 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Use ES6 classes to imitate Vue to write an example of two-way binding
Use ES6 classes to imitate Vue to write an example of two-way binding
Use ES6 classes to imitate Vue to write an example of two-way binding
This article mainly introduces how to use ES6 classes to imitate Vue to write a two-way binding sample code. The content is quite good. I will share it with you now and give it as a reference.
This article introduces how to use ES6 classes to imitate Vue to write a two-way binding sample code and share it with everyone. The details are as follows:
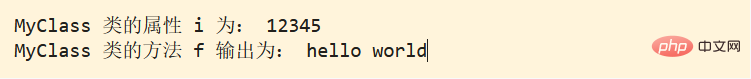
The final effect is as follows:

Constructor(constructor)
Construct a TinyVue object, including basic el, data, methods
class TinyVue{
constructor({el, data, methods}){
this.$data = data
this.$el = document.querySelector(el)
this.$methods = methods
// 初始化
this._compile()
this._updater()
this._watcher()
}
}Compiler(compile)
is used to parse the click event @click of the v-model and element bound to the input box and drop-down box.
First create a function to load events:
// el为元素tagName,attr为元素属性(v-model,@click)
_initEvents(el, attr, callBack) {
this.$el.querySelectorAll(el).forEach(i => {
if(i.hasAttribute(attr)) {
let key = i.getAttribute(attr)
callBack(i, key)
}
})
}Load input box event
this._initEvents('input, textarea', 'v-model', (i, key) => {
i.addEventListener('input', () => {
Object.assign(this.$data, {[key]: i.value})
})
})Load selection box event
this._initEvents('select', 'v-model', (i, key) => {
i.addEventListener('change', () => Object.assign(this.$data, {[key]: i.options[i.options.selectedIndex].value}))
}) Loading the click event
The click event corresponds to the event in methods
this._initEvents('*', '@click', (i, key) => {
i.addEventListener('click', () => this.$methods[key].bind(this.$data)())
})View updater(updater)
In the same way, first create a public function to process the views in different elements, including the value of input, textarea, the selection value of select, and the innerHTML of p
_initView(el, attr, callBack) {
this.$el.querySelectorAll(el, attr, callBack).forEach(i => {
if(i.hasAttribute(attr)) {
let key = i.getAttribute(attr),
data = this.$data[key]
callBack(i, key, data)
}
})
}Update the input box view
this._initView('input, textarea', 'v-model', (i, key, data) => {
i.value = data
})Update the selection box View
this._initView('select', 'v-model', (i, key, data) => {
i.querySelectorAll('option').forEach(v => {
if(v.value == data) v.setAttribute('selected', true)
else v.removeAttribute('selected')
})
})Update innerHTML
The implementation method here is a bit low, I only think of regular replacement {{text}}
let regExpInner = /\{{ *([\w_\-]+) *\}}/g
this.$el.querySelectorAll("*").forEach(i => {
let replaceList = i.innerHTML.match(regExpInner) || (i.hasAttribute('vueID') && i.getAttribute('vueID').match(regExpInner))
if(replaceList) {
if(!i.hasAttribute('vueID')) {
i.setAttribute('vueID', i.innerHTML)
}
i.innerHTML = i.getAttribute('vueID')
replaceList.forEach(v => {
let key = v.slice(2, v.length - 2)
i.innerHTML = i.innerHTML.replace(v, this.$data[key])
})
}
})Listener (watcher)
Update the view after data changes
<p id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="text1"><br>
<input type="text" v-model="text2"><br>
<textarea type="text" v-model="text3"></textarea><br>
<button @click="add">加一</button>
<h1>您输入的是:{{text1}}+{{text2}}+{{text3}}</h1>
<select v-model="select">
