
[Thread] Single task flow in Java program. We implement each task in a relatively independent thread. main is the main thread
[Concurrency] Complete multiple tasks at the same time. The steps of program execution are all in order, but many times we need to process a problem concurrently instead of processing a problem in sequence
[Multi-threading] Threads are also regarded as objects, and multi-threading refers to multiple thread objects
[Classes that support threads in the API] java.lang.Thread. The object of the Thread class is the thread object
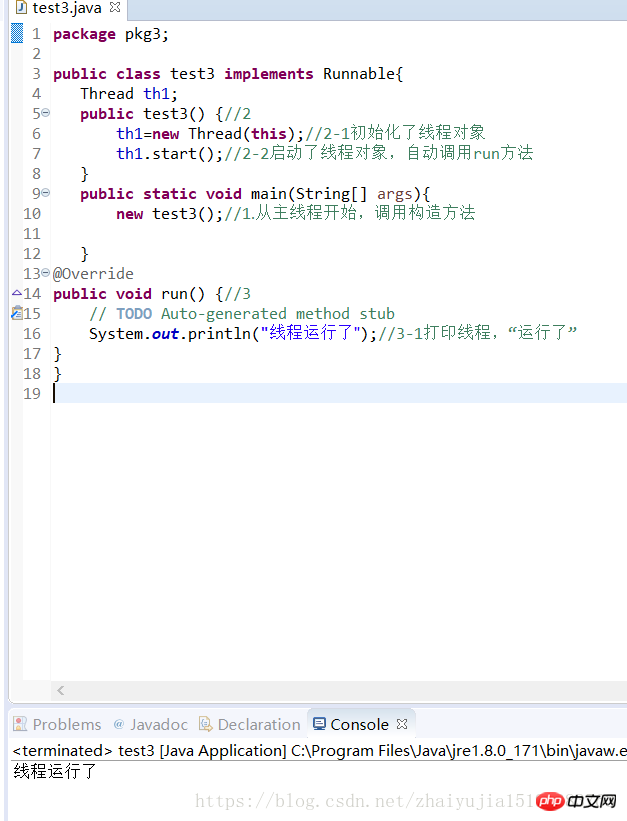
Exercise 1. Initialize the thread object and print the thread
package pkg3;public class test3 implements Runnable{
Thread th1; public test3() {//2
th1=new Thread(this);//2-1初始化了线程对象
th1.start();//2-2启动了线程对象,自动调用run方法
} public static void main(String[] args){ new test3();//1.从主线程开始,调用构造方法
}@Overridepublic void run() {//3
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("线程运行了");//3-1打印线程,“运行了”}
}
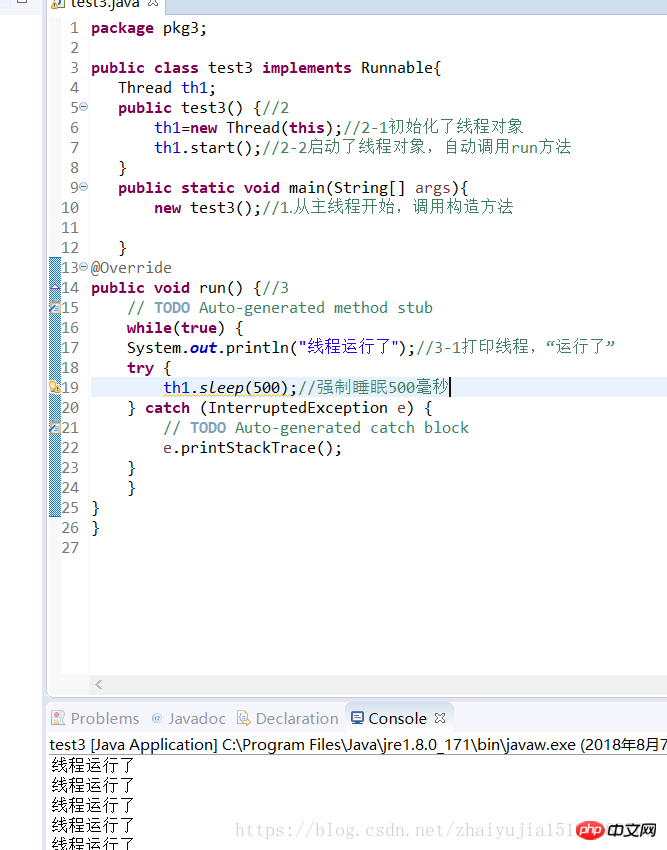
Exercise 2. The life cycle of the thread: new, runnable, not runnable, dead
package pkg3;public class test3 implements Runnable{
Thread th1; public test3() {//2
th1=new Thread(this);//2-1初始化了线程对象
th1.start();//2-2启动了线程对象,自动调用run方法
} public static void main(String[] args){ new test3();//1.从主线程开始,调用构造方法
