
This article brings you a detailed introduction (code) about reference assignment and value assignment of PHP variables. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you. .
// 定义一个变量 $a = range(0, 10000); var_dump(memory_get_usage()); // 定义变量b,将a变量的值赋值给b $b = $a; var_dump(memory_get_usage()); // 对a进行修改 // COW: Copy-On-Write $a = range(0, 10000); var_dump(memory_get_usage());
Output result:
int(989768) int(989856) int(1855608)
$a = range(0, 10000);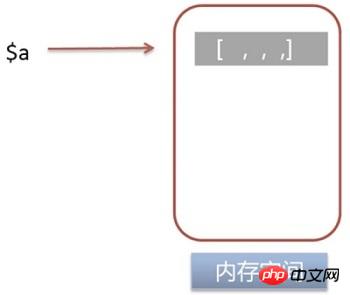
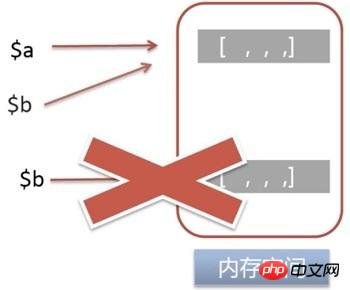
COW was first used in Unix systems to optimize thread and memory usage, and was later widely used in various programming languages, such as C's STL, etc.
In the PHP kernel, COW is also the main memory optimization method.
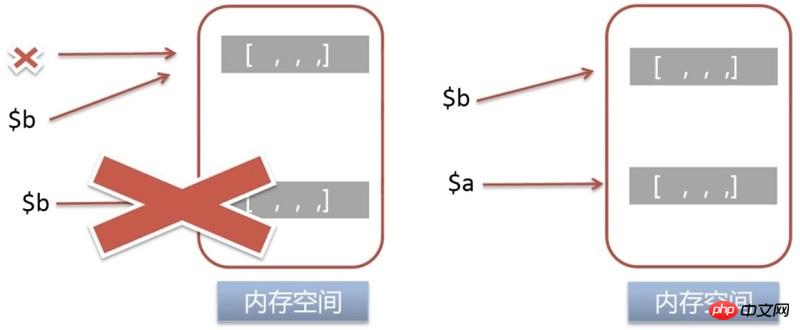
When assigning a value to a variable through variable assignment, new memory will not be allocated to store the value of the new variable, but the memory will simply be shared through a counter. Only when the value of the variable pointed to by one of the references changes, new space is allocated to save the value content to reduce memory usage.
In many scenarios, PHP uses COW for memory optimization. For example: multiple assignments of variables, passing function parameters, and modifying actual parameters in the function body, etc.
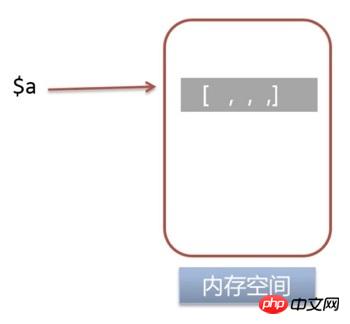
// 定义一个变量 $a = range(0, 10000); var_dump(memory_get_usage()); // 定义变量b,将a变量的引用赋给b $b = &$a; var_dump(memory_get_usage()); // 对a进行修改 $a = range(0, 10000); var_dump(memory_get_usage());
int(989760) int(989848) int(989840)
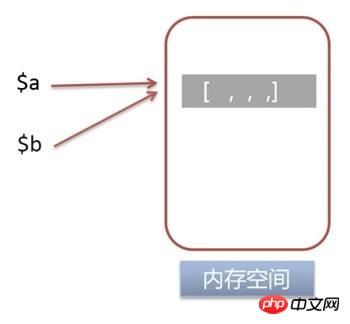
 2. Use
2. Use
Used to display variable information. The xdebug extension needs to be installed. 1. Pass-by-value assignment
$a = 1;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
// 定义变量b,把a的值赋值给b
$b = $a;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
xdebug_debug_zval('b');
// a进行写操作
$a = 2;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
xdebug_debug_zval('b');a: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=1 a: (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=1 b: (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=1 a: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=2 b: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=1
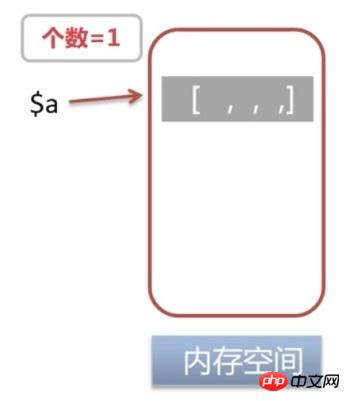
a: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=1
means that the number of references to the memory address pointed to by the variable becomes 1is_ref=0
means that the variable Instead of quoting
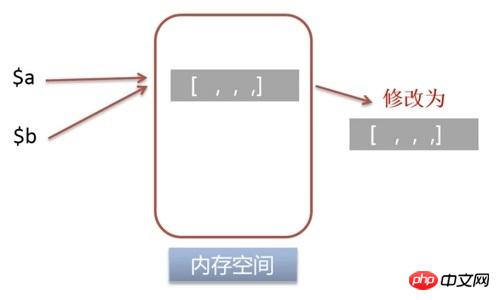
$a to $b, $b = $a;$b = $a;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
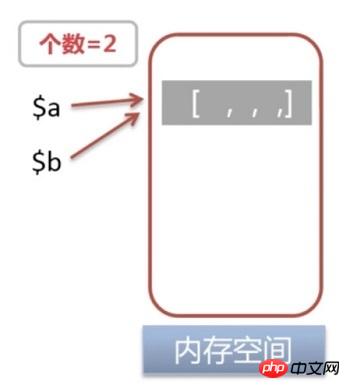
xdebug_debug_zval('b');a: (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=1 b: (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=1
indicates that the variable points to The number of references to the memory address becomes 2is_ref=0
, indicating that the variable is not a reference
 ## Write operation to variable
## Write operation to variable
<div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">$a = 2;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
