
// style is also same as `v-bind:style`
style: {
color: 'red',
fontSize: '14px'
},
// other special top-level properties
key: 'key',
ref: 'ref',
// assign the `ref` is used on elements/components with v-for
refInFor: true,
slot: 'slot'
})
}render (h) {
return (
<p
// normal attributes or component props.
id="foo"
// DOM properties are prefixed with `domProps`
domPropsInnerHTML="bar"
// event listeners are prefixed with `on` or `nativeOn`
onClick={this.clickHandler}
nativeOnClick={this.nativeClickHandler}
// other special top-level properties
class={{ foo: true, bar: false }}
style={{ color: 'red', fontSize: '14px' }}
key="key"
ref="ref"
// assign the `ref` is used on elements/components with v-for
refInFor
slot="slot">
</p>
)
}const data = {
class: ['b', 'c']
}
const vnode = <p class="a" {...data}/>{ class: ['a', 'b', 'c'] }Vue command
JSX does not support most of the Vue built-in commands, the only exception isv-show, which can be used v- The syntax of show={value}. Most instructions can be implemented programmatically. For example, v-if is a ternary expression, v-for is a array.map ()wait.
v-name={value} syntax, but the modified syntax does not support the instruction parameters arguments and modifiers modifier. There are two solutions:
v-name={{ value, modifier: true }}
const directives = [
{ name: 'my-dir', value: 123, modifiers: { abc: true } }
]
return <p {...{ directives }}/>JS implements the simplest search, sorting, and deduplication algorithm
How to use jQuery to achieve acquisition random color
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the steps to use jsx syntax of vue component. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
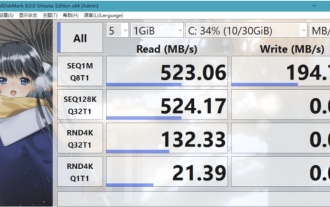 What software is crystaldiskmark? -How to use crystaldiskmark?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
What software is crystaldiskmark? -How to use crystaldiskmark?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
CrystalDiskMark is a small HDD benchmark tool for hard drives that quickly measures sequential and random read/write speeds. Next, let the editor introduce CrystalDiskMark to you and how to use crystaldiskmark~ 1. Introduction to CrystalDiskMark CrystalDiskMark is a widely used disk performance testing tool used to evaluate the read and write speed and performance of mechanical hard drives and solid-state drives (SSD). Random I/O performance. It is a free Windows application and provides a user-friendly interface and various test modes to evaluate different aspects of hard drive performance and is widely used in hardware reviews
 How to download foobar2000? -How to use foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
How to download foobar2000? -How to use foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
foobar2000 is a software that can listen to music resources at any time. It brings you all kinds of music with lossless sound quality. The enhanced version of the music player allows you to get a more comprehensive and comfortable music experience. Its design concept is to play the advanced audio on the computer The device is transplanted to mobile phones to provide a more convenient and efficient music playback experience. The interface design is simple, clear and easy to use. It adopts a minimalist design style without too many decorations and cumbersome operations to get started quickly. It also supports a variety of skins and Theme, personalize settings according to your own preferences, and create an exclusive music player that supports the playback of multiple audio formats. It also supports the audio gain function to adjust the volume according to your own hearing conditions to avoid hearing damage caused by excessive volume. Next, let me help you
 How to use NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
How to use NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
NetEase Mailbox, as an email address widely used by Chinese netizens, has always won the trust of users with its stable and efficient services. NetEase Mailbox Master is an email software specially created for mobile phone users. It greatly simplifies the process of sending and receiving emails and makes our email processing more convenient. So how to use NetEase Mailbox Master, and what specific functions it has. Below, the editor of this site will give you a detailed introduction, hoping to help you! First, you can search and download the NetEase Mailbox Master app in the mobile app store. Search for "NetEase Mailbox Master" in App Store or Baidu Mobile Assistant, and then follow the prompts to install it. After the download and installation is completed, we open the NetEase email account and log in. The login interface is as shown below
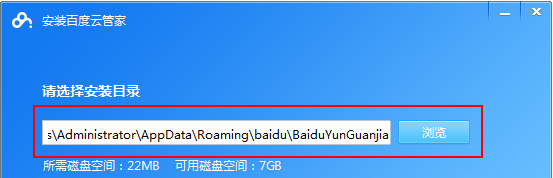 How to use Baidu Netdisk app
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
How to use Baidu Netdisk app
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
Cloud storage has become an indispensable part of our daily life and work nowadays. As one of the leading cloud storage services in China, Baidu Netdisk has won the favor of a large number of users with its powerful storage functions, efficient transmission speed and convenient operation experience. And whether you want to back up important files, share information, watch videos online, or listen to music, Baidu Cloud Disk can meet your needs. However, many users may not understand the specific use method of Baidu Netdisk app, so this tutorial will introduce in detail how to use Baidu Netdisk app. Users who are still confused can follow this article to learn more. ! How to use Baidu Cloud Network Disk: 1. Installation First, when downloading and installing Baidu Cloud software, please select the custom installation option.
 BTCC tutorial: How to bind and use MetaMask wallet on BTCC exchange?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
BTCC tutorial: How to bind and use MetaMask wallet on BTCC exchange?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
MetaMask (also called Little Fox Wallet in Chinese) is a free and well-received encryption wallet software. Currently, BTCC supports binding to the MetaMask wallet. After binding, you can use the MetaMask wallet to quickly log in, store value, buy coins, etc., and you can also get 20 USDT trial bonus for the first time binding. In the BTCCMetaMask wallet tutorial, we will introduce in detail how to register and use MetaMask, and how to bind and use the Little Fox wallet in BTCC. What is MetaMask wallet? With over 30 million users, MetaMask Little Fox Wallet is one of the most popular cryptocurrency wallets today. It is free to use and can be installed on the network as an extension
 Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Windows operating system is one of the most popular operating systems in the world, and its new version Win11 has attracted much attention. In the Win11 system, obtaining administrator rights is an important operation. Administrator rights allow users to perform more operations and settings on the system. This article will introduce in detail how to obtain administrator permissions in Win11 system and how to effectively manage permissions. In the Win11 system, administrator rights are divided into two types: local administrator and domain administrator. A local administrator has full administrative rights to the local computer
 Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in OracleSQL In OracleSQL, division operation is a common and important mathematical operation, used to calculate the result of dividing two numbers. Division is often used in database queries, so understanding the division operation and its usage in OracleSQL is one of the essential skills for database developers. This article will discuss the relevant knowledge of division operations in OracleSQL in detail and provide specific code examples for readers' reference. 1. Division operation in OracleSQL
 Teach you how to use the new advanced features of iOS 17.4 'Stolen Device Protection'
Mar 10, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
Teach you how to use the new advanced features of iOS 17.4 'Stolen Device Protection'
Mar 10, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
Apple rolled out the iOS 17.4 update on Tuesday, bringing a slew of new features and fixes to iPhones. The update includes new emojis, and EU users will also be able to download them from other app stores. In addition, the update also strengthens the control of iPhone security and introduces more "Stolen Device Protection" setting options to provide users with more choices and protection. "iOS17.3 introduces the "Stolen Device Protection" function for the first time, adding extra security to users' sensitive information. When the user is away from home and other familiar places, this function requires the user to enter biometric information for the first time, and after one hour You must enter information again to access and change certain data, such as changing your Apple ID password or turning off stolen device protection.




