 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 200 lines of code to implement blockchain Detailed explanation of blockchain examples
200 lines of code to implement blockchain Detailed explanation of blockchain examples
200 lines of code to implement blockchain Detailed explanation of blockchain examples
This article mainly introduces the relevant knowledge of blockchain in 200 lines of code. It is very good and has reference value. Friends who need it can refer to it
Understanding the concept of blockchain is very simple (block Chain, transaction chain block): It is distributed (i.e. not placed on the same machine, but on different network devices) The database supports hosting a growing list of records. But it is also easy to confuse blockchain with the goal we are trying to help him solve - at that moment in people's minds, the word is quite strongly associated with the concept of transactions, contracts or smart cryptocurrencies.
Only here blockchain - is not the same thing as Bitcoin, and understanding the basics of blockchain is easier than it seems, especially when, it is based on source code. In this article, we propose a simple model built with 200 lines of code in JavaScript. The source code for this project, which we call NaiveChain, can be found on GitHub. Part 1 and 2: If you need to brush up on its functionality, use our cheat sheet and we'll use standard ECMAScript 6.
Block Structure
Step 1 - Determine the elements that should contain the block. For the sake of simplicity, we include only the most necessary: index of the previous block (exponent), time stamp (timestamp), data (data), hash and hash, to be recorded in order to maintain the structural integrity of the circuit.
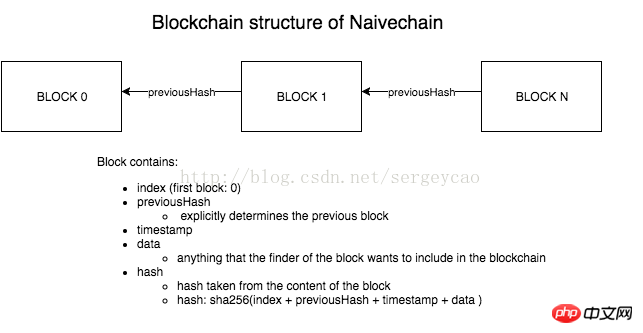
class Block {
constructor(index, previousHash, timestamp, data, hash) {
this.index = index;
this.previousHash = previousHash.toString();
this.timestamp = timestamp;
this.data = data;
this.hash = hash.toString();
}
}Hash unit
The hash block needs to keep the data Integrity. In our case, this applies to algorithm SHA-256. This type of hashing is not relevant for mining because in this case we are not implementing protection with proof of performance.
var calculateHash = (index, previousHash, timestamp, data) => {
return CryptoJS.SHA256(index + previousHash + timestamp + data).toString();
};Generation Unit
To generate a block we need to know the hash of the previous block so that we The structure already determines the rest of the elements. Data is provided by the end user.
var generateNextBlock = (blockData) => {
var previousBlock = getLatestBlock();
var nextIndex = previousBlock.index + 1;
var nextTimestamp = new Date().getTime() / 1000;
var nextHash = calculateHash(nextIndex, previousBlock.hash, nextTimestamp, blockData);
return new Block(nextIndex, previousBlock.hash, nextTimestamp, blockData, nextHash);
};Storage unit
Use blockchain storage array. The first block is always hardcoded "Genesis Block".
var getGenesisBlock = () => {
return new Block(0, "0", 1465154705, "my genesis block!!", "816534932c2b7154836da6afc367695e6337db8a921823784c14378abed4f7d7");
};
var blockchain = [getGenesisBlock()];Confirming Block Integrity
We must always be able to confirm the integrity of a unit or circuit. Especially when you get new units from other units, you have to decide whether to accept them or not.
var isValidNewBlock = (newBlock, previousBlock) => {
if (previousBlock.index + 1 !== newBlock.index) {
console.log('invalid index');
return false;
} else if (previousBlock.hash !== newBlock.previousHash) {
console.log('invalid previoushash');
return false;
} else if (calculateHashForBlock(newBlock) !== newBlock.hash) {
console.log(typeof (newBlock.hash) + ' ' + typeof calculateHashForBlock(newBlock));
console.log('invalid hash: ' + calculateHashForBlock(newBlock) + ' ' + newBlock.hash);
return false;
}
return true;
};Select the longest chain
The order of blocks in the circuit must be explicitly specified, but in the event of a conflict In the case of (e.g. two nodes generating the same block and the same number at the same time), we choose the circuit which contains a larger number of blocks.
var replaceChain = (newBlocks) => {
if (isValidChain(newBlocks) && newBlocks.length > blockchain.length) {
console.log('Received blockchain is valid. Replacing current blockchain with received blockchain');
blockchain = newBlocks;
broadcast(responseLatestMsg());
} else {
console.log('Received blockchain invalid');
}
};Messages to other network nodes
An integral part of the website - the exchange of data with other nodes. The following rules are used to maintain network synchronization:
When a node generates a new unit, it reports it to the network;
When the local machine connects to a new feast, it asks for information about the last generated block;
When A node is faced with a block that has an indicator larger than it, and he adds a block to the circuit or requests the information of the complete chain.
