In-depth analysis of springCloud's Eureka practice
1. First introduction to springcloud
Microservices are an architectural approach that will ultimately require a technical architecture to be implemented.
There are many ways to implement microservices, but the most popular one is Spring Cloud
What Spring is best at is integration, taking the best frameworks in the world and integrating them into your own projects middle.
The same is true for Spring Cloud. It integrates some of the most popular technologies now and implements functions such as: configuration management, service discovery, intelligent routing, load balancing, fuses, control bus, cluster status and so on. Its main components include:
-
Eureka: Registration Center
- Zuul: Service Gateway
Ribbon: Load Balancing
Feign: Service Call
Hystix: fuse
Today we mainly get to know springcloud’s registration center Eureka
Here is an example in life:
Before the emergence of online ride-hailing, people could only call a taxi when going out. Some private cars want to be rented but are not qualified and are called black cars. Many people want to book a taxi, but unfortunately there are too few taxis and it is inconvenient. There are many private cars but they dare not stop them, and among the cars on the street, who knows which ones are willing to carry people. One wants and the other is willing to give, but there is a lack of introduction and management.
At this time, online ride-hailing platforms like Didi appeared. All private cars that want to carry passengers must register with Didi, and record your car model (service type) and identity information (contact information). Private cars that provide such services can be found on Didi, and they are clearly visible at a glance.
Anyone who wants to call a car at this time only needs to open the APP, enter your destination, select a car model (service type), and Didi will automatically arrange a car that meets your needs to serve you.
Back to springcloud’s Eureka, Eureka is like Didi, responsible for managing and recording service provider information. Service callers do not need to find services themselves, but tell Eureka their needs, and then Eureka will tell you the services that meet your needs. At the same time, the "heartbeat" mechanism is used to monitor the relationship between the service provider and Eureka. When a problem occurs with a service provider, Eureka will naturally remove it from the service list.
This realizes automatic registration, discovery, and status monitoring of services.
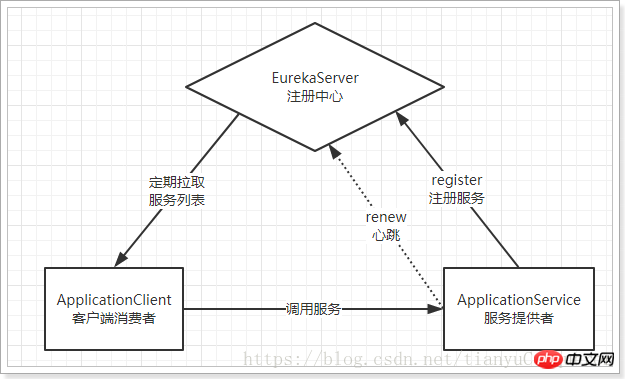
Eureka: It is the service registration center (can be a cluster), exposing its own address to the outside world
Provider: Register your own information with Eureka after startup ( address, what services are provided)
Consumer: Subscribe to Eureka for a service, Eureka will send a list of all provider addresses of the corresponding service to the consumer, and regularly update
heartbeat (renewal) : Providers regularly refresh their status to Eureka through http
Practice:
Eureka registration center structure chart:

<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.3.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Finchley.RELEASE</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer // 声明这个应用是一个EurekaServer
public class SpringcloudEurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringcloudEurekaServerApplication.class, args);
}
}server:
port: 8081 # 端口
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server # 应用名称,会在Eureka中显示
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: false # 是否注册自己的信息到EurekaServer,默认是true
fetch-registry: false # 是否拉取其它服务的信息,默认是true
service-url: # EurekaServer的地址,现在是自己的地址,如果是集群,需要加上其它Server的地址。
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:${server.port}/eurekaThe above is the detailed content of In-depth analysis of springCloud's Eureka practice. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Interview feedback Spring Cloud's 25-shot series
Aug 24, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
Interview feedback Spring Cloud's 25-shot series
Aug 24, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
Spring Cloud is currently quite popular, and it is almost one of the necessary skills for Java developers. It is normal to be asked this question during the interview. Many people may have used it for a long time but failed the interview without understanding the principles.
