 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 How does Laravel operate the database? Three ways to operate Laravel database (code)
How does Laravel operate the database? Three ways to operate Laravel database (code)
How does Laravel operate the database? Three ways to operate Laravel database (code)
Laravel is a PHP Web development framework (PHP Web Framework). It can free you from messy code; it can help you build a perfect network APP, and every line of code can be concise and expressive. So, how does the laravel framework operate the database? Please take a look at the specific content.
Laravel provides 3 ways to operate the database: DB facade (original way), query builder and Eloquent ORM.
#The database configuration file is in database.php in the config directory. Open this file and find the configuration items of mysql.
#There is an env here, which actually calls laravel The .env file in the root directory, this file stores Laravel database configuration information. Open it. Just modify it to the database information of the project.

1.
DB facade for database operations
# In app->Http->Controllers Create a newStudent controller, StudentController.php in the directory. StudentController.php code is as follows:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB;class StudentController extends Controller {
}1 .laravel database query Add a test1 method in the Student controller. The query uses the static method select() of the DB class, and the parameters are native sql statement, returns a two-dimensional array. dd() is a method provided by laravel, which can display an array in the form of a node tree. The specific code is as follows:
public function test1()
{
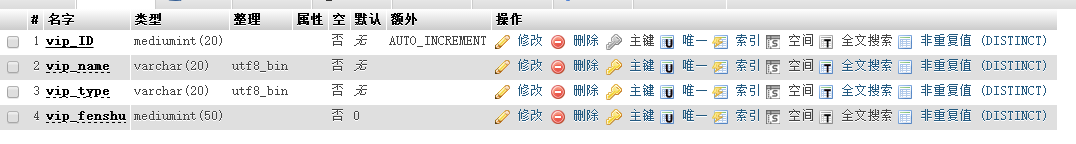
$student=DB::select("select * from vipinfo"); //返回一个二维数组
$student var_dump($student); //以节点树的形式输出结果
dd($student);
}Route::get('test1',['uses'=>'StudentController @test1']);
URL access: http://localhost/
aravel/public/index.php/test1 , will print out the result.
## 2. New operation
The newly used static method insert() of the DB class is used. The first parameter is the sql statement, and the second parameter is an array. The data to be inserted is placed in the array. here? It is a placeholder that prevents SQL injection through the database interface layer pdo. What is returned is the result of execution. Returns true if the insertion is successful, otherwise false.
##public function test1()
{
$student=DB::select("select * from vipinfo"); //返回一个二维数组
$student var_dump($student); //以节点树的形式输出结果
dd($student);
}
The update uses the static method update() of the DB class. The first parameter is the sql statement, and the second parameter is an array. The elements respectively correspond to the question marks in the sql statement. Returns true if the update is successful.
$bool=DB::update('update vipinfo set vip_fenshu= ? where vip_ID= ? ',[700,5]);
var_dump($bool); //更新成功返回true
删除使用的是DB类的静态方法delete(),第一个参数是sql语句,第二个参数是一个数组,数组里的元素分别对应sql语句里的问号。返回的是删除的行数。 二、数据库操作之查询构造器 laravel查询构造器提供了方便流畅的接口,用来建立及执行数据库查找语法。使用了pdo参数绑定,使应用程序免于sql注入,因此传入的参数不需要额外转义特殊字符。基本上可以满足所有的数据库操作,而且在所有支持的数据库系统上都可以执行。 1.使用查询构造器实现增删改查 同样在Student控制器里测试以下代码: (1)新增 (2)修改 (3)删除 (4)查询 2.使用聚合函数 四、数据库操作之 - Eloquent ORM 1.简介、模型的建立及查询数据 简介:laravel所自带的Eloquent ORM 是一个ActiveRecord实现,用于数据库操作。每个数据表都有一个与之对应的模型,用于数据表交互。 建立模型,在app目录下建立一个Student模型,即Student.php,不需要带任何后缀。 在Student控制器里增加一个test3方法,配置路由Route::get('test3',['uses'=>'StudentController@test3']); 2 . 新增数据、自定义时间戳、批量赋值 (1)使用save方法新增 laravel会默认维护created_at,updated_at 两个字段,这两个字段都是存储时间戳,整型11位的,因此使用时需要在数据库添加这两个字段。如果不需要这个功能,只需要在模型里加一个属性:public $timestamps=false; 以及一个方法,可以将当前时间戳存到数据库 这样就不需要那两个字段了。 控制器里写: 从数据库里取得某条记录的时间戳时,默认取得的是按日期格式化好的时间戳,如果想取得原本的时间戳,则在模型里增加asDateTime方法。 (2)使用create方法新增时,需要在模型里增加: 控制器里写: 这样即可新增成功! (3)firstOrCreate()以属性查找记录,若没有则新增 (4)firstOrNew()以属性查找记录,若没有则会创建新的实例。若需要保存,则自己调用save方法() 3. 修改数据 4. 删除数据 $num=DB::delete('delete from vipinfo where vip_ID= ?',[5]);
echo $num; $bool=DB::table("vipinfo")->insert(['vip_ID'=>6,'vip_name'=>'zls','vip_type'=>"出行",'vip_fenshu'=>800]);
echo $bool; //返回bool值