Automatic search for peers is not performed, all links are added manually.
Control of Units
The user should be able to control the node in some way, by putting the HTTP server to the server. When interacting with nodes have the following functions:
Print a list of all units;
Create new units with user-generated content;
Print the list, or add a festival.
The most direct way to interact - via curl:
List of all blocks on a node
curl http://localhost:3001 /blocks
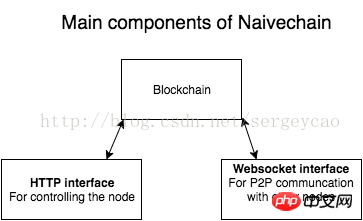
Architecture
It is worth noting that the website refers to two web servers: HTTP to the user-controlled device and to the WebSocket HTTP to install P2P connections between nodes.
The following is 200 lines of js code
'use strict';
var CryptoJS = require("crypto-js");
var express = require("express");
var bodyParser = require('body-parser');
var WebSocket = require("ws");
var http_port = process.env.HTTP_PORT || 3001;
var p2p_port = process.env.P2P_PORT || 6001;
var initialPeers = process.env.PEERS ? process.env.PEERS.split(',') : [];
class Block {
constructor(index, previousHash, timestamp, data, hash) {
this.index = index;
this.previousHash = previousHash.toString();
this.timestamp = timestamp;
this.data = data;
this.hash = hash.toString();
}
}
var sockets = [];
var MessageType = {
QUERY_LATEST: 0,
QUERY_ALL: 1,
RESPONSE_BLOCKCHAIN: 2
};
var getGenesisBlock = () => {
return new Block(0, "0", 1465154705, "my genesis block!!", "816534932c2b7154836da6afc367695e6337db8a921823784c14378abed4f7d7");
};
var blockchain = [getGenesisBlock()];
var initHttpServer = () => {
var app = express();
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.get('/blocks', (req, res) => res.send(JSON.stringify(blockchain)));
app.post('/mineBlock', (req, res) => {
var newBlock = generateNextBlock(req.body.data);
addBlock(newBlock);
broadcast(responseLatestMsg());
console.log('block added: ' + JSON.stringify(newBlock));
res.send();
});
app.get('/peers', (req, res) => {
res.send(sockets.map(s => s._socket.remoteAddress + ':' + s._socket.remotePort));
});
app.post('/addPeer', (req, res) => {
connectToPeers([req.body.peer]);
res.send();
});
app.listen(http_port, () => console.log('Listening http on port: ' + http_port));
};
var initP2PServer = () => {
var server = new WebSocket.Server({port: p2p_port});
server.on('connection', ws => initConnection(ws));
console.log('listening websocket p2p port on: ' + p2p_port);
};
var initConnection = (ws) => {
sockets.push(ws);
initMessageHandler(ws);
initErrorHandler(ws);
write(ws, queryChainLengthMsg());
};
var initMessageHandler = (ws) => {
ws.on('message', (data) => {
var message = JSON.parse(data);
console.log('Received message' + JSON.stringify(message));
switch (message.type) {
case MessageType.QUERY_LATEST:
write(ws, responseLatestMsg());
break;
case MessageType.QUERY_ALL:
write(ws, responseChainMsg());
break;
case MessageType.RESPONSE_BLOCKCHAIN:
handleBlockchainResponse(message);
break;
}
});
};
var initErrorHandler = (ws) => {
var closeConnection = (ws) => {
console.log('connection failed to peer: ' + ws.url);
sockets.splice(sockets.indexOf(ws), 1);
};
ws.on('close', () => closeConnection(ws));
ws.on('error', () => closeConnection(ws));
};
var generateNextBlock = (blockData) => {
var previousBlock = getLatestBlock();
var nextIndex = previousBlock.index + 1;
var nextTimestamp = new Date().getTime() / 1000;
var nextHash = calculateHash(nextIndex, previousBlock.hash, nextTimestamp, blockData);
return new Block(nextIndex, previousBlock.hash, nextTimestamp, blockData, nextHash);
