Introduction to the caching mechanism of js and css
This article mainly introduces the relevant knowledge of localStorage's black technology-js and css caching mechanism, which has certain reference value. Let's take a look at it together
1. The cause of discovering black technology
I saw a technical blog post on the WeChat public account today and wanted to use Evernote to collect it, so I sent the article link to my PC. Then I habitually open the console, look at the source code, and want to know what new technologies WeChat has recently used.
Haha, the following aroused my desire to be a detective. The abnormal point after the page is loaded is that only one js is loaded, as shown in the following figure:
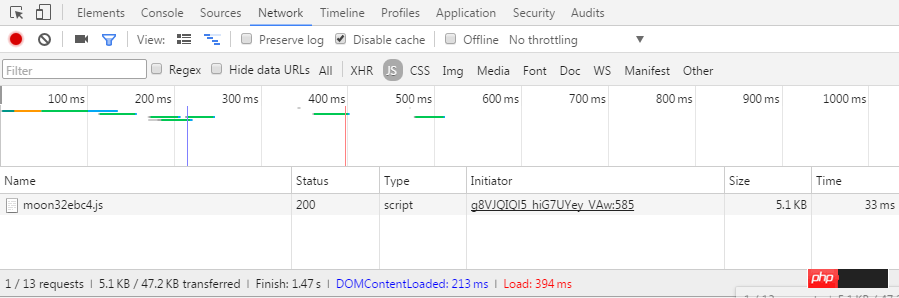
I am very surprised, why has Disable cache been turned on and only one js is loaded? And it’s so small. Then, I held down Ctrl O to search for resource files and found that I had been "fooled". In fact, there is more than one js file at all.
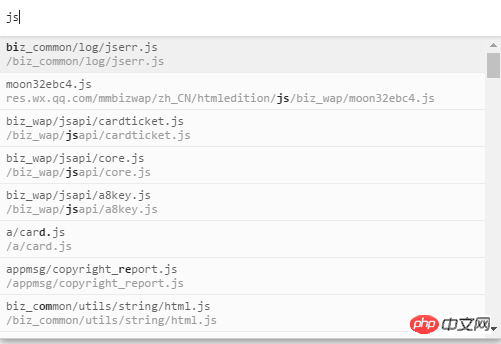
An idea flashed in my head. Could it be that I used localStorage to cache it? ! I quickly took a look at localStronge, and it was true. . . .
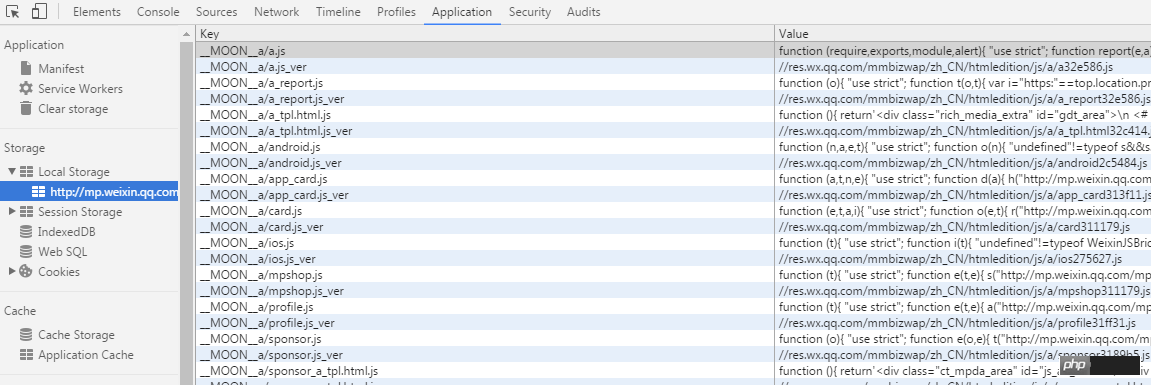
My heart was surging. Isn’t this the idea of optimizing loading performance that I wanted to achieve before! Darling, I am ignorant, a front-end team has already implemented the code.
2. Let’s talk about the optimization ideas for file loading
Usually, the front-end resource file loading optimization is to load as many files as possible without modifying and iterating the file. Make optimal use of caching to avoid downloading the same file multiple times.
The general approach is to extend the validity period of the resource as much as possible, that is, set the max-age in Cache-Control so that the return code of the page resource request is 304, so that the browser can directly use the local cache.
Although the negotiation cache (304) on the PC side is very fast, due to network reasons, the negotiation cache effect on the mobile side is not as good as that on the PC side. Moreover, the phone will frequently clear the local cache, so the file cache time will not be very long.
At this time, localStorage comes in handy.
Compared with cookies, localStorage can cache large volumes of data and is permanently valid. Therefore, if you store js resources and css resources in localStorage, you can save the time spent sending http requests and greatly improve the user's browsing experience.
