 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Python code to implement client-side and server-side image transmission
Python code to implement client-side and server-side image transmission
Python code to implement client-side and server-side image transmission
The content of this article is about the code for python to realize client and server-side image transmission. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Problem: Use windows as the client and linux as the server to transfer the graph
Program:
'''
Fuction:客户端发送图片和数据
Date:2018.9.8
Author:snowking
'''
###客户端client.py
import socket
import os
import sys
import struct
def sock_client_image():
while True:
try:
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect(('服务器的ip', 6666)) #服务器和客户端在不同的系统或不同的主机下时使用的ip和端口,首先要查看服务器所在的系统网卡的ip
# s.connect(('127.0.0.1', 6666)) #服务器和客户端都在一个系统下时使用的ip和端口
except socket.error as msg:
print(msg)
print(sys.exit(1))
filepath = input('input the file: ') #输入当前目录下的图片名 xxx.jpg
fhead = struct.pack(b'128sq', bytes(os.path.basename(filepath), encoding='utf-8'), os.stat(filepath).st_size) #将xxx.jpg以128sq的格式打包
s.send(fhead)
fp = open(filepath, 'rb') #打开要传输的图片
while True:
data = fp.read(1024) #读入图片数据
if not data:
print('{0} send over...'.format(filepath))
break
s.send(data) #以二进制格式发送图片数据
s.close()
# break #循环发送
if __name__ == '__main__':
sock_client_image()###服务器端server.py
import socket
import os
import sys
import struct
def socket_service_image():
try:
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
# s.bind(('127.0.0.1', 6666))
s.bind(('服务器的ip', 6666))
s.listen(10)
except socket.error as msg:
print(msg)
sys.exit(1)
print("Wait for Connection.....................")
while True:
sock, addr = s.accept() #addr是一个元组(ip,port)
deal_image(sock, addr)
def deal_image(sock, addr):
print("Accept connection from {0}".format(addr)) #查看发送端的ip和端口
while True:
fileinfo_size = struct.calcsize('128sq')
buf = sock.recv(fileinfo_size) #接收图片名
if buf:
filename, filesize = struct.unpack('128sq', buf)
fn = filename.decode().strip('\x00')
new_filename = os.path.join('./', 'new_' + fn) #在服务器端新建图片名(可以不用新建的,直接用原来的也行,只要客户端和服务器不是同一个系统或接收到的图片和原图片不在一个文件夹下)
recvd_size = 0
fp = open(new_filename, 'wb')
while not recvd_size == filesize:
if filesize - recvd_size > 1024:
data = sock.recv(1024)
recvd_size += len(data)
else:
data = sock.recv(1024)
recvd_size = filesize
fp.write(data) #写入图片数据
fp.close()
sock.close()
break
if __name__ == '__main__':
socket_service_image()Running results:
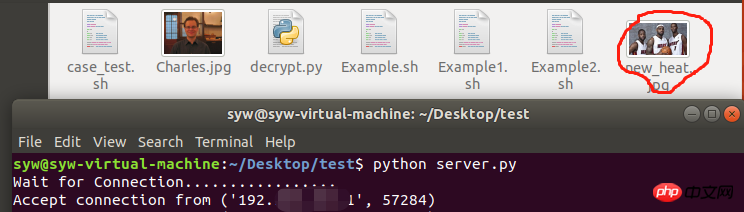
Server side:
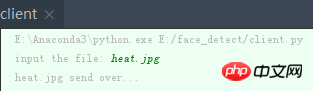
Client side:
Additional instructions:
1. First run server.py (python server.py) under the linux system, then run client.py under the windows python terminal, and enter the name of the image to be transferred in the current directory in the terminal, which is heat .jpg, you can see that the new_heat.jpg image file appears in the server path, proving that the file transfer is successful.
