Architectural analysis of swoole
Aug 06, 2018 am 10:13 AMThe content of this article is about the architectural analysis of swoole. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
The structure diagram is as follows:
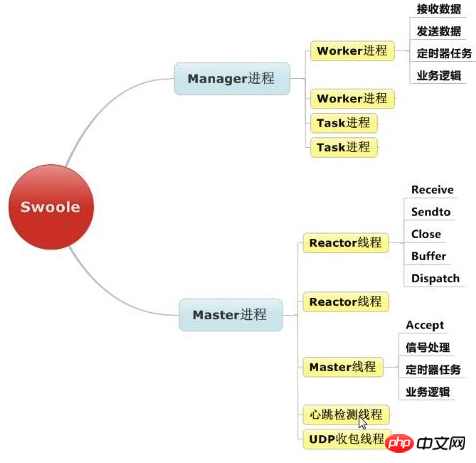
swoole is mainly used by the Master process (main process) and the Manager process to complete its functions.
Master process
is a multi-threaded program. There is a very important group of threads called Reactor threads. It is the thread that actually handles TCP connections and sends and receives data.
Manager process
Manage worker/task process. The worker/task processes are all forked and managed by the Manager process.
Reactor thread
After accepting a new connection, the main thread (Master process) will assign the connection to a fixed Reactor thread, and this thread will be responsible for monitoring the socket. Read the data when the socket is readable, perform protocol analysis, and deliver the request to the Worker process.
Responsible for maintaining client
TCPconnection, processing networkIO, processing protocol, sending and receiving dataCompletely asynchronous non-blocking mode
All are
Ccodes, exceptStart/ShudownExcept the event callback, no PHP code is executedBuffer, splice, and split the data sent by the
TCPclient into a complete request data PackageReactorRun in a multi-threaded manner
Work process
Similar to php- fpm process.
Accept the request packet delivered by the
Reactorthread, and execute thePHPcallback function to process the data-
Generate response data and send it to the
Reactorthread, which is sent by theReactorthread to theTCPclient Yes It is asynchronous mode or synchronous mode
WorkerRun in multi-process mode
TaskWorker process
A process that handles other tasks asynchronously, the usage method is similar to Gearman.
Accept tasks delivered by the
Workerprocess through theswoole_server->task/taskwaitmethodProcess the task and return the result data (
swoole_server->finish) to theWorkerprocessTaskWorkerRun in multi-process mode
Relationship
can be understood as Reactor is nginx, Worker is php-fpm. ReactorThe thread processes the network request asynchronously and in parallel, and then forwards it to the Worker process for processing (processed in the callback function). Reactor and Worker communicate through UnixSocket.
Event processing process
#To understand the swoole event processing process, first understand the two network event processing modes.
Reactor mode
It requires the main thread (I/O processing unit) to only monitor whether there is an event on the file descriptor, and if so, immediately notify the worker thread/process of the event. (logical unit). Other than that, the main thread doesn't do any other work. Reading and writing data, accepting new connections, and processing customer requests are all done in worker threads.
Proactor mode
Two implementations
Use the I/O asynchronous model to implement the Proactor mode. Principle: All I/O operations are handed over to the main thread, which cooperates with the kernel to handle them, and business logic operations are handed over to the logic unit. For example, use aio_read to achieve this.
Workflow:
The main thread calls the aio_read function to register the read completion event on the socket with the kernel.
The main thread continues to process other I/O events.
When the data on the socket is read into the user buffer, the kernel sends a signal to the application (logical unit) to notify the application that the data is available.
The application reads the data (client request), and after processing, calls the aio_write function to register the write event on the socket with the kernel.
