Analysis of angular component communication
This article mainly introduces the analysis of angular component communication, which has certain reference value. Now I share it with everyone. Friends in need can refer to it.
Single page application component communication has the following This article mainly talks about Angular communication
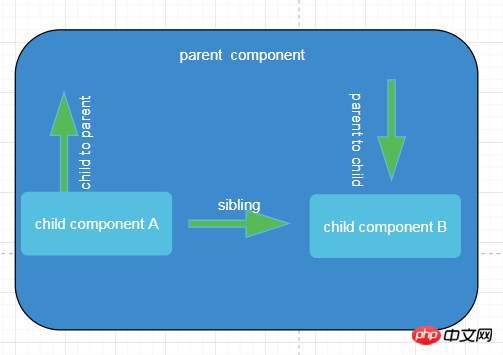
- ##Parent component=> Child component
- Child Component=> Parent Component ##Component A = > Component B
| sibling => sibling | ||
|---|---|---|
|
setters (essentially still @input) |
||
|
ngOnChanges() (deprecated) |
||
| # #Local variables |
||
|
service |
||
| Observalbe for Rxjs | Observalbe of Rxjs | |
| localStorage,sessionStorage | localStorage,sessionStorage | |
|
The above chart summarizes the communication solutions that can be used. The last three types in the period are universal. These three types can be used among Angular components. Among them, Rxjs is the most powerful usage, dumping redux. promise, these are also based on functional state management. , let’s talk about them one by one. Parent component=> Child component@input, the most commonly used method@Component({
selector: 'app-parent',
template: '<p>childText:<app-child></app-child></p>',
styleUrls: ['./parent.component.css']
})
export class ParentComponent implements OnInit {
varString: string;
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
this.varString = '从父组件传过来的' ;
}
}Copy after login import { Component, OnInit, Input } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-child',
template: '<h1 id="textContent">{{textContent}}</h1>',
styleUrls: ['./child.component.css']
})
export class ChildComponent implements OnInit {
@Input() public textContent: string ;
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
}
}Copy after login setterSetter is to intercept the @input attribute. Because when we communicate with components, we often need to process the input attributes, so we need a setter. Setter and getter are often used together. Slightly modify the above child.component.ts import { Component, OnInit, Input } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-child',
template: '<h1 id="textContent">{{textContent}}</h1>',
styleUrls: ['./child.component.css']
})
export class ChildComponent implements OnInit {
_textContent:string;
@Input()
set textContent(text: string){
this._textContent = !text: "啥都没有给我" ? text ;
} ;
get textContent(){
return this._textContent;
}
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
}
}Copy after login onChangeThis is detected through the angular life cycle hook. It is not recommended to use it. If you want to use it, you can Refer to angular documentation @ViewChild()@ViewChild() is generally used to call non-private methods of sub-components import {Component, OnInit, ViewChild} from '@angular/core';
import {ViewChildChildComponent} from "../view-child-child/view-child-child.component";
@Component({
selector: 'app-parent',
templateUrl: './parent.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./parent.component.css']
})
export class ParentComponent implements OnInit {
varString: string;
@ViewChild(ViewChildChildComponent)
viewChildChildComponent: ViewChildChildComponent;
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
this.varString = '从父组件传过来的' ;
}
clickEvent(clickEvent: any) {
console.log(clickEvent);
this.viewChildChildComponent.myName(clickEvent.value);
}
}Copy after login import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-view-child-child',
templateUrl: './view-child-child.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./view-child-child.component.css']
})
export class ViewChildChildComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
name: string;
myName(name: string) {
console.log(name);
this.name = name ;
}
ngOnInit() {
}
}Copy after login Local variablesLocal variables Similar to viewChild, it can only be used in html templates. Modify parent.component.html and use the variable <p> <input> <button>局部变量传值</button> <app-view-child-child></app-view-child-child> </p> Copy after login child component is as follows @Component({
selector: 'app-view-child-child',
templateUrl: './view-child-child.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./view-child-child.component.css']
})
export class ViewChildChildComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
name: string;
myName(name: string) {
console.log(name);
this.name = name ;
}
ngOnInit() {
}
}Copy after login Child component=> Parent component@output()Output, a common communication, essentially passes a # to the child component ##function parent.component.ts
@Component({
selector: 'app-child-to-parent',
templateUrl: './parent.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./parent.component.css']
})
export class ChildToParentComponent implements OnInit {
childName: string;
childNameForInject: string;
constructor( ) { }
ngOnInit() {
}
showChildName(name: string) {
this.childName = name;
}
}Copy after login <p>
</p><p>output方式 childText:{{childName}}</p>
<br>
<app-output-child></app-output-child>
Copy after login child.component.ts
export class OutputChildComponent implements OnInit {
// 传入的回调事件
@Output() public childNameEventEmitter: EventEmitter<any> = new EventEmitter();
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
}
showMyName(value) {
//这里就执行,父组件传入的函数
this.childNameEventEmitter.emit(value);
}
}</any>Copy after login export class OutputChildComponent implements OnInit {
// 注入父组件
