 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Java implements mongodb, generic encapsulation, addition, deletion, query, modification, conditional query and other operations
Java implements mongodb, generic encapsulation, addition, deletion, query, modification, conditional query and other operations
Java implements mongodb, generic encapsulation, addition, deletion, query, modification, conditional query and other operations
This article implements a general generic encapsulation implementation class, which requires a given collection object, similar to the table corresponding to java in mysql; the idea is to parse out all non-null fields of the given object and save them into a BasicDBObject, here Be sure to ensure that the java object has the same name as the document field in mongodb, because in order to achieve universality, the code defaults to the query field of the java object as the BasicDBObject.
Core code 1: This is to convert java objects into query conditions.
/**
* 通过反射获取非空字段信息
* @param record
* @param <Q>
* @return
*/
private <Q> BasicDBObject getCondition(Q record) {
BasicDBObject cond = new BasicDBObject();
Class clazz = record.getClass();
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
Object value = field.get(record);
if (value != null)
cond.put(field.getName(), value);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return cond;
}Core code 2: This is to convert the queried document into a java object. Here, the fields of the default java object are the same as the fields of the database document. All fields of the user-defined object are dynamically obtained using java reflection. , and then perform the assignment. I judged the int and long types separately during the assignment process, because when inserting into mongodb, it is usually stored as double, which will cause a transformation error.
/**
* 将结果转化为自定义对象
* @param document
* @param target
* @param <Q>
* @return
*/
private <Q> Q parseToObject(Document document, Class<Q> target) {
try {
Q result = target.newInstance();
Field[] fields = target.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : fields) {
f.setAccessible(true);
Object value = document.get(f.getName());
if (value == null)
continue;
else if (f.getType() == Integer.class)
f.set(result, ((Number) value).intValue());
else if (f.getType() == Long.class)
f.set(result, ((Number) value).longValue());
else
f.set(result, document.get(f.getName(), f.getType()));
}
return result;
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}Calling method: First convert the query parameters. When querying, id is used to determine the positive and negative order, so there must be an id identification field in the default database.
public <Q> List<Q> queryByCondition(BaseQuery<Q> query,boolean up) {
Q record = query.getQuery();
BasicDBObject cond = getCondition(record);
FindIterable<Document> findIterable;
if (query.getStart() != null && query.getRows() != null)
findIterable = thisCollection().find(cond)
.sort(new BasicDBObject("id", up ? 1 : -1))
.skip((query.getStart() - 1) * query.getRows())
.limit(query.getRows());
else
findIterable = thisCollection().find(cond)
.sort(new BasicDBObject("id", up ? 1 : -1));
MongoCursor<Document> iterator = findIterable.iterator();
List<Q> result = new ArrayList<>();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Document document = iterator.next();
result.add((Q) parseToObject(document, record.getClass()));
}
iterator.close();
return result;
}The BaseQuery passed in here is as follows: the query inside is a java object that needs to be queried, and start&rows is used for paging. The lombok plug-in is used here, which simplifies a lot of gettter&setter and other codes.