};
var calculateHashForBlock = (block) => {
return calculateHash(block.index, block.previousHash, block.timestamp, block.data);
};
var calculateHash = (index, previousHash, timestamp, data) => {
return CryptoJS.SHA256(index + previousHash + timestamp + data).toString();
};
var addBlock = (newBlock) => {
if (isValidNewBlock(newBlock, getLatestBlock())) {
blockchain.push(newBlock);
}
};
var isValidNewBlock = (newBlock, previousBlock) => {
if (previousBlock.index + 1 !== newBlock.index) {
console.log('invalid index');
return false;
} else if (previousBlock.hash !== newBlock.previousHash) {
console.log('invalid previoushash');
return false;
} else if (calculateHashForBlock(newBlock) !== newBlock.hash) {
console.log(typeof (newBlock.hash) + ' ' + typeof calculateHashForBlock(newBlock));
console.log('invalid hash: ' + calculateHashForBlock(newBlock) + ' ' + newBlock.hash);
return false;
}
return true;
};
var connectToPeers = (newPeers) => {
newPeers.forEach((peer) => {
var ws = new WebSocket(peer);
ws.on('open', () => initConnection(ws));
ws.on('error', () => {
console.log('connection failed')
});
});
};
var handleBlockchainResponse = (message) => {
var receivedBlocks = JSON.parse(message.data).sort((b1, b2) => (b1.index - b2.index));
var latestBlockReceived = receivedBlocks[receivedBlocks.length - 1];
var latestBlockHeld = getLatestBlock();
if (latestBlockReceived.index > latestBlockHeld.index) {
console.log('blockchain possibly behind. We got: ' + latestBlockHeld.index + ' Peer got: ' + latestBlockReceived.index);
if (latestBlockHeld.hash === latestBlockReceived.previousHash) {
console.log("We can append the received block to our chain");
blockchain.push(latestBlockReceived);
broadcast(responseLatestMsg());
} else if (receivedBlocks.length === 1) {
console.log("We have to query the chain from our peer");
broadcast(queryAllMsg());
} else {
console.log("Received blockchain is longer than current blockchain");
replaceChain(receivedBlocks);
}
} else {
console.log('received blockchain is not longer than received blockchain. Do nothing');
}
};
var replaceChain = (newBlocks) => {
if (isValidChain(newBlocks) && newBlocks.length > blockchain.length) {
console.log('Received blockchain is valid. Replacing current blockchain with received blockchain');
blockchain = newBlocks;
broadcast(responseLatestMsg());
} else {
console.log('Received blockchain invalid');
}
};
var isValidChain = (blockchainToValidate) => {
if (JSON.stringify(blockchainToValidate[0]) !== JSON.stringify(getGenesisBlock())) {
return false;
}
var tempBlocks = [blockchainToValidate[0]];
for (var i = 1; i < blockchainToValidate.length; i++) {
if (isValidNewBlock(blockchainToValidate[i], tempBlocks[i - 1])) {
tempBlocks.push(blockchainToValidate[i]);
} else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
};
var getLatestBlock = () => blockchain[blockchain.length - 1];
var queryChainLengthMsg = () => ({'type': MessageType.QUERY_LATEST});
var queryAllMsg = () => ({'type': MessageType.QUERY_ALL});
var responseChainMsg = () =>({
'type': MessageType.RESPONSE_BLOCKCHAIN, 'data': JSON.stringify(blockchain)
});
var responseLatestMsg = () => ({
'type': MessageType.RESPONSE_BLOCKCHAIN,
'data': JSON.stringify([getLatestBlock()])
});
var write = (ws, message) => ws.send(JSON.stringify(message));
var broadcast = (message) => sockets.forEach(socket => write(socket, message));
connectToPeers(initialPeers);
initHttpServer();
initP2PServer();The above is what I compiled for everyone. I hope it will be helpful to everyone in the future.
