Analysis of vuex state+mapState practical project
This time I will bring you an analysis of the vuex state mapState practical project. What are the precautions for vuex state mapState? The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
First use vue cli to build your own vue project
1.npm i -g vue-cli
2.vue init webpack sell (sell is you Project name)
3. Press Enter all the way (during this process you will be prompted whether to install some dependent packages, such as vue-router, es6 grammar check, etc., select Y/N based on your personal habits or hobbies)
4.npm i (This is the dependency package of the installation project)
5.npm run dev (start your vue project) At this time, if you see the vue logo on the page, it means that your vue project base has been built Completed, then you can delete the useless components
6. Webpack sell does not install vuex by default, so you need to install vuex; press ctrl c twice on the command line to end the server, npm install vuex –save to install vuex.
7. Create a new vue component in your src directory. Let’s name it helloVuex (you can name it as you like, just be happy). This component is mainly used as the main container and only displays content
8. Then create a new one What the hell is the component called (I'll call it the display component here) is used to accept the state in the state
9. Next, we create a new folder called store in the src directory, and create a new js file under the store called test. js (the store here is our front-end data warehouse) uses vuex for state management. Store is the core of vuex, so it is named store. Create a new store file in the src directory, and create a new test.js file in the store directory (as shown below). You can see that before using vuex, you need to tell vue to use it, Vue.use(Vuex); We only have one variable count to manage here, so when creating the store object, pass parameters to the constructor, there is only one count under the state, and Initialized to 0.
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
}
export default storeNow all the status, that is, the variables are placed in test.js, so how can our component get the status modification value? There are two steps to be performed here
1. Vue provides an injection mechanism, which is to inject our store object into the root instance. The root instance of vue is the new Vue constructor, and then in all subcomponents, this.$store points to the store object. In test.js, we export store and the store has been exposed. new Vue() is in main.js, so we can directly introduce the store in main.js and inject it.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
import store from './store/test'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,
template: '<App/>',
components: { App }
})2. In child components, use the computed attribute. The computed attribute is automatically updated based on its dependencies. So as long as the state in the store changes, it will automatically change. Make the following changes in display.vue. This.$store in the subcomponent points to the store object. We change the count in test.js to 8, and it becomes 8 on the page.
<template>
<p>
<h3>Count is {{count}}</h3>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
computed: {
count () {
return this.$store.state.count
}
}
}
</script>3. The status value can be obtained through the computed attribute, but every attribute (such as count) in the component is a function. If there are 10, then 10 functions must be written, and 10 must be written repeatedly. It is not very convenient to return this.$store.state all the time. Vue provides the mapState function, which maps state directly to our components.
Of course you must introduce mapState before using it. It can be used in two ways, either accepting an object or an array. Still under the display.vue component.
The object usage is as follows:
<script>
import {mapState} from "vuex"; // 引入mapState
export default {
// 下面这两种写法都可以
computed: mapState({
count: state => state.count // 组件内的每一个属性函数都会获得一个默认参数state, 然后通过state 直接获取它的属性更简洁
count: 'count' // 'count' 直接映射到state 对象中的count, 它相当于 this.$store.state.count,
})
}
</script>The array method is as follows:
<script>
import {mapState} from "vuex";
export default {
computed: mapState([ // 数组
"count"
])
}
</script>4, There is one last question, what if we also have computed properties inside our components? It doesn't belong in mapState. Then we use object segmentation to divide the objects generated by the mapState function into one by one. Just like at the beginning, we listed the calculated attributes one by one. If there are 10 attributes, we will write 10 functions.
The... in es6 is used for splitting, but it can only split arrays. It can split objects in ECMAScript stage-3, so babel-stage-3 is also used at this time; npm install babel-preset-stage-3 --save-dev. After the installation is complete, don’t forget to add babel in babelrc In the configuration file, write stage-3,
, otherwise an error will always be reported. Add a p tag to the page to display the calculation familiarity of our component
babelrc
{
"presets": [
["env", {
"modules": false,
"targets": {
"browsers": ["> 1%", "last 2 versions", "not ie <= 8"]
}
}],
"stage-3"
],
"plugins": ["transform-runtime"],
"env": {
"test": {
"presets": ["env", "stage-3"],
"plugins": ["istanbul"]
}
}
}display.vue After the component is changed
<template>
<p>
<h3>Count is {{count}}</h3>
<p>组件自己的内部计算属性 {{ localComputed }}</p>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from "vuex";
export default {
computed: {
localComputed () {
return this.count + 10;
},
...mapState({
count: "count"
})
}
}
</script>put test. Change state.count in js to 10 to see an effect

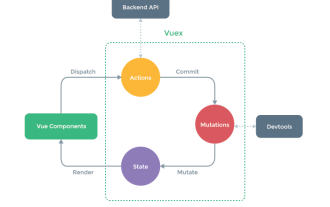
Let’s take a look at the usage of mapState in Vuex
I encountered a pitfall when using Vuex today. It can also be said to be my own ignorance. After struggling for a long time, I finally discovered the error in my code. It’s really thunderous~~~~~~
index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import mutations from './mutations'
import actions from './action'
import getters from './getters'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const state = {
userInfo: { phone: 111 }, //用户信息
orderList: [{ orderno: '1111' }], //订单列表
orderDetail: null, //订单产品详情
login: false, //是否登录
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
getters,
actions,
mutations,
})
computed: {
...mapState([
'orderList',
'login'
]),
},
mounted(){
console.log(typeof orderList); ==>undefind
console.log(typeof this.orderList)==>object
}mapState通过扩展运算符将store.state.orderList 映射this.orderList 这个this 很重要,这个映射直接映射到当前Vue的this对象上。
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of Analysis of vuex state+mapState practical project. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
![How to solve the problem 'Error: [vuex] do not mutate vuex store state outside mutation handlers.' when using vuex in a Vue application?](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/164/168760467048976.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) How to solve the problem 'Error: [vuex] do not mutate vuex store state outside mutation handlers.' when using vuex in a Vue application?