@Setter
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public class BaseQuery<Q> {
private Integer start;
private Integer rows;
private Q query;
public BaseQuery(Class clazz) {
try {
this.query = (Q) clazz.newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Test condition query method: The entities used here are as follows:
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Accessors(chain = true)
public class User_info {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Integer role;
}public static void main(String[] args) {
User_info record = new User_info();
BaseQuery<User_info> query = new BaseQuery<>();
query.setQuery(record);
BaseMongoDao dao = new BaseMongoDao("test");
List<User_info> result = dao.queryByCondition(query, true);
for (User_info user : result) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}Because the query conditions used here are empty, all items in the database will be matched:
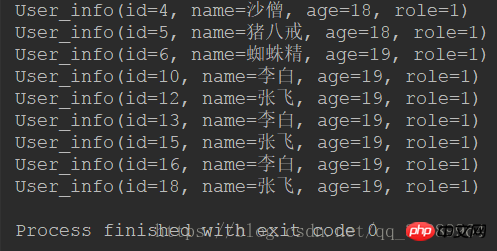
Now test the data with permission set to 1:
public static void main(String[] args) {
User_info record = new User_info();
record.setRole(1);
BaseQuery<User_info> query = new BaseQuery<>();
query.setQuery(record);
BaseMongoDao dao = new BaseMongoDao("test");
List<User_info> result = dao.queryByCondition(query, true);
for (User_info user : result) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}Output:

This conditional query method is an example , other deletions, additions, and modifications are all based on this principle, as follows:
1.public List
queryByCondition(BaseQuery
query,boolean up)
2.public Integer queryCoditionCount(BaseQuery
query)
3.public boolean insertOne(Q record)
4.public boolean insertList(List
records)
5.public boolean deleteById(Integer id)
6.public boolean deleteByIds(List
7.public void updateById(Q record)
Put all the code:
package cn.wzy.dao;
import com.mongodb.*;
import com.mongodb.client.FindIterable;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCursor;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import org.bson.Document;
import org.cn.wzy.query.BaseQuery;
import org.cn.wzy.util.PropertiesUtil;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Create by Wzy
* on 2018/7/28 18:15
* 不短不长八字刚好
*/
public class BaseMongoDao {
private static final MongoClient mongoClient;
private static final MongoDatabase mongo;
static {
MongoClientOptions options = MongoClientOptions.builder()
.connectionsPerHost(150)
.maxWaitTime(2000)
.socketTimeout(2000)
.maxConnectionLifeTime(5000)
.connectTimeout(5000).build();
ServerAddress serverAddress = new ServerAddress(PropertiesUtil.StringValue("mongo.host"),
PropertiesUtil.IntegerValue("mongo.port"));
List addrs = new ArrayList<>();
addrs.add(serverAddress);
MongoCredential credential = MongoCredential.createScramSha1Credential(
PropertiesUtil.StringValue("mongo.user")
, PropertiesUtil.StringValue("mongo.db")
, PropertiesUtil.StringValue("mongo.pwd").toCharArray());
mongoClient = new MongoClient(addrs, credential, options);
mongo = mongoClient.getDatabase(PropertiesUtil.StringValue("mongo.db"));
}
public BaseMongoDao(String colName) {
this.colName = colName;
}
private String colName;
private MongoCollection thisCollection() {
return mongo.getCollection(colName);
}
public <Q> List<Q> queryByCondition(BaseQuery<Q> query,boolean up) {
Q record = query.getQuery();
BasicDBObject cond = getCondition(record);
FindIterable<Document> findIterable;
if (query.getStart() != null && query.getRows() != null)
findIterable = thisCollection().find(cond)
.sort(new BasicDBObject("id", up ? 1 : -1))
.skip((query.getStart() - 1) * query.getRows())
.limit(query.getRows());
else
findIterable = thisCollection().find(cond)
.sort(new BasicDBObject("id", up ? 1 : -1));
MongoCursor<Document> iterator = findIterable.iterator();
List<Q> result = new ArrayList<>();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Document document = iterator.next();
result.add((Q) parseToObject(document, record.getClass()));
}
iterator.close();
return result;
}
public Integer queryCoditionCount(BaseQuery query) {
Q record = query.getQuery();
BasicDBObject cond = getCondition(record);
return (int) thisCollection().countDocuments(cond);
}
public boolean insertOne(Q record) {
BasicDBObject cond = getCondition(record);
try {
int top = getTop();
cond.put("id",++top);
thisCollection().insertOne(new Document(cond));
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
public boolean insertList(List records) {
try {
List list = new ArrayList<>(records.size());
if (!changeIds(records))
return false;
for (Q record : records) {
list.add(new Document(getCondition(record)));
}
thisCollection().insertMany(list);
return true;
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
public boolean deleteById(Integer id) {
try {
if (id == null)
return false;
thisCollection().deleteOne(new BasicDBObject("id",id));
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
public boolean deleteByIds(List ids) {
BasicDBObject cond = new BasicDBObject("id",new BasicDBObject("$in",ids.toArray()));
try {
thisCollection().deleteMany(cond);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 只通过id更改,查询就只是搜索id
* @param record
* @param
*/
public void updateById(Q record) {
BasicDBObject cond = getCondition(record);
BasicDBObject update = new BasicDBObject("$set",cond);
BasicDBObject query = new BasicDBObject("id",cond.get("id"));
thisCollection().updateOne(query,update);
}
/**
* 通过反射获取非空字段信息
* @param record
* @param <Q>
* @return
*/
private <Q> BasicDBObject getCondition(Q record) {
BasicDBObject cond = new BasicDBObject();
Class clazz = record.getClass();
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