//如果想得到新增的id,则使用insertGetId方法
$id=DB::table("vipinfo")->insertGetId(['vip_ID'=>5,'vip_name'=>'wyp','vip_type'=>"出行",'vip_fenshu'=>800]);
echo $id;
//插入多条数据
$bool=DB::table("vipinfo")->insert([
['vip_ID'=>5,'vip_name'=>'wyp','vip_type'=>"出行",'vip_fenshu'=>800],
['vip_ID'=>6,'vip_name'=>'zls','vip_type'=>"出行",'vip_fenshu'=>800],
]);
echo $bool; //返回bool值
$bool=DB::table("vipinfo")->where('vip_ID',6)->update(['vip_fenshu'=>500]);
echo $bool;
//自增
$bool=DB::table("vipinfo")->where('vip_ID',6)->increment("vip_fenshu");//自增1
$bool=DB::table("vipinfo")->where('vip_ID',6)->increment("vip_fenshu",3);//自增3
echo $bool;
//自减
$bool=DB::table("vipinfo")->where('vip_ID',6)->decrement("vip_fenshu");//自1
$bool=DB::table("vipinfo")->where('vip_ID',6)->decrement("vip_fenshu",3);//自增3
echo $bool;
//自增时再修改其他字段
$bool=DB::table("vipinfo")->where('vip_ID',6)->increment("vip_fenshu",3,['vip_name'=>'dbdibi']);//自增3$num=DB::table("vipinfo")->where('vip_ID',6)->delete();//删除1条
$num=DB::table("vipinfo")->where('vip_ID','>',4)->delete();//删除多条
echo $num; //删除的行数
$num=DB::table("vipinfo")->truncate();//删除整表,不能恢复,谨慎使用//get()返回多条数据
$student=DB::table("vipinfo")->get();
var_dump($student);
//first()返回1条数据
$student=DB::table("vipinfo")->first(); //结果集第一条记录
$student=DB::table("vipinfo")->orderBy('vip_ID','desc')->first();//按vip_ID倒序排序
var_dump($student);
//where()条件查询
$student=DB::table("vipinfo")->where('vip_ID','>=',2)->get(); //一个条件
$student=DB::table("vipinfo")->whereRaw('vip_ID> ? and vip_fenshu >= ?',[2,300])->get(); //多个条件
dd($student);
//pluck()指定字段,后面不加get
$student=DB::table("vipinfo")->pluck('vip_name');
dd($student);
//lists()指定字段,可以指定某个字段作为下标
$student=DB::table("vipinfo")->lists('vip_name','vip_ID'); //指定vip_ID为下标
dd($student);
$student=DB::table("vipinfo")->lists('vip_name'); //不指定下标,默认下标从0开始
//select()指定某个字段
$student=DB::table("vipinfo")->select('vip_name','vip_ID')->get();
dd($student);
//chunk()每次查n条
$student=DB::table("vipinfo")->chunk(2,function($students){ //每次查2条
var_dump($students);
if(.......) return false; //在满足某个条件下使用return就不会再往下查了
});//count()统计记录条数$nums=DB::table("vipinfo")->count();
echo $nums;//max()某个字段的最大值,同理min是最小值$max=DB::table("vipinfo")->max("vip_fenshu");
echo $max;//avg()某个字段的平均值$avg=DB::table("vipinfo")->avg("vip_fenshu");
echo $avg;//sum()某个字段的和$sum=DB::table("vipinfo")->sum("vip_fenshu");
echo $sum;<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Student extends Model{
//指定表名
protected $table= 'vipinfo';
//指定主键
protected $primaryKey= 'vip_ID';
}public function test3(){// all()方法查询所有数据$studnets=Student::all();
dd($studnets);//find()查询一条,依据主键查询。findOrFail()查找不存在的记录时会抛出异常
$student=Student::find(5); //主键为5的记录
var_dump($student['attributes']);//查询构造器的使用,省略了指定表名
$student=Student::get();
var_dump($student);
} protected function getDateFormat(){
return time();
} $student=new Student(); //设定数据
$student->vip_name='xiaoming';
$student->vip_type='出行';
$student->vip_fenshu=900;
$bool=$student->save(); //保存
echo $bool; protected function asDateTime($val){
return $val;
}protected $fillable=['vip_name','vip_fenshu','vip_type']; //允许批量赋值的字段
Student::create(['vip_name'=>'mmm','vip_fenshu'=>999,'vip_type'=>'出行']);
$student=Student::firstOrCreate(['vip_name'=>'mmm']);
echo $student; $student=Student::firstOrNew(['vip_name'=>'mmm']);
$student->save();
echo $student; //通过模型更新数据
$student=Student::find(2);
$student->vip_fenshu=10000;
$student->save(); //返回bool值
//通过查询构造器更新
$num=Student::where('vip_ID','>',2)->update(['vip_fenshu'=>2000]);
echo $num; //返回更新的行数 //(1)通过模型删除数据
$student=Student::find(11);
$student->delete(); //返回bool值
//(2)通过主键删除
$num=Student::destroy(10); //删除主键为10的一条记录
echo $num; //返回删除的行数
$num=Student::destroy(10,5); //删除多条 或者$num=Student::destroy([10,5]);
echo $num; //返回删除的行数
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of How does Laravel operate the database? Three ways to operate Laravel database (code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Alipay PHP SDK transfer error: How to solve the problem of 'Cannot declare class SignData'?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:21 AM