<option value="volvo">Volvo</option>
<option value="saab">Saab</option>
</select>
<select v-model="select">
<option value="volvo">Volvo</option>
<option value="saab">Saab</option>
</select>
<h1>您选择了:{{select}}</h1>
</p>
<script src="./TinyVue.js"></script>
<script>
let app = new TinyVue({
el: '#app',
data: {
text1: 123,
text2: 456,
text3: '文本框',
select: 'saab'
},
methods: {
add() {
this.text1 ++
this.text2 ++
}
}
})
</script>TinyVue full code
class TinyVue{
constructor({el, data, methods}){
this.$data = data
this.$el = document.querySelector(el)
this.$methods = methods
this._compile()
this._updater()
this._watcher()
}
_watcher(data = this.$data) {
let that = this
Object.keys(data).forEach(i => {
let value = data[i]
Object.defineProperty(data, i, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function () {
return value;
},
set: function (newVal) {
if (value !== newVal) {
value = newVal;
that._updater()
}
}
})
})
}
_initEvents(el, attr, callBack) {
this.$el.querySelectorAll(el).forEach(i => {
if(i.hasAttribute(attr)) {
let key = i.getAttribute(attr)
callBack(i, key)
}
})
}
_initView(el, attr, callBack) {
this.$el.querySelectorAll(el, attr, callBack).forEach(i => {
if(i.hasAttribute(attr)) {
let key = i.getAttribute(attr),
data = this.$data[key]
callBack(i, key, data)
}
})
}
_updater() {
this._initView('input, textarea', 'v-model', (i, key, data) => {
i.value = data
})
this._initView('select', 'v-model', (i, key, data) => {
i.querySelectorAll('option').forEach(v => {
if(v.value == data) v.setAttribute('selected', true)
else v.removeAttribute('selected')
})
})
let regExpInner = /\{{ *([\w_\-]+) *\}}/g
this.$el.querySelectorAll("*").forEach(i => {
let replaceList = i.innerHTML.match(regExpInner) || (i.hasAttribute('vueID') && i.getAttribute('vueID').match(regExpInner))
if(replaceList) {
if(!i.hasAttribute('vueID')) {
i.setAttribute('vueID', i.innerHTML)
}
i.innerHTML = i.getAttribute('vueID')
replaceList.forEach(v => {
let key = v.slice(2, v.length - 2)
i.innerHTML = i.innerHTML.replace(v, this.$data[key])
})
}
})
}
_compile() {
this._initEvents('*', '@click', (i, key) => {
i.addEventListener('click', () => this.$methods[key].bind(this.$data)())
})
this._initEvents('input, textarea', 'v-model', (i, key) => {
i.addEventListener('input', () => {
Object.assign(this.$data, {[key]: i.value})
})
})
this._initEvents('select', 'v-model', (i, key) => {
i.addEventListener('change', () => Object.assign(this.$data, {[key]: i.options[i.options.selectedIndex].value}))
})
}
}The above is the entire content of this article, I hope it will be helpful to everyone's learning, and more For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!
Related recommendations:
Vue2.0 Multi-Tab switching component encapsulation introduction
About Vue form demo v-model Two-way binding problem
The above is the detailed content of Use ES6 classes to imitate Vue to write an example of two-way binding. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Can two WeChat accounts be bound to the same bank card?
Aug 25, 2023 pm 03:13 PM
Can two WeChat accounts be bound to the same bank card?
Aug 25, 2023 pm 03:13 PM
Two WeChat accounts cannot be bound to the same bank card. Bind a bank card to a WeChat account: 1. Open the WeChat application, click the "Me" option, and then select the "Pay" option; 2. Select the "Add Bank Card" option and enter the bank card information as prompted; 3. Once the bank card is successfully bound, users can use the bank card to make payments and transfers in WeChat.
