
Use php to disable the cache problem of IE and Firefox. I found many ways on the Internet and finally solved it. Friends who need to know more can refer to it.
I found many ways on the Internet speed and finally solved it.
In fact, the easiest way is to add the tag in the header
You can also use programs control
<?php
header("Cache-control:no-cache,no-store,must-revalidate");
header("Pragma:no-cache");
header("Expires:0");
?>If in or header("Cache-control:no-cache,no-store ,must- revalidate"); without no-store, Firefox's cache cannot be solved
The following will give you a specific analysis:
Two differences between Firefox and IE browser caches An important difference
When you establish a WEB service, there are usually two types of cache that need to be configured:
Set the html resources to expire immediately when the website is updated, so that users who are browsing can quickly
Set all other resources (such as images, CSS, javascript scripts) to expire after a certain period of time.
This caching solution covers some of the ideas on how to handle updates mentioned in the Two Simple Rules for HTTP Caching article .
Now that HttpWatch 6.0 supports Firefox, we would like to discuss how Firefox is different from IE in handling cache. The method of setting a longer expiration time (the second item above) can still be used directly in Firefox, but configure 1 There are still subtle differences between the two.
In the previous article, we divided the first one into:
Sometimes dynamic HTML pages need to be updated instantly from the server to be displayed at any time - even using When using the back button. For example, displaying the status of a bank account or an online order.
Static HTML pages, such as contact, FAQs or sitemaps, if they set the Last-Modified response header, allow the browser to By revalidating, you can take advantage of the cache.
The remainder of this article discusses two important differences that affect HTML page caching in Firefox.
1. Use no-cache to prevent Firefox from caching. Invalid
You can simply set the following response header to prevent IE from caching anything:
Cache-Control: no-cache
Pages using this response header will not be saved in the cache, IE It will always be reloaded from the server; even if you use the back button. The following example uses HttpWatch to monitor an online store. When we click the back button after submitting the order form, the result is as follows: 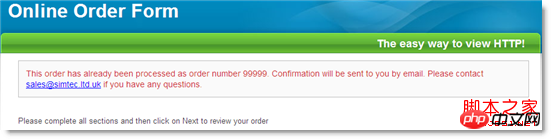
However, this The response header does not prevent Firefox from caching. This means that under normal access, Firefox will always use the cached page until it sends a GET request to recheck. And if the page is accessed through the back button, Firefox will not access it again. Access the server, but simply load directly from the cache.
So how can you turn off the cache in Firefox? The answer is simple, it cannot be turned off. Because Firefox relies on the copy in the cache for "File-> Save As Serves operations such as ","View Source". However, you can control where the page is cached and which cache entries can be used for display.
The following response headers in Firefox prevent persistent caching, forcing the page to be Cache into memory:
Cache-Control:no-store
This header can also prevent the cached page from being accessed when using the back button, which will trigger an HTTP GET request.
The values of these two response headers Used in combination, you can get the expected results in IE and Firefox:
Cache-Control: no-cache, no-store
As shown in the following HttpWatch response header tags: 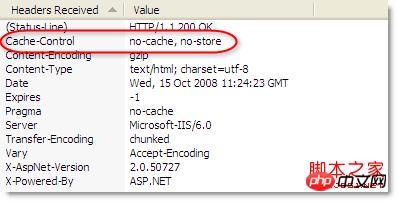
2. If you do not set an expiration time, Firefox will set one for you. When IE encounters an http response without an Expires header, it thinks that the cache entry can never be automatically used until it re-verifies from the service. Since IE A setting item of the temporary file "Check for a newer version of the web page" defaults to "automatic", so it is usually done once per session.
This provides a reasonable way to control the caching of static html content .The user's newly opened IE will get the latest version of html, and the cached version will be used until I close IE.
Firefox handles missing Expires headers differently. If there is a Last-Modified header in the impact, it will Use a tentative expiration value specified in the HTTP 1.1 specification RFC2616:
( Reference specification :)
And, if the response has a Last-Modified time value, the tentative expiration value cannot A ratio of the time interval exceeding this value to the present. Generally, this ratio is set to 10%.
The calculation method is as follows:
Expiration time = current time 0.1 * (the time difference from Last-Modified to the present)
For example, If your static HTML file was last modified 100 days ago, the expiration time is 10 days later. The following example is an HttpWatch cache tag without an Expires header page:
pic3
Firefox automatically sets the expiration time is 8 days later, because the page has not been modified for approximately 80 days.
This means that, in order to maintain control of your HTML pages, as we discussed in the Two Simple Rules for HTTP Caching article, you'd better For your static resources such as HTML, images, CSS files, etc., set an appropriate Expires value on your WEB server.
Conclusion
In order to ensure consistent caching behavior between IE and Firefox, you should:
Always specify an Expires header. Generally set -1 to use html pages to refresh immediately or set a specific expiration time for other resources such as images, CSS, and javascript scripts.
If you want to force the page to refresh, even when clicking the background button, then set Cache-Control: no-cache, no-store
The above is the entire content of this article , I hope it will be helpful to everyone’s learning. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!
Related recommendations:
How to use PHP to obtain website domain name and address
About the development of PHP and jQuery registration module
The above is the detailed content of How to use php to disable the cache problem of IE and Firefox. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