Alipay PHP SDK transfer error: How to solve the problem of 'Cannot declare class SignData'?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:21 AM
Alipay PHP...
 Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JWT is an open standard based on JSON, used to securely transmit information between parties, mainly for identity authentication and information exchange. 1. JWT consists of three parts: Header, Payload and Signature. 2. The working principle of JWT includes three steps: generating JWT, verifying JWT and parsing Payload. 3. When using JWT for authentication in PHP, JWT can be generated and verified, and user role and permission information can be included in advanced usage. 4. Common errors include signature verification failure, token expiration, and payload oversized. Debugging skills include using debugging tools and logging. 5. Performance optimization and best practices include using appropriate signature algorithms, setting validity periods reasonably,
 Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.
Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PM
Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.
Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PM
Article discusses late static binding (LSB) in PHP, introduced in PHP 5.3, allowing runtime resolution of static method calls for more flexible inheritance.Main issue: LSB vs. traditional polymorphism; LSB's practical applications and potential perfo
 Framework Security Features: Protecting against vulnerabilities.
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:11 PM
Framework Security Features: Protecting against vulnerabilities.
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:11 PM
Article discusses essential security features in frameworks to protect against vulnerabilities, including input validation, authentication, and regular updates.
 Customizing/Extending Frameworks: How to add custom functionality.
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
Customizing/Extending Frameworks: How to add custom functionality.
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
The article discusses adding custom functionality to frameworks, focusing on understanding architecture, identifying extension points, and best practices for integration and debugging.
 How to send a POST request containing JSON data using PHP's cURL library?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to send a POST request containing JSON data using PHP's cURL library?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
Sending JSON data using PHP's cURL library In PHP development, it is often necessary to interact with external APIs. One of the common ways is to use cURL library to send POST�...
 Describe the SOLID principles and how they apply to PHP development.
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Describe the SOLID principles and how they apply to PHP development.
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The application of SOLID principle in PHP development includes: 1. Single responsibility principle (SRP): Each class is responsible for only one function. 2. Open and close principle (OCP): Changes are achieved through extension rather than modification. 3. Lisch's Substitution Principle (LSP): Subclasses can replace base classes without affecting program accuracy. 4. Interface isolation principle (ISP): Use fine-grained interfaces to avoid dependencies and unused methods. 5. Dependency inversion principle (DIP): High and low-level modules rely on abstraction and are implemented through dependency injection.
 What exactly is the non-blocking feature of ReactPHP? How to handle its blocking I/O operations?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
What exactly is the non-blocking feature of ReactPHP? How to handle its blocking I/O operations?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
An official introduction to the non-blocking feature of ReactPHP in-depth interpretation of ReactPHP's non-blocking feature has aroused many developers' questions: "ReactPHPisnon-blockingbydefault...