constructor(private childToParentComponent: ChildToParentComponent) { }
ngOnInit() {
}
showMyName(value) {
this.childToParentComponent.childNameForInject = value;
}
}Copy after login . When you inject a service into a module, all the components of this module can get the properties and methods of this service. They are shared, so you often inject the log service in app.moudule.ts. , http interception service. The service injected in the sub-module can only be shared by this sub-module. The service injected in the component can only be obtained by the sub-component. The following is the service injected into app.module.ts. To demonstrate user.service.ts
@Injectable()
export class UserService {
age: number;
userName: string;
constructor() { }
}
app.module.ts
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
SiblingAComponent,
SiblingBComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule
],
providers: [UserService],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
SiblingBComponent.ts
@Component({
selector: 'app-sibling-b',
templateUrl: './sibling-b.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./sibling-b.component.css']
})
export class SiblingBComponent implements OnInit {
constructor(private userService: UserService) {
this.userService.userName = "王二";
}
ngOnInit() {
}
}
SiblingAComponent.ts
@Component({
selector: 'app-sibling-a',
templateUrl: './sibling-a.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./sibling-a.component.css']
})
export class SiblingAComponent implements OnInit {
userName: string;
constructor(private userService: UserService) {
}
ngOnInit() {
this.userName = this.userService.userName;
}
}Copy after login component, which is very cumbersome and has to be done once for each component. If it is based on Rx.js, you can put this in app.component.ts Prompt component, and then app.component.ts subscribes to the public service, which is easier. The code is as follows import {Injectable} from "@angular/core";
import {Subject} from "rxjs/Subject";
@Injectable()
export class AlertService {
private messageSu = new Subject<string>(); //
messageObserve = this.messageSu.asObservable();
private setMessage(message: string) {
this.messageSu.next(message);
}
public success(message: string, callback?: Function) {
this.setMessage(message);
callback();
}
}</string>Copy after login @Component({
selector: 'app-sibling-a',
templateUrl: './sibling-a.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./sibling-a.component.css']
})
export class SiblingAComponent implements OnInit {
userName: string;
constructor(private userService: UserService, private alertService: AlertService) {
}
ngOnInit() {
this.userName = this.userService.userName;
// 改变alertService的信息源
this.alertService.success("初始化成功");
}
}Copy after login @Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'app';
message: string;
constructor(private alertService: AlertService) {
//订阅alertServcie的message服务
this.alertService.messageObserve.subscribe((res: any) => {
this.message = res;
});
}
}Copy after login |
The above is the detailed content of Analysis of angular component communication. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
HTML defines the web structure, CSS is responsible for style and layout, and JavaScript gives dynamic interaction. The three perform their duties in web development and jointly build a colorful website.
 How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
There are two ways to create a Bootstrap split line: using the tag, which creates a horizontal split line. Use the CSS border property to create custom style split lines.
 Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WebdevelopmentreliesonHTML,CSS,andJavaScript:1)HTMLstructurescontent,2)CSSstylesit,and3)JavaScriptaddsinteractivity,formingthebasisofmodernwebexperiences.
 What Does H5 Refer To? Exploring the Context
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:03 AM
What Does H5 Refer To? Exploring the Context
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:03 AM
H5referstoHTML5,apivotaltechnologyinwebdevelopment.1)HTML5introducesnewelementsandAPIsforrich,dynamicwebapplications.2)Itsupportsmultimediawithoutplugins,enhancinguserexperienceacrossdevices.3)SemanticelementsimprovecontentstructureandSEO.4)H5'srespo
 How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
To set up the Bootstrap framework, you need to follow these steps: 1. Reference the Bootstrap file via CDN; 2. Download and host the file on your own server; 3. Include the Bootstrap file in HTML; 4. Compile Sass/Less as needed; 5. Import a custom file (optional). Once setup is complete, you can use Bootstrap's grid systems, components, and styles to create responsive websites and applications.
 How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
To adjust the size of elements in Bootstrap, you can use the dimension class, which includes: adjusting width: .col-, .w-, .mw-adjust height: .h-, .min-h-, .max-h-
 How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
There are several ways to insert images in Bootstrap: insert images directly, using the HTML img tag. With the Bootstrap image component, you can provide responsive images and more styles. Set the image size, use the img-fluid class to make the image adaptable. Set the border, using the img-bordered class. Set the rounded corners and use the img-rounded class. Set the shadow, use the shadow class. Resize and position the image, using CSS style. Using the background image, use the background-image CSS property.




