
This article brings you an introduction to the four attributes of positioning in CSS. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
CSS position attribute
There are four attributes in total:
static
The default value is this attribute under normal circumstances. Generally, there is no need to write it. .
relative
To offset elements, use top, right, left, bottom to offset, and use z-index to separate levels.
<head>
<style>
div{
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: pink;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
margin-left: 10px;
}
.box{
position: relative;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>1</div>
<div class="box">2</div>
<div>3</div>
</body>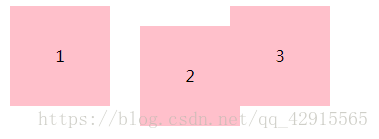
relative is an offset based on its original value. That is, positions relative to itself.
absolute
Positioned relative to body or relative to the nearest positioned parent element .
<head>
<style>
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
left: 250px;
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: pink;
position: relative;
top: 10px;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: blue;
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">1</div>
<div class="box2">
2 <div class="box3">3</div>
</div>
</body>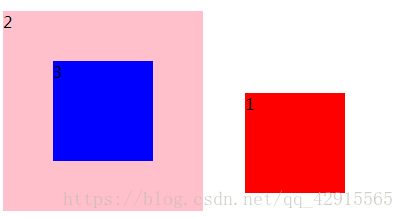
fixed
The fixed positioning specification is always positioned according to the upper left corner of the browser window. No matter how you roll the mouse, it will be positioned according to the upper left corner of the browser window after you move it. For example, the navigation bar of many official websites uses fixed positioning, so that it can always feel the peak loneliness at the top.
Note: These three positionings will break away from the document flow, so they must be used appropriately!
Related recommendations:
Summary of commonly used styles in CSS and summary of commonly used attributes in css
How to implement cards in css Image flip effect? (Special effects example)
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to the four properties of positioning in CSS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




