Package css styles separately in webpack
This time I will bring you the separate packaging of CSS styles in webpack. What are the precautions for packaging CSS styles separately in webpack? The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
Zero, introduction
The following are some basic knowledge summarized in personal projects. Record them here to deepen your impression and let others know. Everyone can understand webpack more quickly and conveniently, and use it. Due to limited capabilities, if there are errors or problems, please help point them out.
Webpack treats all resources as a module. CSS, Image, and JS font files are all resources and can be packaged into a bundle.js file.
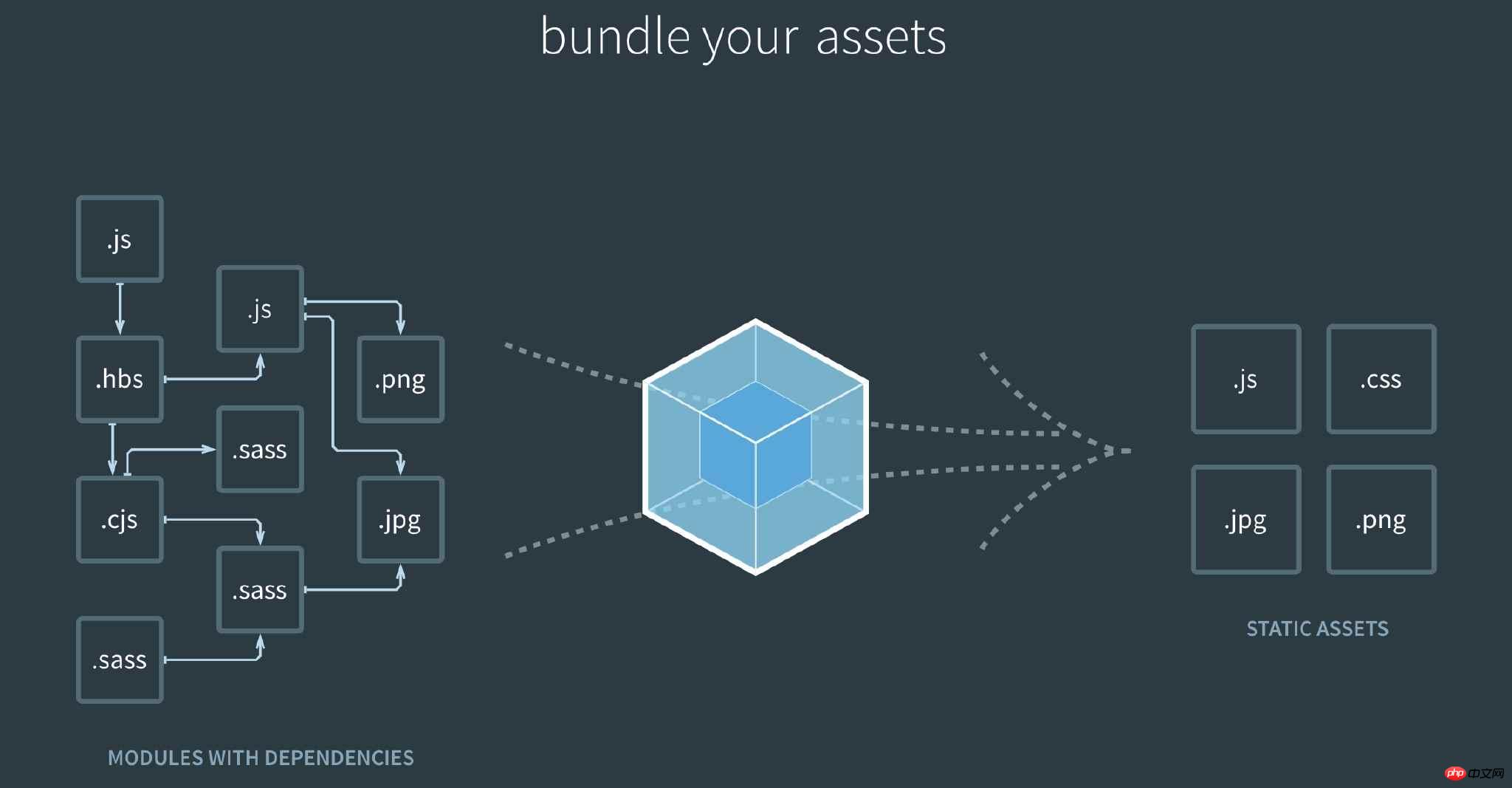
The basic use of webpack is very simple, but it would be a lot to explain all aspects, so here we mainly explain how to use webpack to package css separately.
