C++ summary: basic concepts of object-oriented
Object-oriented language
In the first semester of freshman year, we learned C language. It is a very classic and very basic language. All computer science students probably have not escaped its clutches. C++ is very clear from its name. It is a derivative of C. It includes almost all the contents of C. However, their design ideas are quite different. C is a process-oriented program, while C++ is object-oriented. program, let’s explain the difference between the two.
Process-oriented: Analyze the steps required to solve the problem, and then use functions to implement these steps step by step. When using, just call them one by one.
Object-oriented: is to decompose the transaction that constitutes the problem into various objects. The purpose of establishing the object is not to complete a step, but to describe the behavior of something in the entire step of solving the problem.
For example, in backgammon, the process-oriented design idea is to first analyze the steps of the problem: 1. Start the game, 2. Black stones move first, 3. Draw the picture, 4. Judge winning or losing, 5. It’s White’s turn, 6. Draw the picture, 7. Determine winning or losing, 8. Return to step 2, 9. Output the final result. Implement each of the above steps with separate functions and the problem will be solved.
Object-oriented design solves problems from another perspective. The entire backgammon can be divided into 1. the black and white sides, whose behaviors are exactly the same; 2. the chessboard system, which is responsible for drawing the picture; 3. the rules system, which is responsible for determining fouls, winning and losing, etc. The first type of object (player object) is responsible for accepting user input and informing the second type of object (chessboard object) about the changes in the chess piece layout. After the chessboard object receives the i changes of the chess pieces, it is responsible for displaying this change on the screen, and at the same time using The third type of object (rule system) is used to judge the chess game.
It can be clearly seen that object-oriented divides problems by functions, not steps. It is also drawing a chess game. Such behavior is dispersed in multiple steps in process-oriented design, and different drawing versions are likely to appear, because usually designers will make various simplifications taking into account the actual situation. In object-oriented design, drawing can only appear in the chessboard object, thus ensuring the unity of drawing.
The unification of functions ensures the scalability of object-oriented design. For example, if I want to add the function of regretting chess, if I want to change the process-oriented design, then the series of steps from input to judgment to display must be changed, and even the order between steps must be adjusted on a large scale. If it is object-oriented, you only need to change the chessboard object. The chessboard system saves the chess records of the black and white sides, and you can simply backtrack. The display and rule judgment do not need to be taken into account. At the same time, the entire order of calling the object functions remains unchanged. The changes are only partial.
For another example, I want to change this backgammon game to a Go game. If you are designing for process, then the backgammon rules are distributed in every corner of your program. If you want to change it, it is better to rewrite it. But if you had an object-oriented design from the beginning, then you only need to change the rule objects. Isn't the difference between backgammon and Go the rules? (Of course, the size of the chessboard seems to be different, but do you think this is a problem? Just make some small changes in the chessboard object.) The general steps of playing chess have not changed at all from an object-oriented perspective. .
Of course, to make the changes only partial, the designer needs to have enough experience. Using objects does not guarantee that your program is object-oriented. Beginners or very poor programmers are likely to be process-oriented in an imaginary way. In fact, it is difficult for so-called object-oriented programs designed in this way to have good portability and scalability.
(This is the answer I found on Baidu! I didn’t write it myself. Thank you to the guy who answered the question!!!)
-
For Basic concepts of objects
1. Object
Scientific explanation: The object in the object-oriented method is an entity used to describe objective facts in the system. It is a basic unit used to constitute the system. An object consists of a set of properties and a set of behaviors.
Self-explanation: For example, "person" is a very big concept, but when it comes to yourself, you are the object. The one with entity and specific meaning is the object. After reading the introduction to classes I hope you can understand better. After all, I am not good at Chinese. . .
2. Class
Summarizes many things and divides them into some categories. The principle of classification is abstraction, that is, ignoring the non-essential characteristics of things and only paying attention to those essential characteristics related to the current goal, so as to find out the characteristics of things. Commonality refers to dividing things with common properties into one category to derive an abstract concept, such as stones, trees, cars, houses, etc.
3. Encapsulation
Encapsulation is an important principle of object-oriented methods, which is to combine the properties and services of an object into an independent system unit and hide the internal details of the object as much as possible.
4. inherit
Inheritance is one of the important reasons why object-oriented technology can improve the efficiency of software development. Its definition is: objects of a special class have all the properties and services of its general class, which is called the inheritance of a general class by a special class.