Related articles:
NodeJS parent process and child process resource sharing principles and implementation methods
Vue implements active click switching method
The above is the detailed content of 200 lines of code to implement blockchain Detailed explanation of blockchain examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 VUE3 Getting Started Example: Making a Simple Video Player
Jun 15, 2023 pm 09:42 PM
VUE3 Getting Started Example: Making a Simple Video Player
Jun 15, 2023 pm 09:42 PM
As the new generation of front-end frameworks continues to emerge, VUE3 is loved as a fast, flexible, and easy-to-use front-end framework. Next, let's learn the basics of VUE3 and make a simple video player. 1. Install VUE3 First, we need to install VUE3 locally. Open the command line tool and execute the following command: npminstallvue@next Then, create a new HTML file and introduce VUE3: <!doctypehtml>
 Stead: A Revolutionary RWA Project Enabling Decentralized Funding for Floating Infrastructure in Southeast Asia
Aug 08, 2024 am 06:46 AM
Stead: A Revolutionary RWA Project Enabling Decentralized Funding for Floating Infrastructure in Southeast Asia
Aug 08, 2024 am 06:46 AM
Stead is an RWA project based in Southeast Asia. It serves as a decentralized funding platform for floating infrastructure, including fishing and transport boats, fish cages, and floating houses.
 Learn best practice examples of pointer conversion in Golang
Feb 24, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
Learn best practice examples of pointer conversion in Golang
Feb 24, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
Golang is a powerful and efficient programming language that can be used to develop various applications and services. In Golang, pointers are a very important concept, which can help us operate data more flexibly and efficiently. Pointer conversion refers to the process of pointer operations between different types. This article will use specific examples to learn the best practices of pointer conversion in Golang. 1. Basic concepts In Golang, each variable has an address, and the address is the location of the variable in memory.
 The relationship between the number of Oracle instances and database performance
Mar 08, 2024 am 09:27 AM
The relationship between the number of Oracle instances and database performance
Mar 08, 2024 am 09:27 AM
The relationship between the number of Oracle instances and database performance Oracle database is one of the well-known relational database management systems in the industry and is widely used in enterprise-level data storage and management. In Oracle database, instance is a very important concept. Instance refers to the running environment of Oracle database in memory. Each instance has an independent memory structure and background process, which is used to process user requests and manage database operations. The number of instances has an important impact on the performance and stability of Oracle database.
 PHP simple web crawler development example
Jun 13, 2023 pm 06:54 PM
PHP simple web crawler development example
Jun 13, 2023 pm 06:54 PM
With the rapid development of the Internet, data has become one of the most important resources in today's information age. As a technology that automatically obtains and processes network data, web crawlers are attracting more and more attention and application. This article will introduce how to use PHP to develop a simple web crawler and realize the function of automatically obtaining network data. 1. Overview of Web Crawler Web crawler is a technology that automatically obtains and processes network resources. Its main working process is to simulate browser behavior, automatically access specified URL addresses and extract all information.
 Verification code usage examples in Gin framework
Jun 23, 2023 am 08:10 AM
Verification code usage examples in Gin framework
Jun 23, 2023 am 08:10 AM
With the popularity of the Internet, verification codes have become a necessary process for login, registration, password retrieval and other operations. In the Gin framework, implementing the verification code function has become extremely simple. This article will introduce how to use a third-party library to implement the verification code function in the Gin framework, and provide sample code for readers' reference. 1. Install dependent libraries Before using the verification code, we need to install a third-party library goCaptcha. To install goCaptcha, you can use the goget command: $goget-ugithub
 Quickly get started with the Django framework: detailed tutorials and examples
Sep 28, 2023 pm 03:05 PM
Quickly get started with the Django framework: detailed tutorials and examples
Sep 28, 2023 pm 03:05 PM
Quickly get started with the Django framework: Detailed tutorials and examples Introduction: Django is an efficient and flexible Python Web development framework driven by the MTV (Model-Template-View) architecture. It has simple and clear syntax and powerful functions, which can help developers quickly build reliable and easy-to-maintain web applications. This article will introduce the use of Django in detail, and provide specific examples and code samples to help readers quickly get started with the Django framework. 1. Install D
 Essential development skills and examples for VUE3 beginners
Jun 16, 2023 am 09:00 AM
Essential development skills and examples for VUE3 beginners
Jun 16, 2023 am 09:00 AM
VUE3 is one of the increasingly used frameworks among front-end frameworks, and more and more developers are beginning to try to learn and use it. Especially in China, the application of VUE3 has covered many fields, both on mobile and PC. Therefore, this article will provide beginners with some essential tips and examples for VUE3 development to help them develop more quickly and efficiently. Use VUE3 scaffolding to quickly create projects. In the process of learning VUE3, many people may build the project step by step, which will take a long time.