 How to implement editable tables in Vue
Nov 08, 2023 pm 12:51 PM
How to implement editable tables in Vue
Nov 08, 2023 pm 12:51 PM
Tables are an essential component in many web applications. Tables usually have large amounts of data, so tables require some specific features to improve user experience. One of the important features is editability. In this article, we will explore how to implement editable tables using Vue.js and provide specific code examples. Step 1: Prepare the data First, we need to prepare the data for the table. We can use a JSON object to store the table's data and store it in the data property of the Vue instance. In this case
 How to use classes and methods in Python
Apr 21, 2023 pm 02:28 PM
How to use classes and methods in Python
Apr 21, 2023 pm 02:28 PM
Concepts and instances of classes and methods Class (Class): used to describe a collection of objects with the same properties and methods. It defines the properties and methods common to every object in the collection. Objects are instances of classes. Method: Function defined in the class. Class construction method __init__(): The class has a special method (construction method) named init(), which is automatically called when the class is instantiated. Instance variables: In the declaration of a class, attributes are represented by variables. Such variables are called instance variables. An instance variable is a variable modified with self. Instantiation: Create an instance of a class, a specific object of the class. Inheritance: that is, a derived class (derivedclass) inherits the base class (baseclass)
 BTCC tutorial: How to bind and use MetaMask wallet on BTCC exchange?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
BTCC tutorial: How to bind and use MetaMask wallet on BTCC exchange?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
MetaMask (also called Little Fox Wallet in Chinese) is a free and well-received encryption wallet software. Currently, BTCC supports binding to the MetaMask wallet. After binding, you can use the MetaMask wallet to quickly log in, store value, buy coins, etc., and you can also get 20 USDT trial bonus for the first time binding. In the BTCCMetaMask wallet tutorial, we will introduce in detail how to register and use MetaMask, and how to bind and use the Little Fox wallet in BTCC. What is MetaMask wallet? With over 30 million users, MetaMask Little Fox Wallet is one of the most popular cryptocurrency wallets today. It is free to use and can be installed on the network as an extension
 Is async for es6 or es7?
Jan 29, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
Is async for es6 or es7?
Jan 29, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
async is es7. async and await are new additions to ES7 and are solutions for asynchronous operations; async/await can be said to be syntactic sugar for co modules and generator functions, solving js asynchronous code with clearer semantics. As the name suggests, async means "asynchronous". Async is used to declare that a function is asynchronous; there is a strict rule between async and await. Both cannot be separated from each other, and await can only be written in async functions.
 How to bind a sub-account on Xiaohongshu? How does it check whether the account is normal?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 10:11 PM
How to bind a sub-account on Xiaohongshu? How does it check whether the account is normal?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 10:11 PM
In today's era of information explosion, the construction of personal brand and corporate image has become increasingly important. As the leading fashion life sharing platform in China, Xiaohongshu has attracted a large number of user attention and participation. For those users who want to expand their influence and improve the efficiency of content dissemination, binding sub-accounts has become an effective means. So, how does Xiaohongshu bind a sub-account? How to check whether the account is normal? This article will answer these questions for you in detail. 1. How to bind a sub-account on Xiaohongshu? 1. Log in to your main account: First, you need to log in to your Xiaohongshu main account. 2. Open the settings menu: click "Me" in the upper right corner, and then select "Settings". 3. Enter account management: In the settings menu, find the "Account Management" or "Account Assistant" option and click
 Steps and methods to bind Douyin in Toutiao
Mar 22, 2024 pm 05:56 PM
Steps and methods to bind Douyin in Toutiao
Mar 22, 2024 pm 05:56 PM
1. Open Toutiao. 2. Click My in the lower right corner. 3. Click [System Settings]. 4. Click [Account and Privacy Settings]. 5. Click the button on the right side of [Douyin] to bind Douyin.
 How to bind the Cainiao app to Pinduoduo? How to add the Cainiao Wrap to Pinduoduo platform?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:30 PM
How to bind the Cainiao app to Pinduoduo? How to add the Cainiao Wrap to Pinduoduo platform?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:30 PM
The Cainiao app is a platform that can provide you with various logistics information. The functions here are very powerful and easy to use. If you have any logistics-related problems, they can be solved here. Anyway, it can bring you a The one-stop service can solve everything in time. Checking the express delivery, picking up the express delivery, sending the express delivery, etc. are all without any problems. We have cooperated with various platforms and all the information can be queried. However, sometimes It will happen that the goods purchased on Pinduoduo cannot display the logistics information. In fact, you need to manually bind Pinduoduo to achieve this. The specific methods have been sorted out below, and everyone can take a look. . How to bind Cainiao to Pinduoduo account: 1. Open Cainiao APP and go to the main page