3. Problems that need to be solved when using localStorage for resource caching
##3.1 Version update mechanism
As long as a project is still under iterative development, it is inevitable to update resource files. Ordinary resource requests can be based on file name md5 http://res.wx.qq.com/mmbizwap/zh_CN/htmledition/js/biz_wap/moon32ebc4.jsor Add a specific suffix after the resource link http://1.ss.faisys.com/js/comm/fai.min.js?v=201612051739 Make a mark to determine whether resources need to be updated. If you use localStorage, you need a new cache update mechanism.
3.2 Build a scaffolding to update the code
If you use localStorage cache, you need a new scaffolding to manage the reading and writing of resource files. .3.3 The background outputs a resource configuration information
Because the front-end needs to update resources, the background needs to output a basis for the front-end to make judgments Use, that is, a piece of resource configuration information is required. The front end performs matching and comparison based on the configuration information, and finally decides whether to use localStorage cache or re-initiate the request to download the latest resource file.3.4 There are XSS security risks
The client can modify the information in localStorage at will. If any hacker wants to practice, he can inject js code at will. Then, when the page is refreshed, the injected code will also be executed.4. Analysis of WeChat practices
4.1 Version identification

4.2 Scaffolding
It can be seen that WeChat uses the scaffolding moon.js developed by itself. The actual file name in this webpage is It's moon32ebc4.js.Because it is a file with obfuscated variable names, it is a bit difficult to see the direction of the specific code, so I will not analyze it here.
4.3 Resource configuration information
Because the scaffolding moon.js requires resource configuration information to work properly, the configuration information must be in moon.js output before.
Looking at the script tags before moon.js in turn, I found the json object window.moon_map.
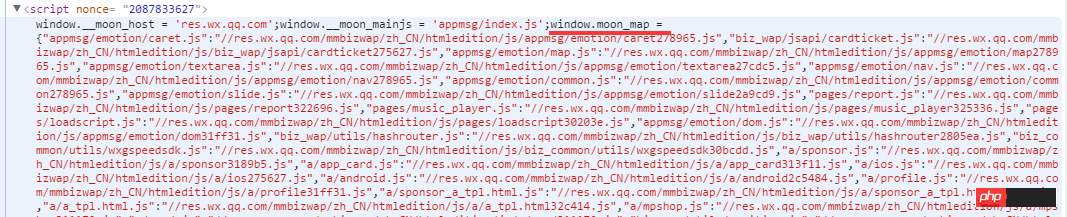
Use the console to output this variable to view the information as follows:

Seeing this, one point can be made clear: this It is the resource configuration information table necessary for the update mechanism.
Moreover, it can be seen that the key of the configuration information json object corresponds to the key in localStorage. In the same way, value values also correspond to one-to-one.
4.4 XSS attack
This is to verify whether there is an XSS attack on WeChat’s caching mechanism. Don’t see the children’s shoes here. To do bad things.
I inserted alert("hehe"); in a js cache code to see if the pop-up window will appear when the page is refreshed to verify whether there is an attack vulnerability.
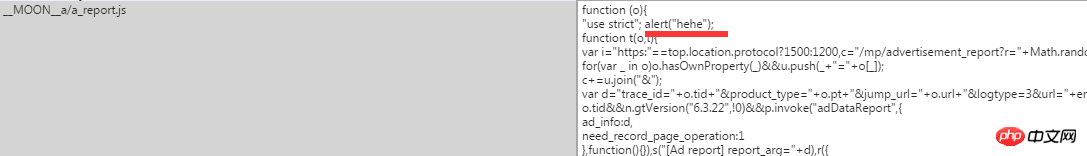
After refreshing the page, the result is as follows:
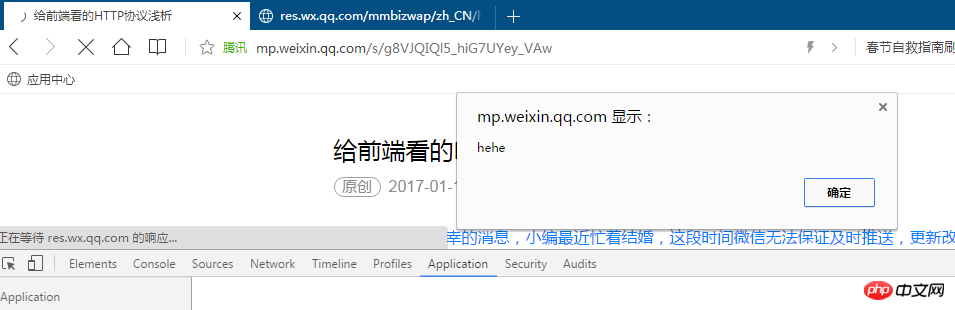
It can be seen that WeChat has not solved this kind of problem. Therefore, this caching mechanism still has inherent shortcomings.
4.5 Test the update mechanism of WeChat
Modify the key in localStorage __MOON__a/a_report.js_verCorresponding value, let WeChat’s scaffolding moon.js update __MOON__a/a_report.js, and erase the code I just actively inserted.
Here, I changed the file name to ***587.js (the original file name was ***586.js). Then F5 refreshes the page.
The result is: report.js code has been updated, and the version number has been restored to ***586.js.

5. Conclusion
localStorage cache has its place, but it is not a panacea. You need to pay attention to the pitfalls mentioned above.
