
boolThe Boolean type in C
Note:
C adds
bool# on top of the basic type system of C language.- ##The only possible values for
bool
in C aretrueandfalse- Theoretically
bool
occupies one bytetrue
represents the true value, The compiler internally uses 1 to representfalse
In C language: is represented by an integer Type value replaces therepresents a non-true value, and the compiler internally uses 0 to representbool
##C has made type enhancements and added a very rigoroustype, commonly used0:flase, 1:true
type, true and false exist as keywords. In the Boolean type of C, the
type only has two values: true and false. The C compiler will convert non-0 values is true, a value of 0 is converted to false. <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>bool b = 0;
printf("b = %d\n", b);
b++;
printf("b = %d\n", b);
b = b - 3;
printf("b = %d\n", b);
// bool类型是否支持数学运算?</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>In fact, in C language, the internal implementation of the Boolean type is implemented as a byte integer. The
type supports mathematical operations, and the compiler will make adjustments internally. Non-0 is true, 0 is false#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
bool b = false;
int a = b;
printf("sizeof(b) = %d\n", sizeof(b));
// sizeof(b) = 1, bool类型占一个字节
printf("b = %d, a = %d\n", b, a); 0
// b = 0, a = 0
b = 3; // b = 1
a = b; // a = 1
printf("b = %d, a = %d\n", b, a);
b = -5; // b = 1
a = b; // a = 1
printf("b = %d, a = %d\n", b, a);
a = 10; // a = 10
b = a; // b = 1
printf("a = %d, b = %d\n", a, b);
a = 0; // a = 0
b = a; // b = 0
printf("a = %d, b = %d\n", a, b);
return 0;
}The ternary operator has been upgraded in CConsider whether the following code is correct, respectively in C language and C Compile and run the test in the environmentcan be defined Global variables of type
- bool
can be defined# Constants of type
- bool
can be defined# A pointer of type ##bool
- bool
can define an array of type
- 2. Ternary operator
......
int a = 1;
int b =2;
(a < b ? a : b) = 3;
printf("a = %d, b = %d\n", a, b);
// 在C语言中报错
// 在C++中,结果a = 3Ternary operator
The ternary operator in C language returns the variable valueWhen all possible returns of the ternary operator are variables,Possible values returned by the ternary operator If one of them is a constant value, it cannot be used as an lvalue.The ternary operator can only be used as an lvalue when all possible returns are variables. A constant and a variable cannot be used as an lvalue. What is the significance of such an upgrade to the ternary operator using
- cannot be used as an lvalue
- #The ternary operator in C can directly return the variable itself
- Can be used as both an rvalue and an lvalue
- Note:
C?
returns the variable itself
, which leads to a new concept: Quote3, Quote
3.1 Variable nameA variable is an alias for an actual continuous storage space. In the program, the storage space is applied for and named through variables. The storage space can be used through the name of the variable. Question: Can a continuous storage space have only one alias?
3.2 Reference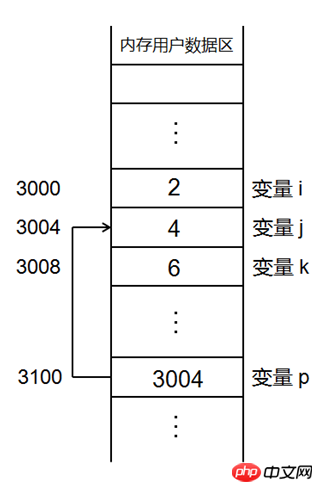
The concept of reference is added in COrdinary references must be initialized with variables of the same type when they are defined. What does C do with the ternary operator?
int a = 4; int& b = a; // b作为a的别名 b = 5; // 操作b就是操作aCopy after login- The reference can be regarded as an alias of a defined variable
- The syntax of the reference:
Type& name = var;- Note:
int a = 1; int b = 2; (a < b ? a : b) = 3; // ok,返回a或b的引用,可作为左值 (a < b ? 1 : b) = 4; // err,返回1或b的值,不能作为左值Copy after login- When the possible returns of the ternary operator are all variables, what is returned is
variable reference
4. Summary# The ##bool- value is returned
When there is a constant in the possible return of the ternary operator, the
type is a newly added basic type of C. The values of the
boolphp boolean (Boolean) type usage exampletype can only betrueand
falseThe ternary operator in C can be used as an lvalueReferences in C can be used as aliases of variablesThe possible returns of the ternary operator are all variables When, the reference is returned
Related articles:PHP Boolean Type data type false true usage introduction
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the usage of C++ Boolean types and references. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 What are the differences between c++ and c language
What are the differences between c++ and c language
 Recommended learning order for c++ and python
Recommended learning order for c++ and python
 Cost-effectiveness analysis of learning python and c++
Cost-effectiveness analysis of learning python and c++
 Is c language the same as c++?
Is c language the same as c++?
 Which is better to learn first, c language or c++?
Which is better to learn first, c language or c++?
 The difference and connection between c language and c++
The difference and connection between c language and c++
 C++ software Chinese change tutorial
C++ software Chinese change tutorial
 Cost-effectiveness analysis of learning python, java and c++
Cost-effectiveness analysis of learning python, java and c++