Object value = field.get(record);
if (value != null)
cond.put(field.getName(), value);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return cond;
}
/**
* 将结果转化为自定义对象
* @param document
* @param target
* @param <Q>
* @return
*/
private <Q> Q parseToObject(Document document, Class<Q> target) {
try {
Q result = target.newInstance();
Field[] fields = target.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : fields) {
f.setAccessible(true);
Object value = document.get(f.getName());
if (value == null)
continue;
else if (f.getType() == Integer.class)
f.set(result, ((Number) value).intValue());
else if (f.getType() == Long.class)
f.set(result, ((Number) value).longValue());
else
f.set(result, document.get(f.getName(), f.getType()));
}
return result;
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 使id自增
* @param records
* @param
* @return
*/
private boolean changeIds(List records) {
if (records == null || records.size() == 0)
return false;
Class clazz = records.get(0).getClass();
try {
Field id = clazz.getDeclaredField("id");
id.setAccessible(true);
int top = getTop();
for (Q record: records) {
id.set(record,++top);
}
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 查找顶针
* @return
*/
private int getTop() {
return ((Number) thisCollection().find().sort(new BasicDBObject("id",-1)).first().get("id")).intValue();
}
}
Related articles:
java operation mongodb: basic addition, deletion, modification and query
MongoDB (6) java operation mongodb addition, deletion, modification and query
Related videos:
Black Horse Cloud Classroom mongodb practical video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Java implements mongodb, generic encapsulation, addition, deletion, query, modification, conditional query and other operations. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to correctly divide business logic and non-business logic in hierarchical architecture in back-end development?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to correctly divide business logic and non-business logic in hierarchical architecture in back-end development?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
Discussing the hierarchical architecture problem in back-end development. In back-end development, common hierarchical architectures include controller, service and dao...
 In back-end development, how to distinguish the responsibilities of the service layer and the dao layer?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 01:51 PM
In back-end development, how to distinguish the responsibilities of the service layer and the dao layer?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 01:51 PM
Discussing the hierarchical architecture in back-end development. In back-end development, hierarchical architecture is a common design pattern, usually including controller, service and dao three layers...
 In Java remote debugging, how to correctly obtain constant values on remote servers?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
In Java remote debugging, how to correctly obtain constant values on remote servers?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
Questions and Answers about constant acquisition in Java Remote Debugging When using Java for remote debugging, many developers may encounter some difficult phenomena. It...
 How to convert names to numbers to implement sorting within groups?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 01:57 PM
How to convert names to numbers to implement sorting within groups?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 01:57 PM
How to convert names to numbers to implement sorting within groups? When sorting users in groups, it is often necessary to convert the user's name into numbers so that it can be different...
 How to restrict access to specific interfaces of nested H5 pages through OAuth2.0's scope mechanism?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 02:30 PM
How to restrict access to specific interfaces of nested H5 pages through OAuth2.0's scope mechanism?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 02:30 PM
How to use OAuth2.0's access_token to achieve control of interface access permissions? In the application of OAuth2.0, how to ensure that the...
 How to choose Java project management tools when learning back-end development?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 02:15 PM
How to choose Java project management tools when learning back-end development?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 02:15 PM
Confused with choosing Java project management tools for beginners. For those who are just beginning to learn backend development, choosing the right project management tools is crucial...
 Ultimate consistency in distributed systems: how to apply and how to compensate for data inconsistencies?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 02:24 PM
Ultimate consistency in distributed systems: how to apply and how to compensate for data inconsistencies?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 02:24 PM
Exploring the application of ultimate consistency in distributed systems Distributed transaction processing has always been a problem in distributed system architecture. To solve the problem...
 How to analyze the cracking process of IntelliJ IDEA and find the lib or class responsible for registration?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 04:00 PM
How to analyze the cracking process of IntelliJ IDEA and find the lib or class responsible for registration?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 04:00 PM
Regarding the analysis method of IntelliJIDEA cracking in the programming world, IntelliJ...



