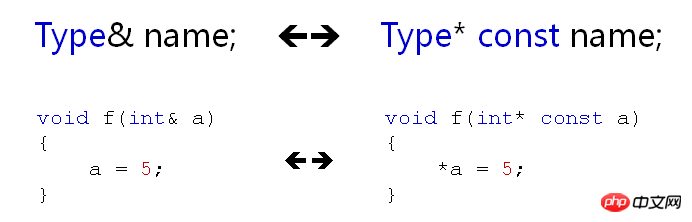
The meaning of C++ references and the nature of references
1. The meaning of reference
References exist as variable alias, so they can replace pointers on some occasions. References are more readable and practical than pointers. Property
// swap函数的实现对比
void swap(int& a, int& b)
{
int t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}Note:The reference parameters in the function do not need to be initialized. The initialization is completed when calling
2. Special references
const reference
In C, you can declare a const reference. The specific usage is as follows:
const Type& name = var;
constReference let The variable has a read-only attribute. This read-only attribute is for the current alias. The variable can be modified in other ways.
int a = 4; // a是一个变量
const int & b = a; // b是a的一个引用,但是b具有只读属性
int * p = (int *)&b; // p = &a
b = 5; // err, 引用b 被const修饰,b是一个只读变量
a = 6; // ok
printf("a = %d\n", a);
*p = 5; // ok
printf("a = %d\n", a);When a constant is used to initialize a const reference, C compiler The processor will allocate space for the constant value and use the reference name as an alias for this space
#include <stdio.h>
void Example()
{
printf("Example:\n");
int a = 4;
const int& b = a;
int* p = (int*)&b;
//b = 5; // b
*p = 5;
printf("a = %d\n", a);
printf("b = %d\n", b);
}
void Demo()
{
printf("Demo:\n");
const int& c = 1;
int* p = (int*)&c;
//c = 5;
*p = 5;
printf("c = %d\n", c);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Example();
printf("\n");
Demo();
return 0;
}Conclusion:Using a constant pair
constAfter initializing the reference, a read-only variable will be generated
Question: Do references have their own storage space?
struct TRef
{
char& r;
}
printf("sizeof(TRef) = %d\n, sizeof(TRef));Verification program:
#include <stdio.h>
struct TRef
{
char& r; // 字符类型引用
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char c = 'c';
char & rc = c;
TRef ref = { c }; // 用C进行初始化, TRef.r 就是 c的别名了
printf("sizeof(char&) = %d\n", sizeof(char&)); // char引用的大小,引用即变量本身,求所对应的变量本身的大小,即sizeof(char) = 1
printf("sizeof(rc) = %d\n", sizeof(rc)); // rc是一个引用,即sizeof(c) = 1
printf("sizeof(TRef) = %d\n", sizeof(TRef)); // sizeof(TRef) = 4
printf("sizeof(ref.r) = %d\n", sizeof(ref.r)); // TRef.r是 c的别名,sizeof(c) = 1
// sizeof(TRef) = 4
// 指针变量本身也是占4个字节
// 引用和指针的关系
return 0;
}3. The nature of reference
The internal implementation of a reference in C is apointer constant
Note:
1. The C compiler uses pointer constants as the internal implementation of references during the compilation process, so the space occupied by references is the same as that of pointers
2 , From the perspective of usage, the reference is just an alias, and C hides the details of the storage space of the reference for the sake of usability.