I can summarize the applicable scenarios into the following points:
1. CSS files required for non-first-screen rendering can be cached in LS.
The css required for first-screen rendering needs to be output in a conventional way because it is required by SEO. Otherwise, when crawlers crawl the page, the page effect will be very poor. For non-first-screen CSS, you can use LS caching to reduce resource download time.
2. Codes that are not the main business logic, such as display classes and animation classes, can be cached in LS.
In this way, security vulnerabilities in the business layer can be avoided to a certain extent. Of course, no matter how the front end is protected, it is only a thin layer of paper. What is important is that the backend interface must be securely protected.
3. The mobile terminal can do LS caching. LS caching on the PC side has little optimization effect.
The above is the entire content of this article. I hope it will be helpful to everyone’s study. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!
Related recommendations:
How to write JS and CSS in the same file
About native js implementation Single page/full screen scrolling method similar to fullpage
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to the caching mechanism of js and css. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Why can't localstorage successfully save data?
Jan 03, 2024 pm 01:41 PM
Why can't localstorage successfully save data?
Jan 03, 2024 pm 01:41 PM
Why does storing data to localstorage always fail? Need specific code examples In front-end development, we often need to store data on the browser side to improve user experience and facilitate subsequent data access. Localstorage is a technology provided by HTML5 for client-side data storage. It provides a simple way to store data and maintain data persistence after the page is refreshed or closed. However, when we use localstorage for data storage, sometimes
 How to set the expiration time of localstorage items
Jan 11, 2024 am 09:06 AM
How to set the expiration time of localstorage items
Jan 11, 2024 am 09:06 AM
How to set the expiration time of localstorage requires specific code examples. With the rapid development of the Internet, front-end development often requires saving data in the browser. Localstorage is a commonly used WebAPI that aims to provide a way to store data locally in the browser. However, localstorage does not provide a direct way to set the expiration time. This article will introduce how to set the expiration time of localstorage through code examples.
 What are the methods to recover deleted Localstorage data?
Jan 11, 2024 pm 12:02 PM
What are the methods to recover deleted Localstorage data?
Jan 11, 2024 pm 12:02 PM
How to recover deleted Localstorage data? Localstorage is a technology used to store data in web pages. It is widely used in various web applications to share data between multiple pages. However, sometimes we may accidentally delete data in Localstorage, which causes us trouble. So, how to recover deleted Localstorage data? Below are specific steps and code examples. Step 1: Stop writing to Loca
 Steps and precautions for using localstorage to store data
Jan 11, 2024 pm 04:51 PM
Steps and precautions for using localstorage to store data
Jan 11, 2024 pm 04:51 PM
Steps and precautions for using localStorage to store data This article mainly introduces how to use localStorage to store data and provides relevant code examples. LocalStorage is a way of storing data in the browser that keeps the data local to the user's computer without going through a server. The following are the steps and things to pay attention to when using localStorage to store data. Step 1: Check whether the browser supports LocalStorage
 Why is localstorage unsafe?
Oct 10, 2023 pm 05:38 PM
Why is localstorage unsafe?
Oct 10, 2023 pm 05:38 PM
The reasons why localstorage is unsafe are unencrypted data, XSS attacks, CERF attacks, capacity limitations, etc. Detailed introduction: 1. Data is not encrypted. Localstorage is a simple key-value pair storage system. It stores data in the user's browser in clear text, which means that anyone can easily access and read the data stored in localstorage. If sensitive information is stored in localstorage, hackers or malicious users can easily obtain this information and so on.
 Why can't local storage save data correctly?
Jan 03, 2024 pm 01:41 PM
Why can't local storage save data correctly?
Jan 03, 2024 pm 01:41 PM
Why can't localstorage save my data normally? In web development, we often need to save the user's data locally so that the data can be quickly loaded or restored the next time the user visits the website. In the browser, we can use localStorage to achieve this function. However, sometimes we find that data saved using localStorage does not work properly. So why does this happen? In understanding why localStorage
 Why localstorage is not safe
Dec 13, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
Why localstorage is not safe
Dec 13, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
The reasons why localstorage is unsafe: 1. The stored content can be tampered with; 2. The data can be stolen; 3. The data can be forged; 4. Cross-site scripting attacks; 5. Clear browser data. Detailed introduction: 1. The stored content can be tampered with. The data in localStorage is stored in the user's browser, which means that anyone with access to the browser can view and modify the data in localStorage; 2. The data can be tampered with. is stolen because the data in localStorage is stored by the user and so on.
 Steps to use localstorage to store data
Jan 11, 2024 am 09:14 AM
Steps to use localstorage to store data
Jan 11, 2024 am 09:14 AM
How to use localstorage to store data? Introduction: localstorage is a browser local storage mechanism provided by HTML5, through which data can be easily stored and read in the browser. This article will introduce how to use localstorage to store data and provide specific code examples. This article is divided into the following parts: 1. Introduction to localstorage; 2. Steps to use localstorage to store data; 3. Code examples; 4. Frequently asked questions