The main thread continues to process other logic.
When the data in the user buffer is written to the socket, the kernel sends a signal to the application to notify the application that the data has been sent.
The application has pre-defined signal processing functions to handle the aftermath, such as closing the socket.
Use the I/O synchronization model to implement Proactor model. Principle: The main thread performs the read and write operations of I/O event data, and the business logic operations are handed over to the logic unit. For example, use epoll to achieve this.
Workflow:
The main thread registers the read-ready event on the socket in the epoll kernel event table.
The main thread calls epoll_wait to wait for data to be read on the socket.
After epoll_wait returns, the main thread reads data from the socket, then encapsulates the read data into a request object (client's request), and inserts it into the request queue.
So the consumer thread of the queue processes the request object, and then registers the write-ready event on the socket in the epoll kernel event table.
The main thread calls epoll_wait to wait for the socket to be writable.
When the socket is writable, epoll_wait notifies the main thread. The main thread writes the request result to the socket.
swoole event architecture diagram
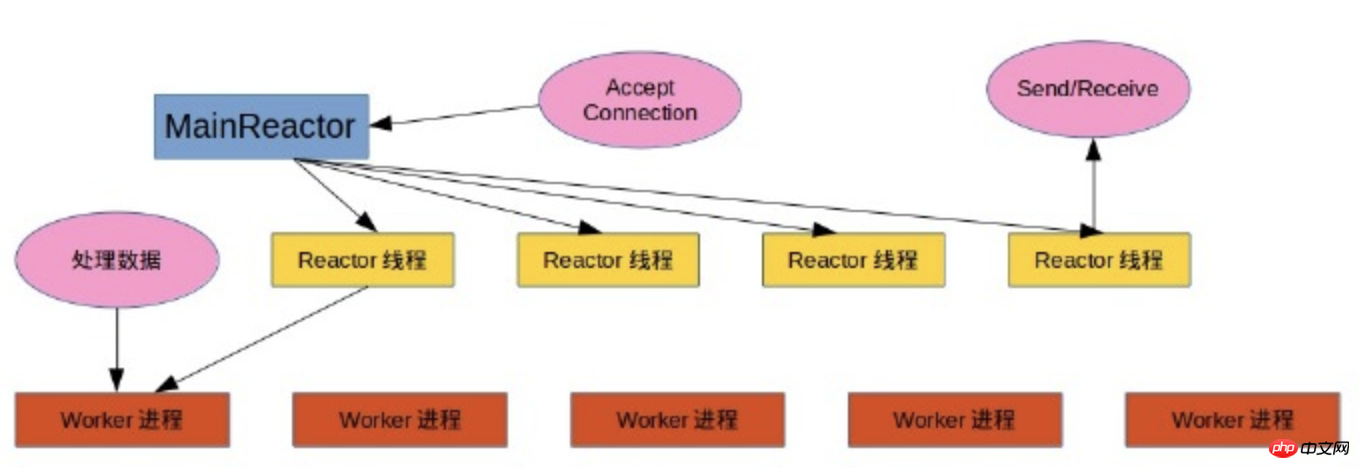
As can be seen from the figure, if we combine the Reactor thread and the Work process, it can be seen as For worker threads, swoole uses the reactor event processing mode.
The steps a request goes through are as follows:
1. The server main thread waits for the client to connect.
2. The Reactor thread processes the connected socket, reads the request data on the socket (Receive), encapsulates the request and delivers it to the work process.
3. The Work process is a logical unit that processes business data.
4. Work process results are returned to the Reactor thread.
5. The Reactor thread writes the result back to the socket (Send).
Please review the above structure introduction for the work of each module.
Related recommendations:
How to customize a Model? Usage of ThinkPHP3.2 custom base class Model
How to use PHP to read the contents of excel files and obtain cell data
The above is the detailed content of Architectural analysis of swoole. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot Article

Hot tools Tags

Hot Article

Hot Article Tags

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 11 Best PHP URL Shortener Scripts (Free and Premium)
Mar 03, 2025 am 10:49 AM
11 Best PHP URL Shortener Scripts (Free and Premium)
Mar 03, 2025 am 10:49 AM
11 Best PHP URL Shortener Scripts (Free and Premium)
 Working with Flash Session Data in Laravel
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PM
Working with Flash Session Data in Laravel
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PM
Working with Flash Session Data in Laravel
 Build a React App With a Laravel Back End: Part 2, React
Mar 04, 2025 am 09:33 AM
Build a React App With a Laravel Back End: Part 2, React
Mar 04, 2025 am 09:33 AM
Build a React App With a Laravel Back End: Part 2, React
 Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel Tests
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel Tests
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel Tests
 cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIs
Mar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIs
Mar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIs
 12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyon
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyon
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyon









