
Spring Boot 2.x has been released for a long time, and now Spring Cloud has also released the Finchley version based on Spring Boot 2.x. Now let’s do an overall framework upgrade for the project.
Before upgrade=> After upgrade
Spring Boot 1.5.x => Spring Boot 2.0.2
Spring Cloud Edgware SR4 => ; Spring Cloud Finchley.RELEASE
Eureka Server dependency update
Before upgrade:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>After upgrade:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>Because the configuration center needs to be registered as a service in the registration center, Eureka Client needs to be upgraded, and other dependencies have not changed.
Eureka Client dependency update
Before upgrade:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId>
</dependency>After upgrade:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>The client instance IP in the registration center is incorrectly displayed
Because the Spring Cloud service client IP address configuration has changed.
Before upgrade:
${spring.cloud.client.ipAddress}After upgrade:
${spring.cloud.client.ip-address} Generally, the registration center and configuration center will use security encryption and will rely on spring-boot-starter-security component, there are two problems after upgrading.
1. The username and password cannot be logged in
Because the parameters of Spring Security have been changed.
Before upgrade:
security:
user:
name:
password:After upgrade:
spring:
security:
user:
name:
password:2. There is no registered instance in the registration center
As shown in the figure, Without a registered instance, the two registration centers cannot register with each other.
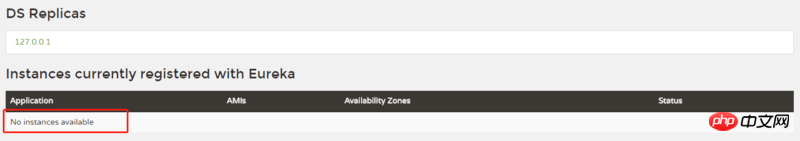
Because Spring Security enables all CSRF attack defenses by default, /eureka’s defense needs to be disabled.
Add ignore configuration in the Application entry class:
@EnableWebSecurity
static class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().ignoringAntMatchers("/eureka/**");
super.configure(http);
}
}3. The configuration center cannot encrypt or decrypt
After upgrading, I found that the access configuration center cannot be read. configuration, the configuration information cannot be encrypted or decrypted, and the link to access the configuration center jumps directly to the login page.
Now I want to change back to the previous basic auth authentication method. I found the source code and found that it automatically configured to jump to the login page. Now rewrite it.
Automatic configuration source code:
org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter#configure(org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity)
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
logger.debug("Using default configure(HttpSecurity). If subclassed this will potentially override subclass configure(HttpSecurity).");
http
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin().and()
.httpBasic();
}After rewriting:
@EnableWebSecurity
static class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().ignoringAntMatchers("/**").and().authorizeRequests().anyRequest()
.authenticated().and().httpBasic();
}
} actually kills formLogin() and returns to the previous basic auth authentication method, as shown in the figure below.
Now we can use the following commands to encrypt and decrypt.
After restoring basic auth, the previous service that required encrypted connection to the configuration center will run normally again.
After upgrading to Spring Boot 2.x, I found that the Maven startup plug-in of Spring Boot is not easy to use, mainly because the Profile cannot be switched freely.
Before upgrade:
spring-boot:run -Drun.profiles=profile1
After upgrade:
spring-boot:run -Dspring-boot.run.profiles=profile1
The above are the solutions summarized after going through all the pitfalls and actually solving the problem The process is far more complicated. The version changes are a bit big. This time, the basic dependencies of Spring Cloud, as well as the registration center (Eureka Server) and configuration center (Config Server) have been successfully upgraded.
Related recommendations:
Related introduction to the startup process of Spring Boot
Detailed explanation of unit testing of Spring Boot
The above is the detailed content of Finchley version analysis based on Spring Boot 2.x. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




