 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 How to install Nodejs and deploy projects on cloud server ECS instances
How to install Nodejs and deploy projects on cloud server ECS instances
How to install Nodejs and deploy projects on cloud server ECS instances
The content of this article is about how to install Nodejs and deploy projects on cloud server ECS instances. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Deploying Node.js project (CentOS)
Node.js is a JavaScript running environment based on the Chrome V8 engine, used to easily build fast and easy-to-expand network applications. Node.js uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model, making it lightweight and efficient, and very suitable for data-intensive real-time applications running on distributed devices. npm, the Node.js package manager, is the world's largest open source library ecosystem. Typical application scenarios include:
Real-time applications: such as online chat, real-time notification push, etc. (such as socket.io)
Distributed applications: using existing applications through efficient parallel I/O Data
Tool applications: A large number of tools, ranging from front-end compression deployment (such as grunt) to desktop graphical interface applications
Game applications: The game field has real-time and concurrency requirements Very high requirements (such as NetEase's pomelo framework)
Use stable interfaces to improve Web rendering capabilities
Unified front-end and back-end programming language environments: front-end developers can quickly switch to server-side development ( Such as the famous pure Javascript full-stack MEAN architecture)
Applicable objects
This document introduces how to use cloud server ECS in Alibaba Cloud CentOS system On the instance, install Nodejs and deploy the project.
Preparation
Before deployment, please make the following preparations:
Purchase ECS instance
The image your instance runs is CentOS7.2
Your instance can connect to the public network
Tools for connecting to Linux instances, such as PuTTY, have been installed locally.
Basic process
The steps to install Nodejs and deploy the project using cloud server ECS are as follows:
Purchase an ECS instance, and connect to the instance.
Choose any of the following methods to deploy the Node.js environment:
Use binary files.
Use NVM to install multiple versions.
Deploy the test project.
Operation steps
Step 1: Create an ECS instance
Create an ECS instance. Select the operating system as the public image CentOS7.2. Log in to the Linux instance as the root user.
Step 2: Deploy the Node.js environment
Use any of the following methods to deploy the Node.js environment.
Installation using binary files
The installation package used in this deployment process is a compiled binary file. After decompression, node and npm already exist in the bin folder, no manual compilation is required.
Installation steps:
wget command to download the Node.js installation package. The installation package is a compiled file. After decompression, node and npm already exist in the bin folder, so there is no need to recompile.
wget https://nodejs.org/dist/v6.9.5/node-v6.9.5-linux-x64.tar.xz
Unzip the file.
tar xvf node-v6.9.5-linux-x64.tar.xz
Create soft links to make node and npm commands globally valid. By creating soft links, you can directly use node and npm commands in any directory:
ln -s /root/node-v6.9.5-linux-x64/bin/node /usr/local/bin/node ln -s /root/node-v6.9.5-linux-x64/bin/npm /usr/local/bin/npm
View node and npm versions.
node -v npm -v
At this point, the Node.js environment has been installed. The software is installed in the /root/node-v6.9.5-linux-x64/ directory by default. If you need to install the software to other directories (such as: /opt/node/), please do the following:
mkdir -p /opt/node/ mv /root/node-v6.9.5-linux-x64/* /opt/node/ rm -f /usr/local/bin/node rm -f /usr/local/bin/npm ln -s /opt/node/bin/node /usr/local/bin/node ln -s /opt/node/bin/npm /usr/local/bin/npm
Use NVM to install multiple versions
NVM (Node version manager) is Node.js version management software allows users to easily switch between various versions of Node.js. It is suitable for people who have been doing node development for a long time or users who need to quickly update node versions and switch node versions quickly.
Installation steps:
Use git directly to clone the source code to the local ~/.nvm directory, and check the latest version.
yum install git git clone https://github.com/cnpm/nvm.git ~/.nvm && cd ~/.nvm && git checkout `git describe --abbrev=0 --tags`
Activate NVM.
echo ". ~/.nvm/nvm.sh" >> /etc/profile source /etc/profile
List all versions of Node.js.
nvm list-remote
Install multiple Node.js versions.
nvm install v6.9.5 nvm install v7.4.0
Run nvm ls to check the installed Node.js version. The current version is v6.9.5. The returned results are as follows.