#include <stdio.h>
struct TRef
{
char* before; // 4字节
char& ref; // 4字节
char* after; // 4字节
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char a = 'a';
char& b = a;
char c = 'c';
TRef r = {&a, b, &c};
printf("sizeof(r) = %d\n", sizeof(r)); // sizeof(r) = 12
printf("sizeof(r.before) = %d\n", sizeof(r.before)); // sizeof(r.before) = 4
printf("sizeof(r.after) = %d\n", sizeof(r.after)); // sizeof(r.after) = 4
printf("&r.before = %p\n", &r.before); // &r.before = 0xbuf8a300c
printf("&r.after = %p\n", &r.after); // &r.after = 0xbuf8a3014
/*
0xbuf8a3014 - 0xbuf8a300c = 8
before占了4个字节,所以ref也是占4个字节
*/
return 0;
}Meaning of reference:
References in C are intended to replace pointers in most cases
Functionality : Can meet most situations where pointers need to be used
Safety: Can avoid memory errors caused by improper pointer operations
Operations : Simple and easy to use, yet powerful
But
references can avoid memory errors in most cases, If the function returns a reference to a local variable, there is no way to avoid
#include <stdio.h>
int& demo()
{
int d = 0;
printf("demo: d = %d\n", d);
return d; // 实际上是返回了局部变量的地址,局部变量函数结束就销毁了,返回错误
}
int& func()
{
static int s = 0;
printf("func: s = %d\n", s);
return s; // 返回静态局部变量的地址,静态局部变量存储在全局区,函数结束生命周期还在,返回成功
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int& rd = demo(); // rd 成为demo里面返回的局部变量d的别名,出现警告,但是通过编译
int& rs = func(); // rs 成为静态局部变量 s 的别名
printf("\n");
printf("main: rd = %d\n", rd); // rd = 13209588,rd代表的是一个不存在的变量,现在是一个野指针
printf("main: rs = %d\n", rs); // rs = 0
printf("\n");
rd = 10;
rs = 11; // 通过rs改变了静态局部变量s的值
demo(); // d = 10
func(); // s = 11
printf("\n");
printf("main: rd = %d\n", rd); // rd = 13209588
printf("main: rs = %d\n", rs); // rs = 11
printf("\n");
return 0;
}4. Summary
References exist as variable aliases and are intended to replace pointers
constReferences can Make variables have read-only attributesReferences are implemented using pointer constants inside the compiler
The ultimate essence of references is pointers
References can avoid memory errors as much as possible
Related articles:
A pitfall of loops and references in PHP, PHP circular references
Usage of double quotes PHP single quotes The difference with double quotes
The above is the detailed content of The meaning of C++ references and the nature of references. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
In C, the char type is used in strings: 1. Store a single character; 2. Use an array to represent a string and end with a null terminator; 3. Operate through a string operation function; 4. Read or output a string from the keyboard.
 Why does an error occur when installing an extension using PECL in a Docker environment? How to solve it?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Why does an error occur when installing an extension using PECL in a Docker environment? How to solve it?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Causes and solutions for errors when using PECL to install extensions in Docker environment When using Docker environment, we often encounter some headaches...
 How to calculate c-subscript 3 subscript 5 c-subscript 3 subscript 5 algorithm tutorial
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:33 PM
How to calculate c-subscript 3 subscript 5 c-subscript 3 subscript 5 algorithm tutorial
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:33 PM
The calculation of C35 is essentially combinatorial mathematics, representing the number of combinations selected from 3 of 5 elements. The calculation formula is C53 = 5! / (3! * 2!), which can be directly calculated by loops to improve efficiency and avoid overflow. In addition, understanding the nature of combinations and mastering efficient calculation methods is crucial to solving many problems in the fields of probability statistics, cryptography, algorithm design, etc.
 Four ways to implement multithreading in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
Four ways to implement multithreading in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
Multithreading in the language can greatly improve program efficiency. There are four main ways to implement multithreading in C language: Create independent processes: Create multiple independently running processes, each process has its own memory space. Pseudo-multithreading: Create multiple execution streams in a process that share the same memory space and execute alternately. Multi-threaded library: Use multi-threaded libraries such as pthreads to create and manage threads, providing rich thread operation functions. Coroutine: A lightweight multi-threaded implementation that divides tasks into small subtasks and executes them in turn.
 distinct function usage distance function c usage tutorial
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:27 PM
distinct function usage distance function c usage tutorial
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:27 PM
std::unique removes adjacent duplicate elements in the container and moves them to the end, returning an iterator pointing to the first duplicate element. std::distance calculates the distance between two iterators, that is, the number of elements they point to. These two functions are useful for optimizing code and improving efficiency, but there are also some pitfalls to be paid attention to, such as: std::unique only deals with adjacent duplicate elements. std::distance is less efficient when dealing with non-random access iterators. By mastering these features and best practices, you can fully utilize the power of these two functions.
 How to apply snake nomenclature in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to apply snake nomenclature in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
In C language, snake nomenclature is a coding style convention, which uses underscores to connect multiple words to form variable names or function names to enhance readability. Although it won't affect compilation and operation, lengthy naming, IDE support issues, and historical baggage need to be considered.
 Usage of releasesemaphore in C
Apr 04, 2025 am 07:54 AM
Usage of releasesemaphore in C
Apr 04, 2025 am 07:54 AM
The release_semaphore function in C is used to release the obtained semaphore so that other threads or processes can access shared resources. It increases the semaphore count by 1, allowing the blocking thread to continue execution.
 How to define an enum type in protobuf and associate string constants?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 03:36 PM
How to define an enum type in protobuf and associate string constants?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 03:36 PM
Issues of defining string constant enumeration in protobuf When using protobuf, you often encounter situations where you need to associate the enum type with string constants...