The difference between the two forms of function declaration
We know that the keyword function is used to define functions; function definitions can be written as function definition expressions or in the form of statements. For example, the following two ways of writing
var f = function(x){return x+1;} //将表达式赋值给一个变量 函数表达式
function f(x){return x+1;} //含有变量的语句 函数声明Although the function declaration statement and the function definition expression contain the same function name; there are still differences between them.
Same points: Both methods create new function objects; both will be "advanced" (functions defined in function statements are displayed to the top of the script or function, so they are visible within the entire script );
Difference: The function name in the function declaration statement is a variable name, and the variable points to the function object. Like declaring variables through var, functions defined in function statements are displayed ahead to the top of the script or function, so they are visible within the entire script;
1. Using var only variables are declared ahead--the initialization of variables However, in the original position, if the function declaration statement is used, the function name and function body are both in advance
Summary: Simply speaking, the function expression method (that is, the var declaration method) can only be called after the var statement is declared; And function declaration (that is, function declaration method) function can be called before function declaration.
These situations are because the function expression is assigned to the variable f during the function running stage; and the function declaration has been assigned to the variable f before the code is run, that is, during the code parsing stage
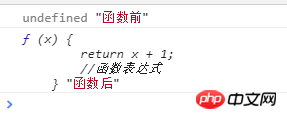
We can look at the following code :
console.log(f,"函数前")
var f = function (x) {
return x + 1;//函数表达式
}
console.log(f,"函数后")And the result of running this code:
 ##
##
console.log(f,"函数前")
function f(x) {
return x + 1;//函数声明
}
console.log(f,"函数后")
The above is the detailed content of The difference between the two forms of function declaration. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Default parameters in C++ function declarations: a comprehensive analysis of their declaration and usage
May 02, 2024 pm 03:09 PM
Default parameters in C++ function declarations: a comprehensive analysis of their declaration and usage
May 02, 2024 pm 03:09 PM
Default parameters in C++ provide the ability to specify default values for function parameters, thereby enhancing code readability, simplicity, and flexibility. Declare default parameters: Add the "=" symbol after the parameter in the function declaration, followed by the default value. Usage: When the function is called, if optional parameters are not provided, the default values will be used. Practical case: A function that calculates the sum of two numbers. One parameter is required and the other is optional and has a default value of 0. Advantages: Enhanced readability, increased flexibility, reduced boilerplate code. Note: It can only be specified in the declaration, it must be at the end, and the types must be compatible.
 What impact does the order of declaration and definition of C++ functions have?
Apr 19, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
What impact does the order of declaration and definition of C++ functions have?
Apr 19, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
In C++, the order of function declarations and definitions affects the compilation and linking process. The most common is that the declaration comes first and the definition comes after; you can also use "forwarddeclaration" to place the definition before the declaration; if both exist at the same time, the compiler will ignore the declaration and only use the definition.
 What is the difference between C++ function declaration and definition?
Apr 18, 2024 pm 04:03 PM
What is the difference between C++ function declaration and definition?
Apr 18, 2024 pm 04:03 PM
A function declaration informs the compiler of the existence of the function and does not contain the implementation, which is used for type checking. The function definition provides the actual implementation, including the function body. Key distinguishing features include: purpose, location, role. Understanding the differences is crucial to writing efficient and maintainable C++ code.
 C++ function declarations and definitions
Apr 11, 2024 pm 01:27 PM
C++ function declarations and definitions
Apr 11, 2024 pm 01:27 PM
Function declaration and definition are necessary in C++. Function declaration specifies the return type, name and parameters of the function, while function definition contains the function body and implementation. First declare the function and then use it in your program passing the required parameters. Use the return statement to return a value from a function.
 C++ compilation error: function call does not match function declaration, how to solve it?
Aug 22, 2023 pm 12:39 PM
C++ compilation error: function call does not match function declaration, how to solve it?
Aug 22, 2023 pm 12:39 PM
C++ compilation error: function call does not match function declaration, how to solve it? When developing C++ programs, you will inevitably encounter some compilation errors. One of the common errors is that the function call does not match the function declaration. This kind of error widely exists among C++ programmers. Due to not paying attention to the correctness of function declaration, it leads to compilation problems, which ultimately wastes time and energy to fix the problem and affects development efficiency. Ways to avoid this mistake require following some norms and standard practices, let’s take a look at them below. What is a function call versus a function declaration?
![[[nodiscard]] in C++ function declarations: Demystifying the consequences of ignoring return values](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/465/014/171455868319393.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) [[nodiscard]] in C++ function declarations: Demystifying the consequences of ignoring return values
May 01, 2024 pm 06:18 PM
[[nodiscard]] in C++ function declarations: Demystifying the consequences of ignoring return values
May 01, 2024 pm 06:18 PM
The [[nodiscard]] attribute indicates that the return value of the function must not be ignored, otherwise it will cause a compiler warning or error to prevent the following consequences: uninitialized exceptions, memory leaks, and incorrect calculation results.
 Detailed syntax of C++ function declaration: from syntax analysis to standard usage analysis
Apr 30, 2024 pm 02:54 PM
Detailed syntax of C++ function declaration: from syntax analysis to standard usage analysis
Apr 30, 2024 pm 02:54 PM
The C++ function declaration syntax is: returnTypefunctionName(parameterType1parameterName1,...,parameterTypeNparameterNameN);, where returnType is the return type, functionName is the function name, parameterType is the parameter type, and parameterName is the parameter name, which must end with a semicolon.
 A step-by-step guide to C++ function declaration: detailed instructions covering every step
May 02, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
A step-by-step guide to C++ function declaration: detailed instructions covering every step
May 02, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
A function declaration tells the compiler that a function exists without providing a function body. The steps are as follows: specify the function return type (void if there is no return value) define the function name and declare the function parameters (optional, including data type and identifier) plus semicolon




