Detailed interpretation of the entry function run in webpack
Webpack is a front-end resource loading/packaging tool. It will perform static analysis based on module dependencies, and then generate corresponding static resources for these modules according to specified rules. This article mainly introduces the compile process of webpack source code - the entry function run. Friends who need it can refer to it
Webpack is currently the main packaging tool for applications developed based on React and Redux. I think many applications developed using Angular 2 or other frameworks also use Webpack.
The process of this section is as shown in the figure:
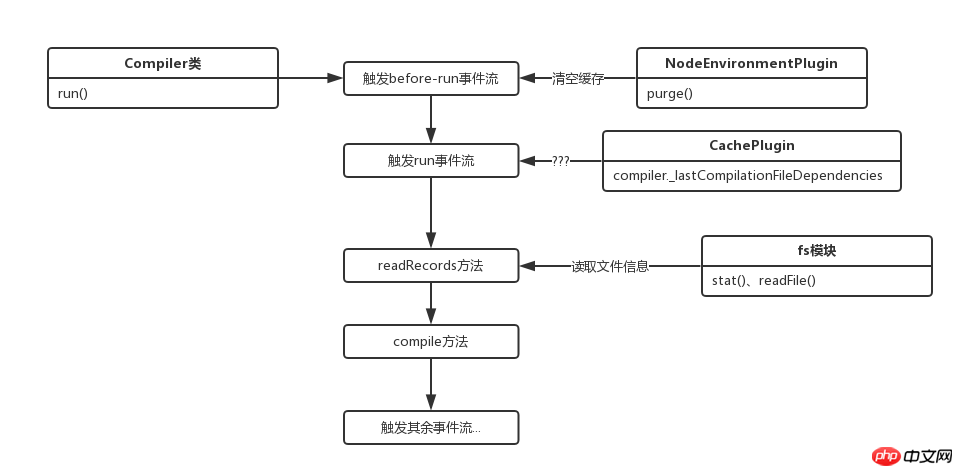
Now we have officially entered the packaging process. The starting method is run:
Compiler.prototype.run = (callback) => {
const startTime = Date.now();
const onCompiled = (err, compilation) => { /**/ };
this.applyPluginsAsync("before-run", this, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.applyPluginsAsync("run", this, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.readRecords(err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.compile(onCompiled);
});
});
});
}Why not introduce the compiler object ? Because there is no initialization method in the constructor, it is just an ordinary variable declaration, there is nothing to talk about.
In the run method, tapable's applyPluginsAsync is first called to execute the before-run event stream. The event stream is defined as follows:
// NodeEnvironmentPlugin
compiler.plugin("before-run", (compiler, callback) => {
if (compiler.inputFileSystem === inputFileSystem)
inputFileSystem.purge();
callback();
});In the file system method of the compiler object In the mounted plug-in, the before-run event stream is injected. Here we first take a look at applyPluginsAsync (slightly modified to adapt to the webpack source code):
// tapable
Tapable.prototype.applyPluginsAsync = (name, ...args, callback) => {
var plugins = this._plugins[name];
if (!plugins || plugins.length === 0) return callback();
var i = 0;
var _this = this;
// args为[args,next函数]
args.push(copyProperties(callback, function next(err) {
// 事件流出错或者全部执行完后调用回调函数
if (err) return callback(err);
i++;
if (i >= plugins.length) {
return callback();
}
// 执行下一个事件
plugins[i].apply(_this, args);
}));
// 执行第一个事件
plugins[0].apply(this, args);
};At that time, this series of events was not mentioned in Section 8 Here is a brief explanation of the flow triggering method:
1. copyProperties is used to copy object properties, similar to Object.assign. However, two functions are passed in here, which are of no use at all! ! ! ! ! (I didn’t write an explanation at the time because I was stuck on what the object copy method is of use here)
2. In webpack, args is this, pointing to the context of the compiler
3. Events injected into this event stream must execute the callback method (as in the above example). At this time, it is not the external callback that is executed, but the next function
4. There are two situations where the external callback will be executed and an error occurs midway. Or all event streams have been executed
It will be very clear. The meaning of the function parameters injected into before-run is as follows:
// before-run
// compiler => this
// callback => next
(compiler, callback) => {
if (compiler.inputFileSystem === inputFileSystem)
inputFileSystem.purge();
callback();
}Since there is only one event in before-run, so before calling After the next method of the internal callback, the external callback will be called directly because i is greater than the event length.