xdebug_debug_zval('b');</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>Outputa: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=2 b: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=1
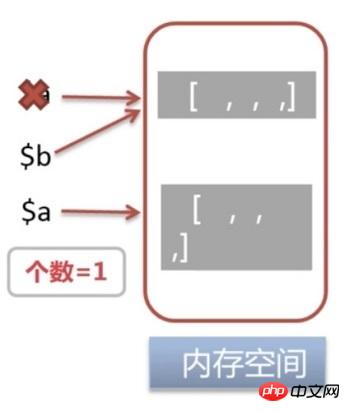
When $a
performs a write operation, a new memory space will be allocated for variable$a to store the value of variable $a. At this time, the number of references to the memory addresses pointed to by $a and
$b becomes 1.
 2. Reference assignment
2. Reference assignment
$a = 1;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
// 定义变量b,把a的引用赋给b
$b = &$a;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
xdebug_debug_zval('b');
// a进行写操作
$a = 2;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
xdebug_debug_zval('b');a: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=1 a: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=1 b: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=1 a: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=2 b: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=2
<div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">$a = 1;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>Outputa: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=1
refcount=1
Indicates that the number of references to the memory address pointed to by the variable becomes 1is_ref=0 Indicates that the variable is not a reference
输出 输出 因为变量 输出 虽然销毁的 输出 输出 输出 输出 因为php中对象本身就是引用赋值。对 此时, ![$v 和 $d[0] 在内存中分别开辟了一块空间](http://md.ws65535.top/xsj/201... ![$v = &$d[0] 改变了 $val 指向的内存地址](http://md.ws65535.top/xsj/201... ![$v = ‘b’ => $d[0] = ‘b’](http://md.ws65535.top/xsj/201... ![$d[2] = ‘b’](http://md.ws65535.top/xsj/201... ![$v = &$d[1]](http://md.ws65535.top/xsj/201... ![$v = ‘c’ => $d[1] = ‘c’](http://md.ws65535.top/xsj/201... ![$d[2] = ‘c’](http://md.ws65535.top/xsj/201... ![$v = &$d[2]](http://md.ws65535.top/xsj/201... 相关推荐:定义变量
$b ,把 $a 的引用赋给 $b, $b = &$a;$b = &$a;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
xdebug_debug_zval('b');a: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=1
b: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=1
refcount=2 表示该变量指向的内存地址的引用个数变为2is_ref=1 表示该变量是引用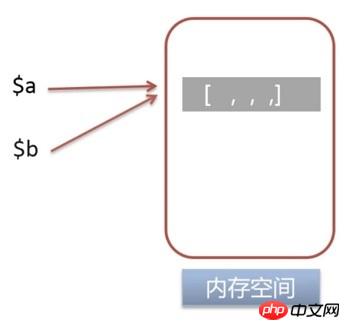
对变量
<div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">$a = 2;
xdebug_debug_zval('a');
xdebug_debug_zval('b');</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>
$a 进行写操作 $a = 2;a: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=2
b: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=2
$a 和变量 $b 指向相同的内存地址,其实引用。
对变量 $a 进行写操作时,会直接修改指向的内存空间的值,因此变量 $b 的值会跟着一起改变。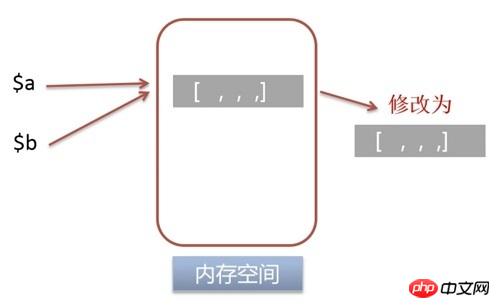
三、当变量时引用时,unset()只会取消引用,不会销毁内存空间
$a = 1;
$b = &$a;
// unset 只会取消引用,不会销毁内存空间
unset($b);
echo $a;
1
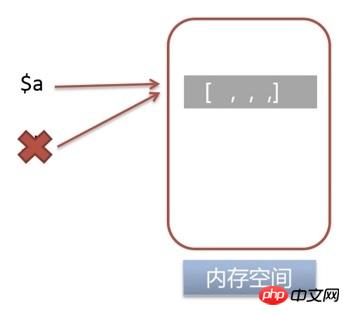
定义变量
$a ,并将 $a 的引用赋给变量 $b$a = 1;
$b = &$a;
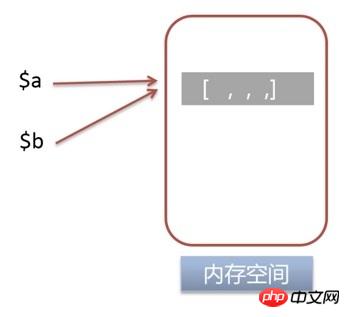
销毁
$bunset($b);
输出
$a$b,但是 $a 的引用和内存空间依旧存在。echo $a;
1
四、php中对象本身就是引用赋值
class Person
{
public $age = 1;
}
$p1 = new Person;
xdebug_debug_zval('p1');
$p2 = $p1;
xdebug_debug_zval('p1');
xdebug_debug_zval('p2');
$p2->age = 2;