[root@iZXXXXZ .nvm]# nvm ls
v6.9.5
-> v7.4.0
system
stable -> 7.4 (-> v7.4.0) (default)
unstable -> 6.9 (-> v6.9.5) (default)Run nvm use v7.4.0 to switch the Node.js version to v7.4.0. The returned results are as follows.
[root@iZXXXXZ .nvm]# nvm use v7.4.0 Now using node v7.4.0
For more operations on NVM, please refer to the help document:
nvm help
Step 3: Deploy the test project
Create a new project file example.js.
cd ~ touch example.js
Use vim editor to open the project file example.js.
yum install vim vim example.js
Enter i to enter editing mode and paste the following project file contents into the file. Use the Esc button to exit editing mode, enter: wq, press Enter, save the file content and exit.
Project file content:
const http = require('http');
const hostname = '0.0.0.0';
const port = 3000;
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.statusCode = 200;
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain');
res.end('Hello World\n');
});
server.listen(port, hostname, () => {
console.log(`Server running at http://${hostname}:${port}/`);
});Note:
3000 in the project file content is the port number, which can be defined by yourself.
Run the project.
node ~/example.js
Note:
You can use the command node ~/example.js & to put the project in the background.
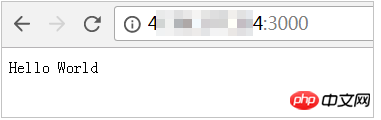
Use the command to check whether the project port exists.
netstat -tpln
登录ECS管理控制台,并在安全组中 添加安全组规则 放行端口(如本示例中为TCP 3000端口)。
(可选)如果您的实例中开启了防火墙,必须添加端口的入站规则(如本示例中为TCP 3000端口)。
在本地机器的浏览器中输入 http://实例公网IP地址:端口号 访问项目。
The above is the detailed content of How to install Nodejs and deploy projects on cloud server ECS instances. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
Steps to start Nginx in Linux: Check whether Nginx is installed. Use systemctl start nginx to start the Nginx service. Use systemctl enable nginx to enable automatic startup of Nginx at system startup. Use systemctl status nginx to verify that the startup is successful. Visit http://localhost in a web browser to view the default welcome page.
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP
 How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Answer to the question: 304 Not Modified error indicates that the browser has cached the latest resource version of the client request. Solution: 1. Clear the browser cache; 2. Disable the browser cache; 3. Configure Nginx to allow client cache; 4. Check file permissions; 5. Check file hash; 6. Disable CDN or reverse proxy cache; 7. Restart Nginx.
 How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
In Linux, use the following command to check whether Nginx is started: systemctl status nginx judges based on the command output: If "Active: active (running)" is displayed, Nginx is started. If "Active: inactive (dead)" is displayed, Nginx is stopped.
 How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
The server does not have permission to access the requested resource, resulting in a nginx 403 error. Solutions include: Check file permissions. Check the .htaccess configuration. Check nginx configuration. Configure SELinux permissions. Check the firewall rules. Troubleshoot other causes such as browser problems, server failures, or other possible errors.
 How to solve nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to solve nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to fix Nginx 403 Forbidden error? Check file or directory permissions; 2. Check .htaccess file; 3. Check Nginx configuration file; 4. Restart Nginx. Other possible causes include firewall rules, SELinux settings, or application issues.
 How to clean nginx error log
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to clean nginx error log
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
The error log is located in /var/log/nginx (Linux) or /usr/local/var/log/nginx (macOS). Use the command line to clean up the steps: 1. Back up the original log; 2. Create an empty file as a new log; 3. Restart the Nginx service. Automatic cleaning can also be used with third-party tools such as logrotate or configured.