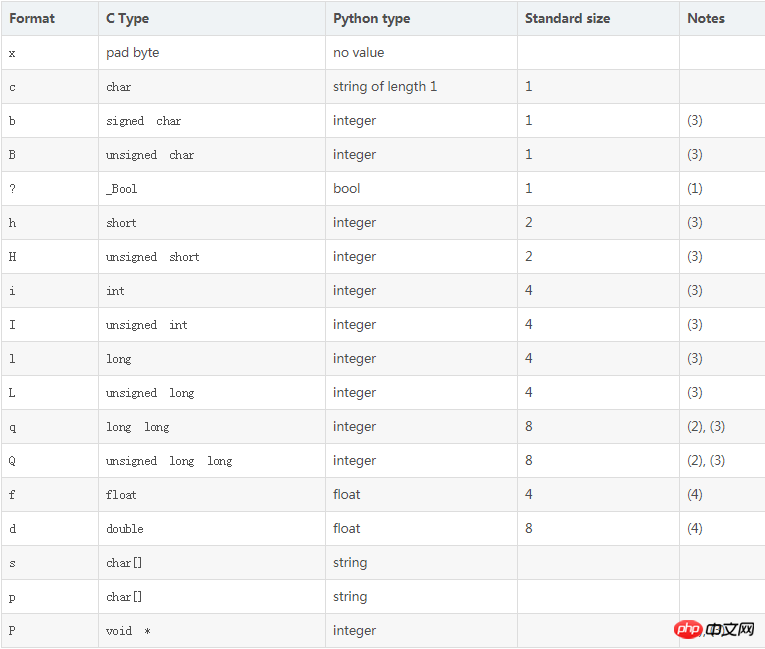
2. At first, various errors occurred when referring to the code on the Internet. During debugging, the received image data kept being lost and the image could not be opened. After understanding the compression format of struct.pack, I found that the reason was The problem with parameter setting was originally 128sl, where l is a long integer. If it exceeds the range, the received picture data will be lost. Therefore, after changing to q, the range becomes larger and pictures can be received normally. The following figure is the compression format and data range correspondence table of struct.pack:
Related recommendations:
Python XML RPC server And client examples
Detailed explanation of the method of implementing TCP server and client in python
The above is the detailed content of Python code to implement client-side and server-side image transmission. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 How to switch Chinese mode with vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:39 PM
How to switch Chinese mode with vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:39 PM
VS Code To switch Chinese mode: Open the settings interface (Windows/Linux: Ctrl, macOS: Cmd,) Search for "Editor: Language" settings Select "Chinese" in the drop-down menu Save settings and restart VS Code
 vscode setting Chinese tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
vscode setting Chinese tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
VS Code supports Chinese settings, which can be completed by following the steps: Open the settings panel and search for "locale". Set "locale.language" to "zh-CN" (Simplified Chinese) or "zh-TW" (Traditional Chinese). Save settings and restart VS Code. The settings menu, toolbar, code prompts, and documents will be displayed in Chinese. Other language settings can also be customized, such as file tag format, entry description, and diagnostic process language.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 vscode Previous Next Shortcut Key
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
vscode Previous Next Shortcut Key
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
VS Code One-step/Next step shortcut key usage: One-step (backward): Windows/Linux: Ctrl ←; macOS: Cmd ←Next step (forward): Windows/Linux: Ctrl →; macOS: Cmd →
 How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is a cross-platform, open source and free code editor developed by Microsoft. It is known for its lightweight, scalability and support for a wide range of programming languages. To install VSCode, please visit the official website to download and run the installer. When using VSCode, you can create new projects, edit code, debug code, navigate projects, expand VSCode, and manage settings. VSCode is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, supports multiple programming languages and provides various extensions through Marketplace. Its advantages include lightweight, scalability, extensive language support, rich features and version
 What is the difference between vscode and pycharm
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
What is the difference between vscode and pycharm
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
The main differences between VS Code and PyCharm are: 1. Extensibility: VS Code is highly scalable and has a rich plug-in market, while PyCharm has wider functions by default; 2. Price: VS Code is free and open source, and PyCharm is paid for professional version; 3. User interface: VS Code is modern and friendly, and PyCharm is more complex; 4. Code navigation: VS Code is suitable for small projects, and PyCharm is more suitable for large projects; 5. Debugging: VS Code is basic, and PyCharm is more powerful; 6. Code refactoring: VS Code is basic, and PyCharm is richer; 7. Code