The purge method here has been seen before. Let’s review the content here:
// NodeEnvironmentPlugin
compiler.inputFileSystem = new CachedInputFileSystem(new NodeJsInputFileSystem(), 60000);
// CachedInputFileSystem
CachedInputFileSystem.prototype.purge = function(what) {
this._statStorage.purge(what);
this._readdirStorage.purge(what);
this._readFileStorage.purge(what);
this._readlinkStorage.purge(what);
this._readJsonStorage.purge(what);
};
// CachedInputFileSystem => Storage
Storage.prototype.purge = function(what) {
if (!what) {
this.count = 0;
clearInterval(this.interval);
this.nextTick = null;
this.data.clear();
this.levels.forEach(function(level) {
level.clear();
});
} else if (typeof what === "string") { /**/ } else { /**/ }
};In one sentence, it can be summarized as: clear all cached data in the package.
Since it is assumed to be the first time, there is no actual operation here. Then the external callback is called and the run event stream is triggered in the same way.
The run event stream has only one method, which comes from the CachePlugin plug-in:
Compiler.plugin("run", (compiler, callback) => {
// 这个属性我暂时也不知道是啥 反正直接callback了
if (!compiler._lastCompilationFileDependencies) return callback();
const fs = compiler.inputFileSystem;
const fileTs = compiler.fileTimestamps = {};
asyncLib.forEach(compiler._lastCompilationFileDependencies, (file, callback) => {
// ...
}, err => {
// ...
});
});When the run event stream is triggered for the first time, that property is undefined, so it will be skipped directly, because I am I parsed it while looking at the source code, so I don’t know what it is, haha.
The next callback is this:
this.readRecords(err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.compile(onCompiled);
});This is another prototype method, the source code is as follows:
Compiler.prototype.readRecords = (callback) => {
// 这个属性也没有
if (!this.recordsInputPath) {
this.records = {};
return callback();
}
this.inputFileSystem.stat(this.recordsInputPath, err => {
// ...
});
}The first time here will also be skipped and the callback will be directed directly. Looking at the source code, you probably pass in a path and read the file information inside and cache it into records.
Now jump two steps, directly enter the prototype method compile, preview this function:
Compiler.prototype.compile = (callback) => {
const params = this.newCompilationParams();
// 依次触发事件流
this.applyPluginsAsync("before-compile", params, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.applyPlugins("compile", params);
const compilation = this.newCompilation(params);
this.applyPluginsParallel("make", compilation, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
compilation.finish();
compilation.seal(err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.applyPluginsAsync("after-compile", compilation, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
return callback(null, compilation);
});
});
});
});
}The core process of compilation and packaging has been clearly seen, and the method triggers before-compile, compile, make, after-compile event flow, and finally the callback function is called.
The above is what I compiled for everyone. I hope it will be helpful to everyone in the future.
Related articles:
How to implement a background video login page using Vue.js 2.0
How to use Vue to develop time conversion instructions ?
How to implement page adaptation in angularjs?
How to monitor window.resize in VueJs and how to implement it specifically?
Detailed interpretation of the concept of $window window object in AngularJS
How to implement React-native bridging to Android, and what are the specific steps?
