
The content of this article is about whether String in Java is mutable? (Detailed explanation of examples) has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
We all know that the design of the String class in Java is immutable. Let’s take a look at the source code of the String class.
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {
/** The value is used for character storage. */
private final char value[];
/** Cache the hash code for the string */
private int hash; // Default to 0
// ...
}It can be seen that the String class is of final type, and String cannot be inherited. Its value value is the encapsulation of the character array, that is, char[]. Its value is defined as private final, which means it cannot be modified by the outside world, that is, it is immutable.
Look at the following example.
String str = "Python"; System.out.println(str); // Python str = "Java"; System.out.println(str); // Java str = str.substring(1); System.out.println(str); // ava
You may ask: Didn’t str change from Python to Java? Then it becomes ava through the substring method?
This is actually a misunderstanding among beginners. Looking at the structure of String above, we can know that strings are composed of character arrays. str is just a reference. The first reference is "Python" , later changed to "Java", and substring also uses the Arrays.copyOfRange method to re-copy the character array to construct a new string.
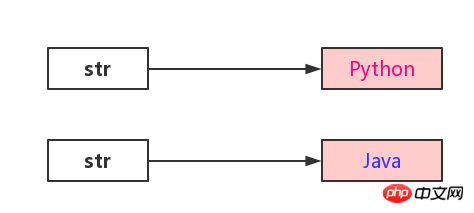
So, the string here is not variable, just the string reference is changed.
Regarding the differences between substring in various versions of JDK, you can read this article "Note: Differences in string substring methods in jkd6, 7, and 8". You can also look at the source code of each version of substring.
The above example is definitely immutable, but the following one is embarrassing.
String str = "Hello Python";
System.out.println(str); // Hello Python
Field field = String.class.getDeclaredField("value");
field.setAccessible(true);
char[] value = (char[])field.get(str);
value[6] = 'J';
value[7] = 'a';
value[8] = 'v';
value[9] = 'a';
value[10] = '!';
value[11] = '!';
System.out.println(str); // Hello Java!!Through reflection, we change the value of the underlying character array and realize the "immutability" of the string. This is a rude operation and is not recommended. It violates Java's requirements for the String class. The immutable design principle can cause some security issues.
The above is the detailed content of Is String mutable in Java? (detailed examples). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!