 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 How to package the koa2 framework app through webpack? What should I do?
How to package the koa2 framework app through webpack? What should I do?
How to package the koa2 framework app through webpack? What should I do?
This article introduces to you the steps and final deployment of using webpack to package the koa2 framework. It is very practical. Friends in need can refer to it.
In the past, when I used koa to write servers, publishing was simply It's a nightmare. All files in src need to be overwritten, and the config configuration file must also be overwritten. If you are not careful, various problems will be reported online, and then you have to roll back and adjust them locally before publishing. I accidentally saw an article about how to use webpack to package koa app. I was shocked. It turns out that webpack can also package the backend. I had never thought of this before.
Key issues
1: All modules in node_modules are not packaged
The core function of webpack is to reference Each module is typed into a file, and various standardized modules are unified and modularized (webpack specification).
However, node contains a large number of fs and path operations. These fs and path operations will have no operation objects after the packaging is completed, and many various errors will be reported.
So the core of using webpack for packaging is to refuse to package all modules in node_modules, and only package the files referenced by relative paths into one file. It happened that we found that webapck provides the externals attribute to exclude modules that do not need to be packaged.
If we dig deeper, we can find that modules like webpack, nodemon, and babel-preset-env are packages that the app development environment depends on, and our program will not require these modules at all.
In summary, we can find that: we only need to exclude all required packages. This module corresponds to the module under dependencies in package.json. It is important to understand the difference between dependencies and devDependencies.
So we can use the externals-dependencies plug-in with the externals attribute to exclude dependencies.
Code:
const webpack = require('webpack');
const _externals = require('externals-dependencies')
module.exports = {
...
externals: _externals(),
...
}Two: target points to node
Official documentation: Compiled into a Node.js-like environment available (use Node.js require to load chunk)
Code:
target: 'node',
Three: Add node configuration
Official documentation: These options can configure whether to polyfill or mock certain Node.js Global variables and modules. This allows code originally written for the Node.js environment to run in other environments such as browsers.
Code:
node: {
console: true,
global: true,
process: true,
Buffer: true,
__filename: true,
__dirname: true,
setImmediate: true,
path: true
},Four: babel configuration
In order to be compatible with the problem that lower versions of node do not natively support async/await. Here I use babel-preset-env{"modules": false} configuration for babel. This configuration will convert es6 syntax to es5 syntax, such as let and const to var.
At the same time, all async/await functions are also converted into the _asyncToGenerator function defined in the polyfill.
In fact, promises are used to implement the functions of async functions.
Of course this function also requires the regeneratorRuntime function when running. So I introduced babel-polyfill globally to provide the regeneratorRuntime function.
Note: If your node version is very high and supports async/await natively, you can omit babel-preset-env and babel-polyfill
Code:
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
const _externals = require('externals-dependencies')
module.exports = {
entry: {
app: [
// 如果polyfill放在这里,打包的时候将不会被external,必须在js里require才能有效external
// 'babel-polyfill',
'./src/index.js'
]
},
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname),
filename: '[name].js'
},
resolve: {
extensions: [".js"]
},
target: 'node',
externals: _externals(),
context: __dirname,
node: {
console: true,
global: true,
process: true,
Buffer: true,
__filename: true,
__dirname: true,
setImmediate: true,
path: true
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js/,
use: ['babel-loader']
}
]
},
plugins: [
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': {
NODE_ENV: '"development"'
}
}),
]
}Deployment
After packaging, deployment is much more convenient. You only need to deploy package.json, app.js, and the html in the view online. Then execute
1. npm install
2. npm run for
on the server and then the server will run in the background. If you need to update and publish, you only need to re-package npm run dev or npm run build locally and drag it to the server to overwrite app.js.
The above is what I compiled for everyone. I hope it will be helpful to everyone in the future.
Related articles:
How to develop component libraries using React
##Using fullpage.js to implement scrolling
The problem of failure to install Electron using npm
The above is the detailed content of How to package the koa2 framework app through webpack? What should I do?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to use Jenkins Pipeline to build a continuous packaging and deployment process for PHP programs?
Jul 30, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
How to use Jenkins Pipeline to build a continuous packaging and deployment process for PHP programs?
Jul 30, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
How to use JenkinsPipeline to build a continuous packaging and deployment process for PHP programs? Jenkins is a very popular continuous integration and deployment tool. It provides a wealth of plug-ins and functions to make the build and deployment process simple and efficient. JenkinsPipeline is the latest plug-in for Jenkins, which allows us to use a complete and extensible DSL (DomainSpecificLanguage) to define continuous integration and deployment.
 How to deploy a trustworthy web interface on a Linux server?