}@Overridepublic void run() {//3
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while(true) {
System.out.println("线程运行了");//3-1打印线程,“运行了”
try {
th1.sleep(500);//强制睡眠500毫秒,进入非运行状态not runnable(睡眠、堵塞、排队)
} catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
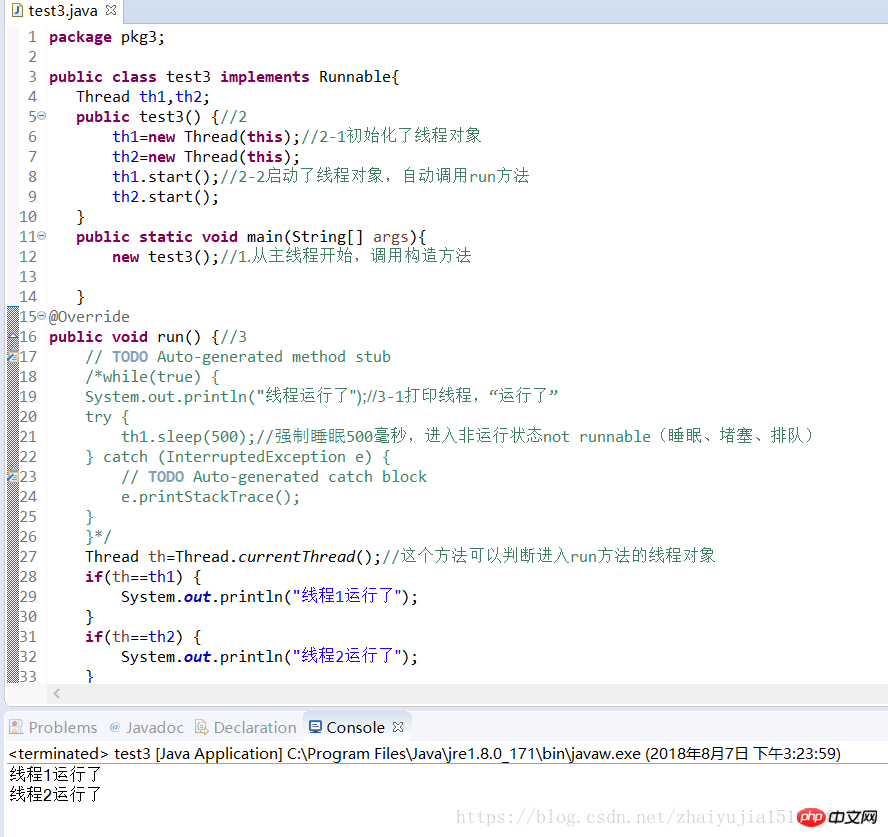
Exercise 3, multi-threading
package pkg3;public class test3 implements Runnable{
Thread th1,th2; public test3() {//2
th1=new Thread(this);//2-1初始化了线程对象
th2=new Thread(this);
th1.start();//2-2启动了线程对象,自动调用run方法
th2.start();
} public static void main(String[] args){ new test3();//1.从主线程开始,调用构造方法
}@Overridepublic void run() {//3
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
/*while(true) {
System.out.println("线程运行了");//3-1打印线程,“运行了”
try {
th1.sleep(500);//强制睡眠500毫秒,进入非运行状态not runnable(睡眠、堵塞、排队)
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}*/
Thread th=Thread.currentThread();//这个方法可以判断进入run方法的线程对象
if(th==th1) {
System.out.println("线程1运行了");
} if(th==th2) {
System.out.println("线程2运行了");
}
}
}
Related recommendations:
Detailed explanation of java threads and the difference between threads and processes
The above is the detailed content of JAVA--Threads and multi-threading Detailed graphic explanation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




