The underlying implementation principle of mysql index
The data structure and algorithm principles behind MySQL index
1. Definition
Index definition: Index (Index) is to help MySQL be efficient Get the data structure of the data.
Essence: Index is a data structure.
2. B-Tree
m-order B-Tree satisfies the following conditions:
1. Each node can have at most m subtrees.
2. The root node only has at least 2 nodes (or in extreme cases, a tree has only one root node. A single-cell organism is a root, a leaf, and a tree).
3. Non-root and non-leaf nodes have at least Ceil (m/2) subtrees (Ceil means rounding up, such as a 5th-order B-tree. Each node has at least 3 subtrees, that is, there are at least 3 cross).
4. The information in non-leaf nodes includes [n,A0,K1,A1,K2,A2,…,Kn,An], where n represents the number of keywords saved in the node, and K is the keyword. And Ki
B-Tree characteristics:
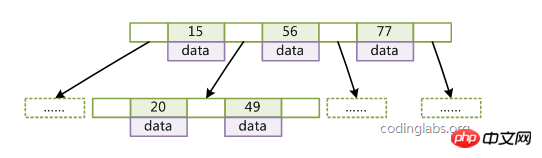
1. The keyword set is distributed throughout the tree;
2. Any keyword appears and only appears in one node;
3. Each node stores date and key;
4. The search may end at a non-leaf node;
5. The keys in a node are arranged non-decreasingly from left to right;
6. All leaf nodes have the same depth, which is equal to the tree height h.
The pseudo code of the search algorithm on B-Tree is as follows: 
3. B Tree

The difference between B Tree and B-Tree is:
1. B Tree non-leaf nodes do not store data, only keys;
2. All keywords are stored on leaf nodes;
3. Each leaf node contains a pointer to the adjacent leaf node. The B-tree with sequential access pointers improves the interval search capability;
4. Non-leaf nodes can be regarded as index parts, and the nodes only contain their children. The largest (or smallest) keyword in the tree (root node);
4. Performance analysis of B/B tree index
Based on: using disk I/O times evaluate the quality of the index structure
The main memory and disk exchange data in units of pages, and set the size of a node equal to one page, so each node can be fully loaded with only one I/O. .
According to the definition of B-tree, it can be seen that a maximum of h nodes need to be accessed for one retrieval
Asymptotic complexity: O(h)=O(logdN)
dmax=floor(pagesize/(keysize datasize pointsize))
In general practical applications, the out-degree d is a very large number, usually more than 100, so h is very small (usually no more than 3, and layer 3 can store about one million data)
B-Tree can retrieve the most at one time Requires h-1 I/O times (the root node is resident in memory)
The nodes in the B Tree do not contain the data domain, so the out-degree d is larger, the h is smaller, the number of I/Os is less, and the efficiency is higher, so B Tree is more suitable for external memory indexes.
5. MySQL index implementation
1. The MyISAM engine uses B Tree as the index structure. The data field of the leaf node stores the address of the data record;
MyISAM main index There is no structural difference from the auxiliary index, except that the primary index requires the key to be unique, while the key of the auxiliary index can be repeated;
2. The InnoDB data file itself is the index file, and the leaf node contains the complete Data records, this index is called a clustered index.
Because InnoDB's data files themselves are aggregated by primary key, InnoDB requires that the table must have a primary key (MyISAM may not have one). If not explicitly specified, the MySQL system will automatically select a column that can uniquely identify the data record as the primary key. If such a column does not exist, MySQL automatically generates an implicit field as the primary key for the InnoDB table.
InnoDB’s auxiliary index data field stores the value of the primary key of the corresponding record instead of the address;
The auxiliary index search needs to retrieve the index twice: first retrieve the auxiliary index to obtain the primary key, and then use the primary key to retrieve the record in the primary index;
3. Page splitting problem

If the primary key is monotonically increasing, each new record will be inserted into the page sequentially. When the page is full, continue Insert into a new page;
If writes are out of order, InnoDB has to frequently do page splitting operations to allocate space for new rows. Page splitting results in the movement of large amounts of data, requiring at least three pages to be modified instead of one for an insert.
If pages are split frequently, pages will become sparse and filled irregularly, so eventually the data will be fragmented.
6. Summary
Understanding the index implementation methods of different storage engines is very helpful for correct use and optimization of indexes
1. Why is it not recommended? Using a field that is too long as primary key?
2. Why choose an auto-increment field as the primary key?
3. Why is it not recommended to create an index for fields that are frequently updated?
4. Why choose a column with high distinction as an index? The formula of distinction is count(distinct col)/count(*)
5. Use covering index as much as possible
7. Optimize LIMIT paging query
SELECT * FROM table where condition LIMIT offset , rows ;
The implementation mechanism of the above SQL statement is:
1. Read offset rows row records from the "table" table.
2. Abandon the previous offset row record and return the subsequent rows row record as the final result.
Covered index:
select a.id, sid, parent_s_id from cashpool_account_relationship a join (select id from cashpool_account_relationship LIMIT 1000000,10)b on a.id = b.id; select id, sid, parent_s_id from cashpool_account_relationship where id >=(select id from cashpool_account_relationship LIMIT 1000000,1) LIMIT 10;
8. Q&A
1. Does InnoDB support hash index? --Ma Xin
InnoDB supports hash indexes, but the hash indexes it supports are adaptive. The InnoDB storage engine will automatically generate a hash index for the table based on the usage of the table, and human intervention is not allowed to generate hash in a table. index.
2. The leaf nodes of the InnoDB primary key index contain complete data records. Is the primary key index file larger than the data file? --Xu Caihou
1). In the Innodb engine, the leaf nodes in the primary key index contain record data, and the primary key index file is the data file.
2). The data_length data counted in the tables table is the primary key index size, and index_length is the counted size of all auxiliary indexes (secondary indexes) in this table. 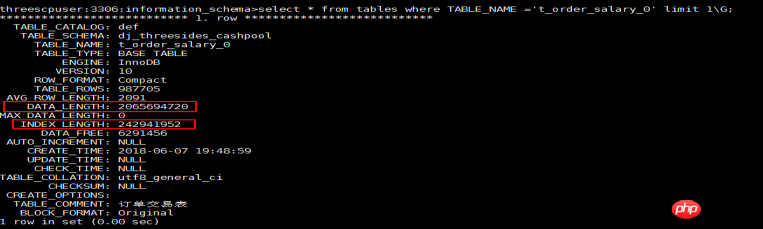
The above is the detailed content of The underlying implementation principle of mysql index. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Several situations of mysql index failure
Feb 21, 2024 pm 04:23 PM
Several situations of mysql index failure
Feb 21, 2024 pm 04:23 PM
Common situations: 1. Use functions or operations; 2. Implicit type conversion; 3. Use not equal to (!= or <>); 4. Use the LIKE operator and start with a wildcard; 5. OR conditions; 6. NULL Value; 7. Low index selectivity; 8. Leftmost prefix principle of composite index; 9. Optimizer decision; 10. FORCE INDEX and IGNORE INDEX.
 Under what circumstances will mysql index fail?
Aug 09, 2023 pm 03:38 PM
Under what circumstances will mysql index fail?
Aug 09, 2023 pm 03:38 PM
MySQL indexes will fail when querying without using index columns, mismatching data types, improper use of prefix indexes, using functions or expressions for querying, incorrect order of index columns, frequent data updates, and too many or too few indexes. . 1. Do not use index columns for queries. In order to avoid this situation, you should use appropriate index columns in the query; 2. Data types do not match. When designing the table structure, you should ensure that the index columns match the data types of the query; 3. , Improper use of prefix index, you can use prefix index.
 When might a full table scan be faster than using an index in MySQL?
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:05 AM
When might a full table scan be faster than using an index in MySQL?
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Full table scanning may be faster in MySQL than using indexes. Specific cases include: 1) the data volume is small; 2) when the query returns a large amount of data; 3) when the index column is not highly selective; 4) when the complex query. By analyzing query plans, optimizing indexes, avoiding over-index and regularly maintaining tables, you can make the best choices in practical applications.
 What are the classifications of mysql indexes?
Apr 22, 2024 pm 07:12 PM
What are the classifications of mysql indexes?
Apr 22, 2024 pm 07:12 PM
MySQL indexes are divided into the following types: 1. Ordinary index: matches value, range or prefix; 2. Unique index: ensures that the value is unique; 3. Primary key index: unique index of the primary key column; 4. Foreign key index: points to the primary key of another table ; 5. Full-text index: full-text search; 6. Hash index: equal match search; 7. Spatial index: geospatial search; 8. Composite index: search based on multiple columns.
 MySQL index left prefix matching rules
Feb 24, 2024 am 10:42 AM
MySQL index left prefix matching rules
Feb 24, 2024 am 10:42 AM
MySQL index leftmost principle principle and code examples In MySQL, indexing is one of the important means to improve query efficiency. Among them, the index leftmost principle is an important principle that we need to follow when using indexes to optimize queries. This article will introduce the principle of the leftmost principle of MySQL index and give some specific code examples. 1. The principle of index leftmost principle The index leftmost principle means that in an index, if the query condition is composed of multiple columns, then only the leftmost column in the index can be queried to fully satisfy the query conditions.
 Explain different types of MySQL indexes (B-Tree, Hash, Full-text, Spatial).
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
Explain different types of MySQL indexes (B-Tree, Hash, Full-text, Spatial).
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
MySQL supports four index types: B-Tree, Hash, Full-text, and Spatial. 1.B-Tree index is suitable for equal value search, range query and sorting. 2. Hash index is suitable for equal value searches, but does not support range query and sorting. 3. Full-text index is used for full-text search and is suitable for processing large amounts of text data. 4. Spatial index is used for geospatial data query and is suitable for GIS applications.
 How to use MySQL indexes rationally and optimize database performance? Design protocols that technical students need to know!
Sep 10, 2023 pm 03:16 PM
How to use MySQL indexes rationally and optimize database performance? Design protocols that technical students need to know!
Sep 10, 2023 pm 03:16 PM
How to use MySQL indexes rationally and optimize database performance? Design protocols that technical students need to know! Introduction: In today's Internet era, the amount of data continues to grow, and database performance optimization has become a very important topic. As one of the most popular relational databases, MySQL’s rational use of indexes is crucial to improving database performance. This article will introduce how to use MySQL indexes rationally, optimize database performance, and provide some design rules for technical students. 1. Why use indexes? An index is a data structure that uses
 Performance optimization strategies for data update and index maintenance of PHP and MySQL indexes and their impact on performance
Oct 15, 2023 pm 12:15 PM
Performance optimization strategies for data update and index maintenance of PHP and MySQL indexes and their impact on performance
Oct 15, 2023 pm 12:15 PM
Performance optimization strategies for data update and index maintenance of PHP and MySQL indexes and their impact on performance Summary: In the development of PHP and MySQL, indexes are an important tool for optimizing database query performance. This article will introduce the basic principles and usage of indexes, and explore the performance impact of indexes on data update and maintenance. At the same time, this article also provides some performance optimization strategies and specific code examples to help developers better understand and apply indexes. Basic principles and usage of indexes In MySQL, an index is a special number




