 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 How to use v-model in vue to achieve parent-child component communication
How to use v-model in vue to achieve parent-child component communication
How to use v-model in vue to achieve parent-child component communication
vue.js is a library for building data-driven web interfaces. The goal of Vue.js is to enable responsive data binding and composed view components with the simplest possible API. The following article mainly introduces relevant information about the communication implementation of v-model parent and child components in the vue project. Friends in need can refer to it.
Preface
In our vue project, we often have such a requirement. The parent component binds v-model, and the sub-component input changes the parent The value bound to component v-model. Many friends are not very clear about this operation, which requires a deeper understanding of v-model. Let’s talk about v-model today.
Vue’s two-way data binding
The v-model command can only be used in ,
This question will be mentioned in many front-end interviews. The interviewer asked you, what is the principle of two-way data binding in Vue? Of course, this is also a familiar question. You can find the answer everywhere by searching on Baidu.
Generally, you will find that Object.defineProperty() is used to monitor data get and set to achieve data hijacking.
If you don’t know much about Object.defineProperty(), you can click on the link above to take a look at its syntax!
Give a simple example:
var blog = {
name: 'haorooms博客'
};
console.log(blog.name); // haorooms博客 If you want to execute console.log(blog.name) at the same time, directly give haorooms How to add a book title to a blog? In other words, what is the attribute value of the monitoring object blog? At this time Object.defineProperty( ) comes in handy. The code is as follows:
var blog= {}
var name = '';
Object.defineProperty(blog, 'name', {
set: function (value) {
name = value;
console.log('欢迎来到' + value);
},
get: function () {
return '《' + name + '》'
}
})
blog.name = 'haorooms博客'; // 欢迎来到haorooms博客
console.log(blog.name); // 《haorooms博客》Execute the above code and you can see the effect!
Regarding Vue’s two-way data binding, how is it implemented? There are also many implementation codes on the Internet, so I won’t go into too much detail here!
Usage of v-model
There is a small gap in the above. I have said so much, but it is actually to illustrate that Vue is a single data flow. , v-model is just syntactic sugar.
<input v-model="haorooms" /> <input v-bind:value="haorooms" v-on:input="haorooms= $event.target.value" />
The first line of code is actually just syntactic sugar for the second line. Then the second line of code can be abbreviated like this:
<input :value="haorooms" @input="haorooms= $event.target.value" />
In other words,
<input v-model="haorooms" />
can also be written as
<input :value="haorooms" @input="haorooms= $event.target.value" />
v-model in the component The use of
is back to our original question? How does v-model communicate between parent and child components in vue? How to use it in components? If you understand my example above, then we can easily use v-model in components.
The parent component code is as follows:
<template>
<p id="demo">
<test-model v-model="haorooms"></test-model>
<span>{{haorooms}}</span>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import testModel from 'src/components/testModel'
export default {
data(){
return{
haorooms: "haorooms"
}
},
components: {
testModel,
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
</style>The child component code is as follows:
<template>
<span>
<input
ref="input"
:value="value"
@input="$emit('balabala', $event.target.value)"
>
</span>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
}
},
props: ["value"],
model: {
prop: 'value',
event: 'balabala'
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
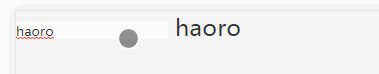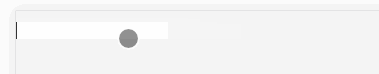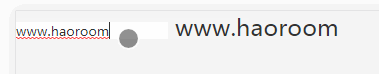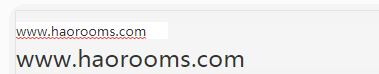
</style>We can use the above code to modify the value of the parent component v-model binding by the child component!
Implementation screenshots are as follows:
Disadvantages and solutions of v-model
When creating common components like check boxes or radio buttons, v-model is not easy to use.
<input type="checkbox" v-model="haorooms" />
We can solve it in the following way:
<input type="checkbox" :checked="status" @change="status = $event.target.checked" />
The parent component can be written as follows:
<my-checkbox v-model="haorooms"></my-checkbox>
Child component:
<input
type="checkbox"
<!--这里就不用 input 了,而是 balabala-->
@change="$emit('balabala', $event.target.checked)"
:checked="value"
/>
export default {
data(){
return{
}
},
props: ['checked'], //这里就不用 value 了,而是 checked
model: {
prop: 'checked',
event: 'balabala'
},
}The above is what I compiled for everyone Yes, I hope it will be helpful to everyone in the future.
Related articles:
How to implement a custom event mechanism using Javascript
##Detailed interpretation of the map data structure in javascript
How to develop a two-dimensional weekly view calendar using Javascript
The above is the detailed content of How to use v-model in vue to achieve parent-child component communication. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 Vue realizes marquee/text scrolling effect
Apr 07, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
Vue realizes marquee/text scrolling effect
Apr 07, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
Implement marquee/text scrolling effects in Vue, using CSS animations or third-party libraries. This article introduces how to use CSS animation: create scroll text and wrap text with <div>. Define CSS animations and set overflow: hidden, width, and animation. Define keyframes, set transform: translateX() at the beginning and end of the animation. Adjust animation properties such as duration, scroll speed, and direction.
 How to use function intercept vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 06:51 AM
How to use function intercept vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 06:51 AM
Function interception in Vue is a technique used to limit the number of times a function is called within a specified time period and prevent performance problems. The implementation method is: import the lodash library: import { debounce } from 'lodash'; Use the debounce function to create an intercept function: const debouncedFunction = debounce(() => { / Logical / }, 500); Call the intercept function, and the control function is called at most once in 500 milliseconds.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.