xdebug_debug_zval('p1');
xdebug_debug_zval('p2');p1: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=class Person { public $age = (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=1 }
p1: (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=class Person { public $age = (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=1 }
p2: (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=class Person { public $age = (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=1 }
p1: (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=class Person { public $age = (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=2 }
p2: (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=class Person { public $age = (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=2 }实例化对象
$p1 = new Person;$p1 = new Person;
xdebug_debug_zval('p1');p1: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=class Person { public $age = (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=1 }refcount=1 表示该变量指向的内存地址的引用个数变为1is_ref=0 表示该变量不是引用把
$p1 赋给 $p2$p2 = $p1;
xdebug_debug_zval('p1');
xdebug_debug_zval('p2');p1: (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=class Person { public $age = (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=1 }
p2: (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=class Person { public $age = (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=1 }refcount=2 表示该变量指向的内存地址的引用个数变为2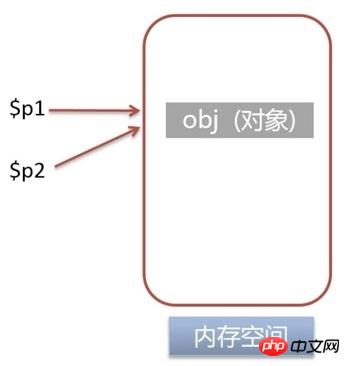
对
$p2 中的属性 age 进行写操作$p2->age = 2;
xdebug_debug_zval('p1');
xdebug_debug_zval('p2');p1: (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=class Person { public $age = (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=2 }
p2: (refcount=2, is_ref=0)=class Person { public $age = (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=2 }$p2 中的属性 age 进行写操作时,会直接修改指向的内存空间的值,因此变量 $p1 的 age 属性的值会跟着一起改变。五、实战例题分析
/**
* 写出如下程序的输出结果
*
* $d = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
*
* foreach($d as $k => $v)
* {
* $v = &$d[$k];
* }
*
* 程序运行时,每一次循环结束后变量 $d 的值是什么?请解释。
* 程序执行完成后,变量 $d 的值是什么?请解释。
*/1. 第一次循环
推算出进入
foreach 时 $v、$d[$k] 的值$k = 0
$v = 'a'
$d[$k] = $d[0] = 'a'
$v 和 $d[0] 在内存中分别开辟了一块空间$v = &$d[0] 改变了 $v 指向的内存地址$v = &$d[0]
第一次循环后 $d 的值:
['a', 'b', 'c']
2. 第二次循环
进入
foreach 时 $v 被赋值为 'b',此时$v指向的内存地址与 $d[0] 相同,且为引用,因此 $d[0] 的值被修改为 'b'$v = 'b' => $d[0] = 'b'推算出进入
foreach 时 $d[$k] 的值$k = 1
$d[$k] = $d[1] = 'b'
$v = &$d[1] 改变了 $v 指向的内存地址$v = &$d[1]
第二次循环后
$d 的值['b', 'b', 'c']
3. 第三次循环
进入
foreach 时 $v 被赋值为 'c',此时$v指向的内存地址与 $d[1] 相同,且为引用,因此 $d[1] 的值被修改为 'c'$v = 'c' => $d[1] = 'c'推算出进入
foreach 时 $d[$k] 的值$k = 2
$d[2] = 'c'
$v = &$d[2] 改变了 $v 指向的内存地址$v = &$d[2]
第三次循环后
$d 的值['b', 'c', 'c']
4. 实测
$d = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
foreach ($d as $k=>$v)
{
$v = &$d[$k];
print_r($d);
}
print_r($d);输出:
Array
(
[0] => a
[1] => b
[2] => c
)
Array
(
[0] => b
[1] => b
[2] => c
)
Array
(
[0] => b
[1] => c
[2] => c
)
Array
(
[0] => b
[1] => c
[2] => c
)
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to reference assignment and value assignment of PHP variables (code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