The above is the detailed content of Detailed interpretation of the entry function run in webpack. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 VUE3 Getting Started Tutorial: Packaging and Building with Webpack
Jun 15, 2023 pm 06:17 PM
VUE3 Getting Started Tutorial: Packaging and Building with Webpack
Jun 15, 2023 pm 06:17 PM
Vue is an excellent JavaScript framework that can help us quickly build interactive and efficient web applications. Vue3 is the latest version of Vue, which introduces many new features and functionality. Webpack is currently one of the most popular JavaScript module packagers and build tools, which can help us manage various resources in our projects. This article will introduce how to use Webpack to package and build Vue3 applications. 1. Install Webpack
 What is the difference between vite and webpack
Jan 11, 2023 pm 02:55 PM
What is the difference between vite and webpack
Jan 11, 2023 pm 02:55 PM
Differences: 1. The startup speed of the webpack server is slower than that of Vite; because Vite does not require packaging when starting, there is no need to analyze module dependencies and compile, so the startup speed is very fast. 2. Vite hot update is faster than webpack; in terms of HRM of Vite, when the content of a certain module changes, just let the browser re-request the module. 3. Vite uses esbuild to pre-build dependencies, while webpack is based on node. 4. The ecology of Vite is not as good as webpack, and the loaders and plug-ins are not rich enough.
 How to use PHP and webpack for modular development
May 11, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
How to use PHP and webpack for modular development
May 11, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
With the continuous development of web development technology, front-end and back-end separation and modular development have become a widespread trend. PHP is a commonly used back-end language. When doing modular development, we need to use some tools to manage and package modules. Webpack is a very easy-to-use modular packaging tool. This article will introduce how to use PHP and webpack for modular development. 1. What is modular development? Modular development refers to decomposing a program into different independent modules. Each module has its own function.
 How does webpack convert es6 to es5 module?
Oct 18, 2022 pm 03:48 PM
How does webpack convert es6 to es5 module?
Oct 18, 2022 pm 03:48 PM
Configuration method: 1. Use the import method to put the ES6 code into the packaged js code file; 2. Use the npm tool to install the babel-loader tool, the syntax is "npm install -D babel-loader @babel/core @babel/preset- env"; 3. Create the configuration file ".babelrc" of the babel tool and set the transcoding rules; 4. Configure the packaging rules in the webpack.config.js file.
 Use Spring Boot and Webpack to build front-end projects and plug-in systems
Jun 22, 2023 am 09:13 AM
Use Spring Boot and Webpack to build front-end projects and plug-in systems
Jun 22, 2023 am 09:13 AM
As the complexity of modern web applications continues to increase, building excellent front-end engineering and plug-in systems has become increasingly important. With the popularity of Spring Boot and Webpack, they have become a perfect combination for building front-end projects and plug-in systems. SpringBoot is a Java framework that creates Java applications with minimal configuration requirements. It provides many useful features, such as automatic configuration, so that developers can build and deploy web applications faster and easier. W
 What is Webpack? Detailed explanation of how it works?
Oct 13, 2022 pm 07:36 PM
What is Webpack? Detailed explanation of how it works?
Oct 13, 2022 pm 07:36 PM
Webpack is a module packaging tool. It creates modules for different dependencies and packages them all into manageable output files. This is especially useful for single-page applications (the de facto standard for web applications today).
 What files can vue webpack package?
Dec 20, 2022 pm 07:44 PM
What files can vue webpack package?
Dec 20, 2022 pm 07:44 PM
In vue, webpack can package js, css, pictures, json and other files into appropriate formats for browser use; in webpack, js, css, pictures, json and other file types can be used as modules. Various module resources in webpack can be packaged and merged into one or more packages, and during the packaging process, the resources can be processed, such as compressing images, converting scss to css, converting ES6 syntax to ES5, etc., which can be recognized by HTML. file type.
 Using Pattern.compile method in Java
Feb 18, 2024 pm 09:04 PM
Using Pattern.compile method in Java
Feb 18, 2024 pm 09:04 PM
Usage of Pattern.compile function in Java The Pattern.compile function in Java is a method used to compile regular expressions. Regular expression is a powerful string matching and processing tool that can be used to find, replace, verify strings and other operations. The Pattern.compile function allows us to compile a string pattern into a Pattern object, which can then be used to perform a series of string operations. Pattern.compi