Jun 24, 2023 pm 07:04 PM
How to solve the problem 'Error: [vuex] do not mutate vuex store state outside mutation handlers.' when using vuex in a Vue application?
Jun 24, 2023 pm 07:04 PM
In Vue applications, using vuex is a common state management method. However, when using vuex, we may sometimes encounter such an error message: "Error:[vuex]donotmutatevuexstorestateoutsidemutationhandlers." What does this error message mean? Why does this error message appear? How to fix this error? This article will cover this issue in detail. The error message contains
![How to solve the problem 'Error: [vuex] unknown action type: xxx' when using vuex in a Vue application?](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/887/227/168766615217161.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) How to solve the problem 'Error: [vuex] unknown action type: xxx' when using vuex in a Vue application?
Jun 25, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to solve the problem 'Error: [vuex] unknown action type: xxx' when using vuex in a Vue application?
Jun 25, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
In Vue.js projects, vuex is a very useful state management tool. It helps us share state among multiple components and provides a reliable way to manage state changes. But when using vuex, sometimes you will encounter the error "Error:[vuex]unknownactiontype:xxx". This article will explain the cause and solution of this error. 1. Cause of the error When using vuex, we need to define some actions and mu
 Best practices for using Vuex to manage global state in Vue2.x
Jun 09, 2023 pm 04:07 PM
Best practices for using Vuex to manage global state in Vue2.x
Jun 09, 2023 pm 04:07 PM
Vue2.x is one of the most popular front-end frameworks currently, which provides Vuex as a solution for managing global state. Using Vuex can make state management clearer and easier to maintain. The best practices of Vuex will be introduced below to help developers better use Vuex and improve code quality. 1. Use modular organization state. Vuex uses a single state tree to manage all the states of the application, extracting the state from the components, making state management clearer and easier to understand. In applications with a lot of state, modules must be used
 How to use Vuex in Vue3
May 14, 2023 pm 08:28 PM
How to use Vuex in Vue3
May 14, 2023 pm 08:28 PM
What does Vuex do? Vue official: State management tool What is state management? State that needs to be shared among multiple components, and it is responsive, one change, all changes. For example, some globally used status information: user login status, user name, geographical location information, items in the shopping cart, etc. At this time, we need such a tool for global status management, and Vuex is such a tool. Single-page state management View–>Actions—>State view layer (view) triggers an action (action) to change the state (state) and responds back to the view layer (view) vuex (Vue3.
 Learn more about the implementation principles of vuex
Mar 20, 2023 pm 06:14 PM
Learn more about the implementation principles of vuex
Mar 20, 2023 pm 06:14 PM
When asked in an interview about the implementation principle of vuex, how should you answer? The following article will give you an in-depth understanding of the implementation principle of vuex. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 How to solve the problem 'TypeError: Cannot read property 'xxx' of undefined' when using vuex in Vue application?
Aug 18, 2023 pm 09:24 PM
How to solve the problem 'TypeError: Cannot read property 'xxx' of undefined' when using vuex in Vue application?
Aug 18, 2023 pm 09:24 PM
Using Vuex in Vue applications is a very common operation. However, occasionally when using Vuex, you will encounter the error message "TypeError: Cannotreadproperty'xxx'ofundefined". This error message means that the undefined property "xxx" cannot be read, resulting in a program error. The reason for this problem is actually very obvious. It is because when calling a certain attribute of Vuex, this attribute is not correctly set.
 How to use vuex in vue3+vite
Jun 03, 2023 am 09:10 AM
How to use vuex in vue3+vite
Jun 03, 2023 am 09:10 AM
Specific steps: 1. Install vuex (vue3 recommended 4.0+) pnpmivuex-S2, configure the global configuration of importstorefrom'@/store'//hx-app in main.js constapp=createApp(App)app.use(store) 3. Create new related folders and files. Here, configure multiple js inside different vuex. Use vuex modules to place different pages and files, and then use a getters.jsindex.js core file. Import.meta.glob is used here. , instead of
 How to use vuex for component communication in Vue?
Jul 19, 2023 pm 06:16 PM
How to use vuex for component communication in Vue?
Jul 19, 2023 pm 06:16 PM
How to use vuex for component communication in Vue? Vue is a popular JavaScript framework that adopts a component-based development model, allowing us to build complex applications more easily. In the component development process of Vue, we often encounter situations that require communication between different components. Vuex is the state management tool officially recommended by Vue. It provides a centralized storage manager and solves the problem of communication between components. This article will introduce how to use Vuex for component communication in Vue