 Comparison and Selection Guide: Function Comparison of Spring Cloud and Spring Boot
Dec 29, 2023 pm 06:36 PM
Comparison and Selection Guide: Function Comparison of Spring Cloud and Spring Boot
Dec 29, 2023 pm 06:36 PM
SpringCloud and SpringBoot are currently the most popular open source frameworks in the Java field. They respectively provide a complete set of microservice architecture and solutions for quickly building applications. This article will compare their functions and give a selection guide to help readers understand their advantages and applicable scenarios. SpringBoot is a framework for developing Java applications. It provides a simplified development process and integrates a large number of commonly used functions and components, reducing the developer's workload.
 SpringCloud-Spring Boot Starter usage test instance analysis
May 16, 2023 am 11:10 AM
SpringCloud-Spring Boot Starter usage test instance analysis
May 16, 2023 am 11:10 AM
What is SpringBootStarter? SpringBootStarter is a concept proposed in the SpringBoot component, which simplifies many cumbersome configurations. By introducing various SpringBootStarter packages, you can quickly build the scaffolding of a project. For example, some of the ones we often use: spring-boot-starter-web: spring-boot-starter-data-redis: spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb: spring-boot-starter-data-jpa: spring-b
 What are the five core components of springcloud
Jun 12, 2023 pm 03:51 PM
What are the five core components of springcloud
Jun 12, 2023 pm 03:51 PM
The five core components of springcloud are: 1. Eureka, which implements service governance; 2. Ribbon, which provides client-side software load balancing algorithms; 3. Hystrix circuit breaker, which prevents an application from trying to perform an operation multiple times; 4. Zuul, which has an API Gateway, routing, load balancing and other functions; 5. Config, for configuration management.
 Comparison and analysis of the application methods of SpringCloud and SpringBoot in the field of microservices
Dec 29, 2023 pm 03:45 PM
Comparison and analysis of the application methods of SpringCloud and SpringBoot in the field of microservices
Dec 29, 2023 pm 03:45 PM
In recent years, with the rise of cloud computing and distributed architecture, the application of microservice architecture has become more and more widespread. As two important frameworks in Java development, Spring Cloud and Spring Boot play an important role in the implementation of microservices. However, many people still have some doubts about their different application methods in the field of microservices. This article will explore the application of Spring Cloud and Spring Boot in microservices from different perspectives. First, let’s learn about Spri
 Idea What are the common methods for springboot springCloud hot loading and hot debugging?
May 18, 2023 pm 05:43 PM
Idea What are the common methods for springboot springCloud hot loading and hot debugging?
May 18, 2023 pm 05:43 PM
Scenario Description During the project development process, when you need to modify and debug, you often need to restart the project every time, which wastes time. The following are two commonly used methods that I have compiled. One is to modify the startup configuration method (mainly for debug mode). Click Startup configuration=》editconfigrations...Modify Updateclassesandresourceson'update'action under configration: Update shortcut keys when the user actively performs updates: Ctrl+F9onframedeactication: When the edit window loses focus
 What is the difference between springcloud and springboot
Dec 28, 2023 pm 03:34 PM
What is the difference between springcloud and springboot
Dec 28, 2023 pm 03:34 PM
The difference between springcloud and springboot: 1. Function; 2. Usage; 3. Original intention of creation; 4. Purpose; 5. Integration; 6. Extensibility; 7. Complexity; 8. Community support; 9. Security; 10 , deployment and operation and maintenance. Detailed introduction: 1. Function. The main function of Spring Boot is to provide a quick way for microservice development, simplify configuration files, and improve work efficiency. Spring Cloud is a comprehensive management framework used to provide a comprehensive management framework for microservices. management framework, etc.
 The difference between SpringCloud and SpringBoot from an architectural perspective
Dec 29, 2023 pm 04:13 PM
The difference between SpringCloud and SpringBoot from an architectural perspective
Dec 29, 2023 pm 04:13 PM
The difference between Spring Cloud and Spring Boot from an architectural perspective Introduction: In today's Internet era, building a distributed system has become a necessary requirement. SpringBoot and SpringCloud were born to meet this need. Although they are both solutions provided by the Spring framework, there are some important differences from an architectural perspective. This article will start from an architectural perspective and analyze SpringBoot and SpringCl.