As for packaging, how to add a hash value, how to replace the reference path in HTML, and how to upload to CND can be achieved using gulp. [Write an article later if you are interested]
1. Extract-text-webpack-plugin usage
Package css separately, in webpack You need to use a plug-in, extract-text-webpack-plugin
1. Install extract-text-webpack-plugin
// use npm npm install extract-text-webpack-plugin --save-dev // or use yarn yarn add extract-text-webpack-plugin
2. Configuration
Write the configuration of the plug-in in the loader (what loader to use), and set the name of the extracted CSS file in the plugins of webpack.
var Ex = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin');
// ...省略
module: {
loaders: [{
test: /\.less/,
loader: Ex.extract('style-loader', 'css-loader','less-loader') // 单独打包出CSS,这里配置注意下
}]
},
plugins: [
new Ex("【name】.css")
]For a little more detail, you can refer to this "Usage and Installation of extract-text-webpack-plugin"
Here are two actual usage examples to facilitate everyone's understanding
2. Single-page application, package the CSS in JS separately
To package a file, you only need to reference the css file in the regular entry js file. To package into multiple CSS files, you can set multiple CSS entries and let webpack use loader to package them. It is the same as splitting and packaging js files separately. Here are two examples.
// webpack 1.x 配置 【早期使用的配置,那时候是1.x】
/* webpack.config.js */
var precss = require('precss');
var cssnext = require('cssnext');
var autoprefixer = require('autoprefixer');
var cssnano = require('cssnano');
var Ex = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
entry: './index.js',
output: {
filename: 'index.js'
},
module: {
loaders: [{
test: /\.less/,
loader: Ex.extract('style-loader', 'css-loader','less-loader') // 单独打包出CSS,这里配置注意下
}]
},
plugins: [
new Ex("【name】.css")
]
}3. How webpack packages multiple CSS files
2. Add the corresponding configuration to the configuration file
Provided directly below A completed multi-entry CSS packaging configuration
// webpack 3.x 的配置
var path = require('path')
var glob = require('globby')
var webpack = require('webpack')
var ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin')
// CSS入口配置
var CSS_PATH = {
css: {
pattern: ['./src/**/[^_]*.less', '!./src/old/**/*.less'],
src: path.join(__dirname, 'src'),
dst: path.resolve(__dirname, 'static/build/webpack'),
}
}
// 遍历除所有需要打包的CSS文件路径
function getCSSEntries(config) {
var fileList = glob.sync(config.pattern)
return fileList.reduce(function (previous, current) {
var filePath = path.parse(path.relative(config.src, current))
var withoutSuffix = path.join(filePath.dir, filePath.name)
previous[withoutSuffix] = path.resolve(__dirname, current)
return previous
}, {})
}
module.exports = [
{
devtool: 'cheap-module-eval-source-map',
context: path.resolve(__dirname),
entry: getCSSEntries(CSS_PATH.css),
output: {
path: CSS_PATH.css.dst,
filename: '[name].css'
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.less$/,
use: ExtractTextPlugin.extract({
use: ['css-loader', 'postcss-loader', 'less-loader']
})
}
]
},
resolve: {
extensions: ['.less']
},
plugins: [
new ExtractTextPlugin('[name].css'),
]
},
// 如果还需要打包js,则可以在这里增加一个单独打包js的处理【根据自己需求来】
// {
// entry:{},
// output:{},
// ... 省略
// }
]Maybe some students are still using webpack1.x, so here is a simple configuration of webpack1.x
// webpack 1.x 版本
// ...其他配置和webpack3.x一样
module: {
loaders: [
{
test: /\.less$/,
loader: ExtractTextPlugin.extract("style-loader","css-loader","postcss-loader","less-loader")
},
]
}
plugins: [
new ExtractTextPlugin('[name].css'),
]
// ...其他配置和webpack3.x一样I believe you have read the case in this article After mastering the method, please pay attention to other related articles on the php Chinese website for more exciting content!
