
The content of this article is about the usage of the position attribute of CSS style layout (with code). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
positionAttribute: used to define the positioning type used to establish the layout of elements. This attribute has multiple values:
|
Value |
describe |
|
static |
default value. Without positioning, the element appears in the normal flow (ignoring top, bottom, left, right or z-index declarations). |
|
relative |
Generate a relatively positioned label, position relative to the original position of the label. Therefore, "left:20" will add 20 pixels to the left position of the label. |
|
absolute |
Generate a relatively positioned label, position the first position relative to the label itself to a non-static parent element. The position of the label is specified through the "left", "top", "right" and "bottom" style attributes. If the parent tag where the tag is located does not set position to non-static, it will be positioned relative to the browser window, but at this time the element will slide as the scroll tone slides. |
|
fixed |
Generate an absolutely positioned label and position it relative to the browser window . At this time, the element will not slide as the scroll tone slides. The position of the element is specified through the "left", "top", "right" and "bottom" attributes. |
(Document flow, also known as normal flow, is a type in which elements are automatically arranged from top to bottom or from left to right during the layout process of HTML elements by default. Order)
Note: Any element can be positioned, but an absolute or fixed element will generate a block-level box, regardless of whether the element itself is a block-level box. A relative element is offset relative to its default position in normal flow. None of the IE browsers support the "inherit" attribute value.
When a tag uses the position CSS style attribute, if its style attribute value is non-static (regardless of inheritance), the tag will be out of the normal document flow. If "left", "top" is not specified, If the attribute values of the "right" and "bottom" style attributes are set, the tag will only stay in the original position, but has been separated from the normal document flow
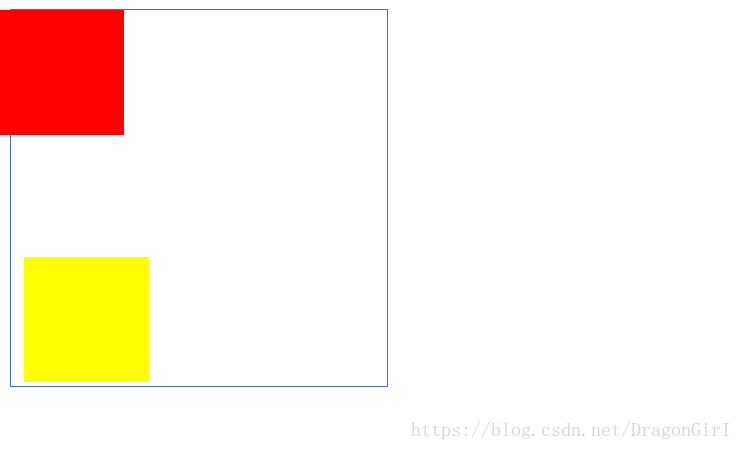
The following is the demo code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
#z{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid royalblue;
position: relative;
}
#a,#b,#c{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
#a{
background: red;
position: relative;
right: 10px;
}
#b{
background: green;
position: fixed;
left: 1000px;
bottom: 20px; /*只需要规定两个方向就可以了,上下,左右各选其一*/
}
#c{
background: yellow;
position: absolute;
left: 10px;
bottom: 3px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="z">
<div id="a"></div>
<div id="b"></div>
//加空格用于复习div的块级元素性质
<div id="c"></div>
//加了空格后,c的div会自动换行 block的属性所致
</div>
</body>
</html>Demo notes:
position:
relative is positioned relative to the original position of the tag and still exists in the document flow
fixed is relative to the entire browser It is positioned by the browser and directly ignores the label element in the browser, which is similar to "floating"
absolute is the first (parent) element relative to the previous level [such as b versus z] (required to be non static attribute) and the positioning standard is determined based on the outer border of the parent element
The following is the demonstration result:

Related recommendations:
##css background-position attribute_html/css_WEB-ITnose
CSS position attribute_html/css_WEB-ITnose
The above is the detailed content of How to use the position attribute of css style layout (with code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!