What is a css selector? Summary of basic css selectors (nine types)
What is a css selector? The css selector specifies the tag that CSS should act on, and the name of that tag is the selector. Meaning: Which container to choose. Elements in HTML pages are controlled through CSS selectors. So, what are the css selectors? Let’s take a look at the commonly used selectors in css
1: css wildcard selector
The wildcard selector is represented by an asterisk (*), for example:
*{
font-size : 12px;
}means that the font size of all elements is 12px;
2: css group selector
When several elements have the same style attributes, you can Called together into a statement, elements are separated by commas. For example:
p, li {
line-height:20px;
color:#c00;
}
#main p, #sider span {
color:#000;
line-height:26px;
}Using the group selector will greatly simplify the CSS code. Elements with multiple identical attributes can be merged into groups for selection, and the same CSS attributes can be defined, which greatly improves coding efficiency. It also reduces the size of CSS files.
3: css tag selector
A complete HTML page is composed of many different tags, and the tag selector determines which tags use the corresponding CSS style, for example:
p{
color: red;
}This code will make all p tags turn red
4: css class selector
class The selector targets any element with the specified class name in the class attribute. The class selector starts with a "." symbol. For example:
.info {
color:black;
}This will change the color of all elements with the class name info. Is black
5:css ID selector
The ID selector can specify a specific style for the HTML element marked with a specific ID; the ID selector starts with a "# ” symbol begins. For example:
#demop{
color:#000;
}This means that the font color of the element with the id demop is set to black.
6: css pseudo-class selector
Sometimes it is necessary to apply the style of an element using other conditions outside the document, such as mouse hover, etc. At this time we need to use pseudo classes. The following is the pseudo-class definition for the linked application. For example:
a:link{
color:green ;
font-size: 50px
}
a:hover{
color:pink;
font-size: 50px
}
a:active{
color:yellow;
font-size: 50px
}
a:visited{
color:red;
font-size: 50px
}Effect:
The label is green when the web page is opened
The label is pink when the mouse is placed on the label
The label is yellow after clicking the label
The label is red after clicking .
7: css descendant selector
The descendant selector is used to select the descendants of a specific element or element group. The selection of the parent element is placed in front, and the selection of the child element is placed first. The selection of elements is placed at the end, separated by a space. There can be more than just two elements in the descendant selector. For multi-level ancestor-descendant relationships, there can be multiple spaces to separate them. For example, if there are three elements with IDs a, b, and c, the descendant selector can be written as #a In the form of #b #c{}, as long as the selection of ancestor elements is separated by spaces before and in the middle of descendant elements. For example:
#people em{
color: red;
}This rule sets the color of any em elements contained in elements with the ID value "people" to red.
8: css combined selector
can combine two or more types of selectors; for example:
p.info {
color:blue;
}It only Select paragraphs that belong to the info class. Other elements that belong to this class and other paragraphs that do not belong to the info class will be ignored.
9: css attribute selector
Format: Basic selector [attribute = 'attribute value']{ }, you can also just write attributes, for example:
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>属性选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
input[type = 'text'] {background-color: red}
input[type = 'password'] {background-color: pink}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form>
name:<input type = "text"><br/>
pass:<input type = "password">
</form>
</body>
</html>Run results: 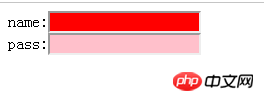
css selector priority size:
!important > Interline style>ID selection Selector> Class|Attribute Selector> Tag> Wildcard> Inheritance> Browser Default Attribute
When there are some complex selectors that cannot be selected by the priority size ratio, then we will use it Weight calculation
css selector weight calculation:
| Infinity |
Interline Style |
| ID Selector | |
| Class|Attribute|Pseudo-class selector | |
| Tag selector | |
| Wildcard Selector
| 0
Convert all selectors on each line into these values and add them up. The larger the result, the higher the priority! Recommended related articles: css class Selectors and id selectors Related course recommendations: |
The above is the detailed content of What is a css selector? Summary of basic css selectors (nine types). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How to resize HTML textbox
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:03 AM
How to resize HTML textbox
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:03 AM
Setting the size of HTML text boxes is a very common operation in front-end development. This article explains how to set the size of a text box and provides specific code examples. In HTML, you can use CSS to set the size of a text box. The specific code is as follows: input[type="text"
 How to adjust a WordPress theme to avoid misaligned display
Mar 05, 2024 pm 02:03 PM
How to adjust a WordPress theme to avoid misaligned display
Mar 05, 2024 pm 02:03 PM
How to adjust WordPress themes to avoid misaligned display requires specific code examples. As a powerful CMS system, WordPress is loved by many website developers and webmasters. However, when using WordPress to create a website, you often encounter the problem of theme misalignment, which affects the user experience and page beauty. Therefore, it is very important to properly adjust your WordPress theme to avoid misaligned display. This article will introduce how to adjust the theme through specific code examples.