Recommended reading:
Vue php handles cross-domain issues
apply Math.max() function usage
The above is the detailed content of Package css styles separately in webpack. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 VUE3 Getting Started Tutorial: Packaging and Building with Webpack
Jun 15, 2023 pm 06:17 PM
VUE3 Getting Started Tutorial: Packaging and Building with Webpack
Jun 15, 2023 pm 06:17 PM
Vue is an excellent JavaScript framework that can help us quickly build interactive and efficient web applications. Vue3 is the latest version of Vue, which introduces many new features and functionality. Webpack is currently one of the most popular JavaScript module packagers and build tools, which can help us manage various resources in our projects. This article will introduce how to use Webpack to package and build Vue3 applications. 1. Install Webpack
 What is the difference between vite and webpack
Jan 11, 2023 pm 02:55 PM
What is the difference between vite and webpack
Jan 11, 2023 pm 02:55 PM
Differences: 1. The startup speed of the webpack server is slower than that of Vite; because Vite does not require packaging when starting, there is no need to analyze module dependencies and compile, so the startup speed is very fast. 2. Vite hot update is faster than webpack; in terms of HRM of Vite, when the content of a certain module changes, just let the browser re-request the module. 3. Vite uses esbuild to pre-build dependencies, while webpack is based on node. 4. The ecology of Vite is not as good as webpack, and the loaders and plug-ins are not rich enough.
 How to use PHP and webpack for modular development
May 11, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
How to use PHP and webpack for modular development
May 11, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
With the continuous development of web development technology, front-end and back-end separation and modular development have become a widespread trend. PHP is a commonly used back-end language. When doing modular development, we need to use some tools to manage and package modules. Webpack is a very easy-to-use modular packaging tool. This article will introduce how to use PHP and webpack for modular development. 1. What is modular development? Modular development refers to decomposing a program into different independent modules. Each module has its own function.
 How does webpack convert es6 to es5 module?
Oct 18, 2022 pm 03:48 PM
How does webpack convert es6 to es5 module?
Oct 18, 2022 pm 03:48 PM
Configuration method: 1. Use the import method to put the ES6 code into the packaged js code file; 2. Use the npm tool to install the babel-loader tool, the syntax is "npm install -D babel-loader @babel/core @babel/preset- env"; 3. Create the configuration file ".babelrc" of the babel tool and set the transcoding rules; 4. Configure the packaging rules in the webpack.config.js file.
 Use Spring Boot and Webpack to build front-end projects and plug-in systems
Jun 22, 2023 am 09:13 AM
Use Spring Boot and Webpack to build front-end projects and plug-in systems
Jun 22, 2023 am 09:13 AM
As the complexity of modern web applications continues to increase, building excellent front-end engineering and plug-in systems has become increasingly important. With the popularity of Spring Boot and Webpack, they have become a perfect combination for building front-end projects and plug-in systems. SpringBoot is a Java framework that creates Java applications with minimal configuration requirements. It provides many useful features, such as automatic configuration, so that developers can build and deploy web applications faster and easier. W
 What files can vue webpack package?
Dec 20, 2022 pm 07:44 PM
What files can vue webpack package?
Dec 20, 2022 pm 07:44 PM
In vue, webpack can package js, css, pictures, json and other files into appropriate formats for browser use; in webpack, js, css, pictures, json and other file types can be used as modules. Various module resources in webpack can be packaged and merged into one or more packages, and during the packaging process, the resources can be processed, such as compressing images, converting scss to css, converting ES6 syntax to ES5, etc., which can be recognized by HTML. file type.
 What is Webpack? Detailed explanation of how it works?
Oct 13, 2022 pm 07:36 PM
What is Webpack? Detailed explanation of how it works?
Oct 13, 2022 pm 07:36 PM
Webpack is a module packaging tool. It creates modules for different dependencies and packages them all into manageable output files. This is especially useful for single-page applications (the de facto standard for web applications today).
 An in-depth analysis of the packaging process and principles of webpack
Aug 09, 2022 pm 05:11 PM
An in-depth analysis of the packaging process and principles of webpack
Aug 09, 2022 pm 05:11 PM
How does Webpack implement packaging? The following article will give you an in-depth understanding of Webpack packaging principles. I hope it will be helpful to you!