Sep 09, 2023 pm 03:27 PM
How to deploy a trustworthy web interface on a Linux server?
Sep 09, 2023 pm 03:27 PM
How to deploy a trustworthy web interface on a Linux server? Introduction: In today's era of information explosion, Web applications have become one of the main ways for people to obtain information and communicate. In order to ensure user privacy and information reliability, we need to deploy a trustworthy Web interface on the Linux server. This article will introduce how to deploy a web interface in a Linux environment and provide relevant code examples. 1. Install and configure the Linux server. First, we need to prepare a Li
 How to use Docker to package and deploy PHP programs?
Jul 29, 2023 pm 05:48 PM
How to use Docker to package and deploy PHP programs?
Jul 29, 2023 pm 05:48 PM
How to use Docker to package and deploy PHP programs? With the widespread application of cloud computing and containerization technology, more and more developers are beginning to use Docker to package and deploy applications. In this article, we will introduce how to use Docker to package and deploy PHP programs and give relevant code examples. 1. Install Docker Before starting, we need to install Docker first. For installation steps, please refer to Docker official documentation and choose the corresponding installation method according to different operating systems.
 How to deploy applications using Docker containerization in FastAPI
Jul 28, 2023 pm 01:25 PM
How to deploy applications using Docker containerization in FastAPI
Jul 28, 2023 pm 01:25 PM
How to use Docker containerization to deploy applications in FastAPI Introduction: Docker is a containerization technology that packages applications and their dependencies into an independent, portable container to achieve rapid deployment and expansion. FastAPI is a modern, high-performance web framework based on Python that provides a simple and fast API development experience. This article will introduce how to use Docker containerization to deploy applications in FastAPI and provide corresponding code examples.
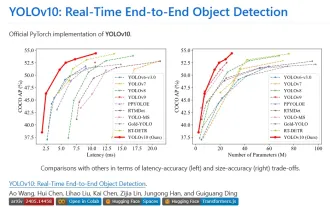 Yolov10: Detailed explanation, deployment and application all in one place!
Jun 07, 2024 pm 12:05 PM
Yolov10: Detailed explanation, deployment and application all in one place!
Jun 07, 2024 pm 12:05 PM
1. Introduction Over the past few years, YOLOs have become the dominant paradigm in the field of real-time object detection due to its effective balance between computational cost and detection performance. Researchers have explored YOLO's architectural design, optimization goals, data expansion strategies, etc., and have made significant progress. At the same time, relying on non-maximum suppression (NMS) for post-processing hinders end-to-end deployment of YOLO and adversely affects inference latency. In YOLOs, the design of various components lacks comprehensive and thorough inspection, resulting in significant computational redundancy and limiting the capabilities of the model. It offers suboptimal efficiency, and relatively large potential for performance improvement. In this work, the goal is to further improve the performance efficiency boundary of YOLO from both post-processing and model architecture. to this end
 How to solve the problem of inaccessibility after Tomcat deploys war package
Jan 13, 2024 pm 12:07 PM
How to solve the problem of inaccessibility after Tomcat deploys war package
Jan 13, 2024 pm 12:07 PM
How to solve the problem that Tomcat cannot successfully access the war package after deploying it requires specific code examples. As a widely used Java Web server, Tomcat allows developers to package their own developed Web applications into war files for deployment. However, sometimes we may encounter the problem of being unable to successfully access the war package after deploying it. This may be caused by incorrect configuration or other reasons. In this article, we'll provide some concrete code examples that address this dilemma. 1. Check Tomcat service
 Gunicorn Deployment Guide for Flask Applications
Jan 17, 2024 am 08:13 AM
Gunicorn Deployment Guide for Flask Applications
Jan 17, 2024 am 08:13 AM
How to deploy Flask application using Gunicorn? Flask is a lightweight Python Web framework that is widely used to develop various types of Web applications. Gunicorn (GreenUnicorn) is a Python-based HTTP server used to run WSGI (WebServerGatewayInterface) applications. This article will introduce how to use Gunicorn to deploy Flask applications, with
 Best practices and common problem solutions for deploying web projects on Tomcat
Dec 29, 2023 am 08:21 AM
Best practices and common problem solutions for deploying web projects on Tomcat
Dec 29, 2023 am 08:21 AM
Best practices for deploying Web projects with Tomcat and solutions to common problems Introduction: Tomcat, as a lightweight Java application server, has been widely used in Web application development. This article will introduce the best practices and common problem solving methods for Tomcat deployment of web projects, and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand and apply. 1. Project directory structure planning Before deploying a Web project, we need to plan the directory structure of the project. Generally speaking, we can organize it in the following way