 What are the elements in the excluded section of css selector
Apr 06, 2024 am 02:42 AM
What are the elements in the excluded section of css selector
Apr 06, 2024 am 02:42 AM
The :not() selector can be used to exclude elements under certain conditions, and its syntax is :not(selector) {style rule}. Examples: :not(p) excludes all non-paragraph elements, li:not(.active) excludes inactive list items, :not(table) excludes non-table elements, div:not([data-role="primary"]) Exclude div elements with non-primary roles.
 What is css selector priority
Apr 25, 2024 pm 05:30 PM
What is css selector priority
Apr 25, 2024 pm 05:30 PM
CSS selector priority is determined in the following order: Specificity (ID > Class > Type > Wildcard) Source order (Inline > Internal style sheet > External style sheet > User agent style sheet) Declaration order (latest declarations take precedence) Importance (!important forces the priority to increase)
 css selectors which are advanced selectors
Oct 07, 2023 pm 02:59 PM
css selectors which are advanced selectors
Oct 07, 2023 pm 02:59 PM
Advanced selectors in CSS selectors include descendant selectors, child element selectors, adjacent sibling selectors, universal sibling selectors, attribute selectors, class selectors, ID selectors, pseudo-class selectors and pseudo-element selectors wait. Detailed introduction: 1. The descendant selector uses a space-separated selector to select the descendant elements of an element; 2. The child element selector uses a selector separated by a greater than sign to select the direct child elements of an element; 3. Adjacent sibling selectors use selectors separated by a plus sign to select the first sibling element immediately following an element, and so on.
 What exactly does H5 page production mean?
Apr 06, 2025 am 07:18 AM
What exactly does H5 page production mean?
Apr 06, 2025 am 07:18 AM
H5 page production refers to the creation of cross-platform compatible web pages using technologies such as HTML5, CSS3 and JavaScript. Its core lies in the browser's parsing code, rendering structure, style and interactive functions. Common technologies include animation effects, responsive design, and data interaction. To avoid errors, developers should be debugged; performance optimization and best practices include image format optimization, request reduction and code specifications, etc. to improve loading speed and code quality.
 Get a deep understanding of the weight and precedence of CSS selector wildcards
Dec 26, 2023 pm 01:36 PM
Get a deep understanding of the weight and precedence of CSS selector wildcards
Dec 26, 2023 pm 01:36 PM
In-depth understanding of the weight and priority of CSS selector wildcards In CSS style sheets, selectors are an important tool for specifying which HTML elements the style applies to. The selector's priority and weight determine which style is applied when multiple rules apply to an HTML element at the same time. Wildcard selectors are a common selector in CSS. It is represented by the "*" symbol, which means it matches all HTML elements. Wildcard selectors are simple but can be very useful in certain situations. However, the weight and precedence of wildcard selectors also
 Learn the basic syntax of using CSS selectors
Jan 13, 2024 am 11:44 AM
Learn the basic syntax of using CSS selectors
Jan 13, 2024 am 11:44 AM
To master basic CSS selector syntax, specific code examples are required. CSS selectors are a very important part of front-end development. They can be used to select and modify various elements of HTML documents. Mastering basic CSS selector syntax is crucial to writing efficient stylesheets. This article will introduce some common CSS selectors and corresponding code examples. Element selector The element selector is the most basic selector, which can select the corresponding element by its tag name. For example, to select all paragraphs (p elements), you can use