For example, after we understand the characteristics of a ship, when we consider a passenger ship, because we know that a passenger ship is also a ship, we can think that it has all the characteristics of a ship, so we only need to focus on the unique features of a passenger ship. Characteristically.
5. Polymorphism
Polymorphism refers to the attributes or behaviors defined in a general class. After being inherited by a special class, it can have different data, types or show different behaviors. (This will be explained later with specific examples!)
-
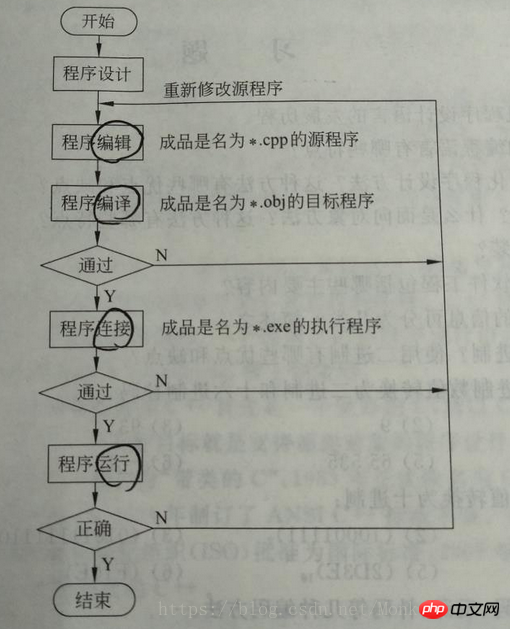
Complete program process
Related recommendations:
C Class & Object | C Manual Tutorial|
Summary of conceptual systems in C#-C#.Net tutorial
The above is the detailed content of C++ summary: basic concepts of object-oriented. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 .NET Deep Dive: Mastering Asynchronous Programming, LINQ, and EF Core
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:07 PM
.NET Deep Dive: Mastering Asynchronous Programming, LINQ, and EF Core
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:07 PM
The core concepts of .NET asynchronous programming, LINQ and EFCore are: 1. Asynchronous programming improves application responsiveness through async and await; 2. LINQ simplifies data query through unified syntax; 3. EFCore simplifies database operations through ORM.
 Advanced C# .NET: Concurrency, Parallelism, and Multithreading Explained
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Advanced C# .NET: Concurrency, Parallelism, and Multithreading Explained
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:01 AM
C#.NET provides powerful tools for concurrent, parallel and multithreaded programming. 1) Use the Thread class to create and manage threads, 2) The Task class provides more advanced abstraction, using thread pools to improve resource utilization, 3) implement parallel computing through Parallel.ForEach, 4) async/await and Task.WhenAll are used to obtain and process data in parallel, 5) avoid deadlocks, race conditions and thread leakage, 6) use thread pools and asynchronous programming to optimize performance.
 How to convert char in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
How to convert char in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
In C language, char type conversion can be directly converted to another type by: casting: using casting characters. Automatic type conversion: When one type of data can accommodate another type of value, the compiler automatically converts it.
 What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
In C, the char type is used in strings: 1. Store a single character; 2. Use an array to represent a string and end with a null terminator; 3. Operate through a string operation function; 4. Read or output a string from the keyboard.
 How to use char array in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:24 PM
How to use char array in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:24 PM
The char array stores character sequences in C language and is declared as char array_name[size]. The access element is passed through the subscript operator, and the element ends with the null terminator '\0', which represents the end point of the string. The C language provides a variety of string manipulation functions, such as strlen(), strcpy(), strcat() and strcmp().
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 How to handle special characters in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to handle special characters in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
In C language, special characters are processed through escape sequences, such as: \n represents line breaks. \t means tab character. Use escape sequences or character constants to represent special characters, such as char c = '\n'. Note that the backslash needs to be escaped twice. Different platforms and compilers may have different escape sequences, please consult the documentation.
 C# .NET Performance Optimization: Real-World Techniques for Faster Applications
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
C# .NET Performance Optimization: Real-World Techniques for Faster Applications
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
Methods to improve the performance of C#.NET applications include: 1. Optimize garbage collection (GC) by reducing object allocation and using array substitution lists; 2. Reasonable use of asynchronous programming to avoid blocking the main thread; 3. Optimize LINQ queries by avoiding method chains and using delayed execution; 4. Use parallel processing such as Parallel.For to improve the performance of complex scenarios; 5. Avoid common errors such as memory leaks and deadlocks, and use debugging tools to fix them.






