 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 About IO streams in Java: stream inheritance relationships, processing streams, and conversion streams
About IO streams in Java: stream inheritance relationships, processing streams, and conversion streams
About IO streams in Java: stream inheritance relationships, processing streams, and conversion streams
1. The inheritance relationship of streams, as well as byte streams and character streams.
2. Node streams FileOutputStream and FileInputStream and processing streams BufferedInputStream and BufferedOutputStream. And the corresponding FileOutputWriter, FileInputReader, BufferedInputReader, BufferedOutputWriter.
3. Convert streams InputStreamReader and OutputStreamWriter
1: Stream inheritance relationship
Byte stream
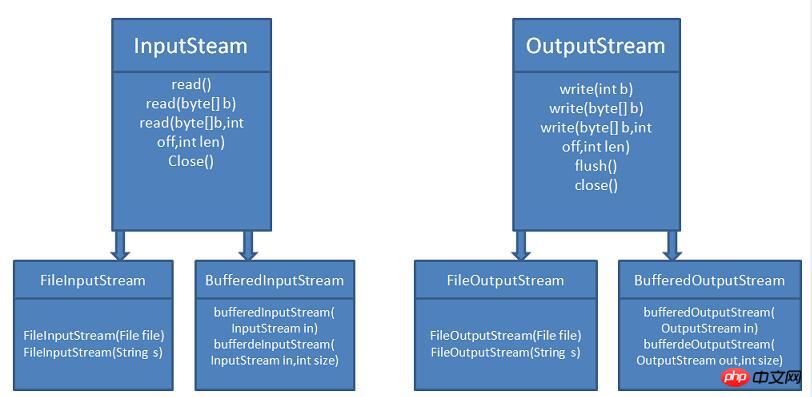
Character stream
Usage scope of character stream and byte stream: Byte stream is generally used to process images, videos, and PPT, Word type files . Character streams are generally used to process plain text files, such as TXT files, etc. Byte streams can be used to process plain text files, but character streams cannot be used to process non-text files such as images and videos.
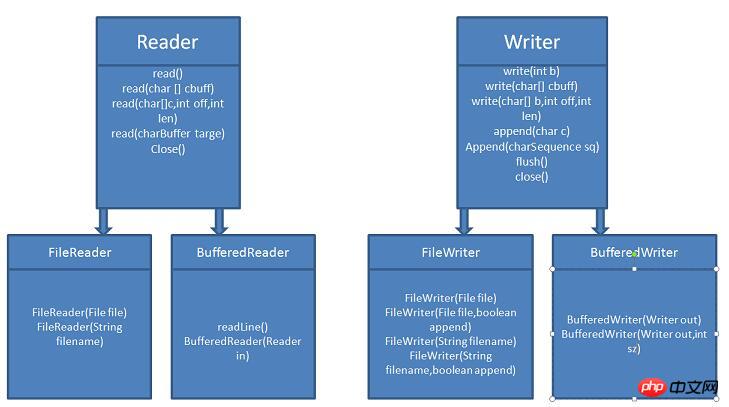
2: Processing streams BufferedReader, BufferedWriter, BufferedInputStream
BufferedOutputsStream must include the upper layer of node streams. In other words, the processing stream is based on the node stream. The stream with Buffered is also called a buffered stream. The buffered stream processes the input and output of files the fastest. Therefore, buffered streams are generally used more frequently.
The following are two simple examples of file copying:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 twenty one twenty two twenty three twenty four 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 |
|
Three: Conversion stream InputStreamReader and OutputStreamWriter
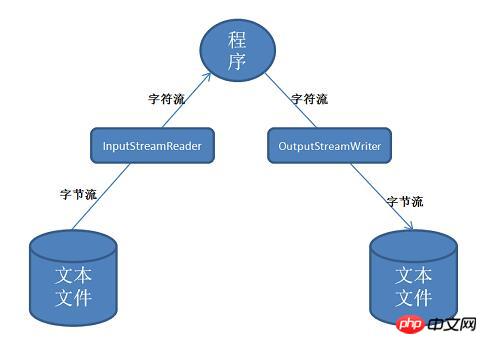
The role of conversion stream, when the text file is stored in the form of byte stream on the hard disk, After reading through InputStreamReader, it is converted into a character stream for processing by the program. The character stream processed by the program is converted into a byte stream through OutputStreamWriter and saved.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 twenty one twenty two twenty three twenty four 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
|
Related articles:
Java IO stream output stream OutputString() use
Java's comprehensive introduction to IO stream
Related videos:
The latest Java complete video tutorial-free online video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of About IO streams in Java: stream inheritance relationships, processing streams, and conversion streams. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How does Java's classloading mechanism work, including different classloaders and their delegation models?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:35 PM
How does Java's classloading mechanism work, including different classloaders and their delegation models?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:35 PM
Java's classloading involves loading, linking, and initializing classes using a hierarchical system with Bootstrap, Extension, and Application classloaders. The parent delegation model ensures core classes are loaded first, affecting custom class loa
 How do I implement multi-level caching in Java applications using libraries like Caffeine or Guava Cache?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:44 PM
How do I implement multi-level caching in Java applications using libraries like Caffeine or Guava Cache?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:44 PM
The article discusses implementing multi-level caching in Java using Caffeine and Guava Cache to enhance application performance. It covers setup, integration, and performance benefits, along with configuration and eviction policy management best pra
 How can I use JPA (Java Persistence API) for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:43 PM
How can I use JPA (Java Persistence API) for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:43 PM
The article discusses using JPA for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading. It covers setup, entity mapping, and best practices for optimizing performance while highlighting potential pitfalls.[159 characters]
 How do I use Maven or Gradle for advanced Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:46 PM
How do I use Maven or Gradle for advanced Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:46 PM
The article discusses using Maven and Gradle for Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution, comparing their approaches and optimization strategies.
 How do I create and use custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
How do I create and use custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
The article discusses creating and using custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management, using tools like Maven and Gradle.



