 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Detailed introduction to python multi-process (with examples)
Detailed introduction to python multi-process (with examples)
Detailed introduction to python multi-process (with examples)
The content of this article is about what is SAPI in PHP? How to achieve? (Pictures and text), it has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Process
Python is a language that runs in the interpreter. Looking for information, we know that there is a global lock (GIL) in Python, which cannot be used when using multiple processes (Thread). Advantages of multi-core. By using Multiprocess, you can take advantage of multi-core to truly improve efficiency.
If the multi-threaded process is CPU-intensive, then multi-threading will not improve efficiency much. On the contrary, it may also cause efficiency to decrease due to frequent switching of threads. It is recommended to use multi-process; if it is IO-intensive , multi-threaded processes can use the idle time while waiting for IO blocking to execute other threads to improve efficiency.
Creating a process
Special methods for Linux and mac systems
1. The principle of creating a child process in Linux:
1). Parent process and child process, if the parent process ends , the child process also ends;
2). There is the parent process first, and then the child process, which is implemented through the fork function;
2. The return value of the fork function: Call this method once, and return two times;
The generated child process returns a 0
The parent process returns the pid of the child process;
3. Can Window also use the fork function?
Windows没有fork函数, Mac有fork函数(Unix -> Linux, Unix-> Mac), 封装了一个模块multiprocessing
4. Commonly used methods:
os.fork()
os.getpid(): Get the pid of the current process;
os.getppid(): parent process id, get the id number of the parent process of the current process;
import os
import time
print("当前进程(pid=%d)正在运行..." %(os.getpid()))
print("当前进程的父进程(pid=%d)正在运行..." %(os.getppid()))
print("正在创建子进程......")
pid = os.fork()
pid2 = os.fork()
print("第1个:", pid)
print("第2个: ", pid2)
if pid == 0:
print("这是创建的子进程, 子进程的id为%s, 父进程的id为%s"
%(os.getpid(), os.getppid()))
else:
print("当前是父进程[%s]的返回值%s" %(os.getpid(), pid))
time.sleep(100)win system
Under the win system, when creating a process using instantiation multiprocessing.Process, you must add 'if __name__=="__main__"', otherwise the following error will appear:
RuntimeError:
An attempt has been made to start a new process before the current process has finished its bootstrapping phase. This probably means that you are not using fork to start your child processes and you have forgotten to use the proper idiom in the main module: if __name__ == '__main__': freeze_support() ... The "freeze_support()" line can be omitted if the program is not going to be frozen to produce an executable.
import multiprocessing
def job():
print("当前子进程的名称为%s" %(multiprocessing.current_process()))
if __name__=="__main__": #win操作系统需要加上,否则会出现异常报错RuntimeError
# 创建一个进程对象(group=None, target=None, name=None, args=(), kwargs={})
p1 = multiprocessing.Process(target=job)
p2 = multiprocessing.Process(target=job)
# 运行多进程, 执行任务
p1.start()
p2.start()
# 等待所有的子进程执行结束, 再执行主进程的内容
p1.join()
p2.join()
print("任务执行结束.......")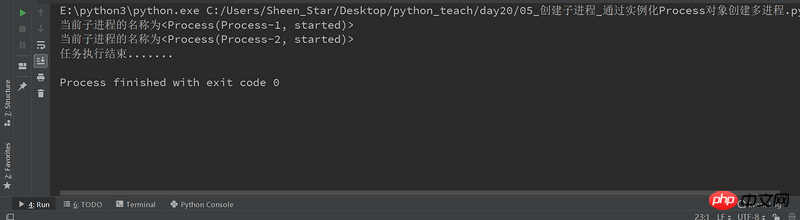
Create multiple processes by overriding the multiprocessing.Process class
from multiprocessing import Process
import multiprocessing
class JobProcess(Process):
# 重写Process的构造方法, 获取新的属性
def __init__(self,queue):
super(JobProcess, self).__init__()
self.queue = queue
# 重写run方法, 将执行的任务放在里面即可
def run(self):
print("当前进程信息%s" %(multiprocessing.current_process()))
if __name__=="__main__":
processes = []
# 启动10个子进程, 来处理需要执行的任务;
for i in range(10):
#示例化类,创建进程
p = JobProcess(queue=3)
processes.append(p)
#启动多进程,执行任务
p.start()
#等待所有的子进程结束,再执行主进程
[pro.join() for pro in processes]
print("任务执行结束") 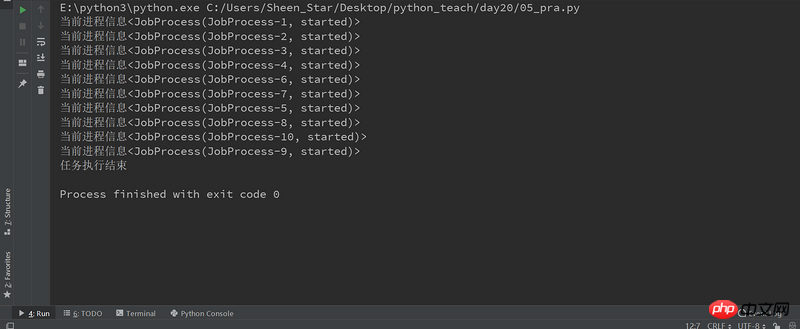
Daemon process
Daemon thread:
setDeamon: True: 主线程执行结束, 子线程不再继续执行; Flase:
Daemon process:
setDeamon: True: 主进程执行结束, 子进程不再继续执行; Flase:
Terminate the process
Some processes may perform infinite loop tasks again. At this time, we manually terminate the process
terminate()
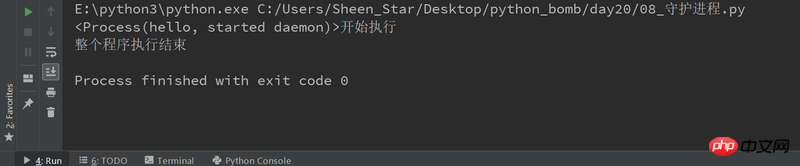
import multiprocessing
import time
def deamon():
#守护进程:当主程序运行结束,子进程也结束
name = multiprocessing.current_process()
print("%s开始执行" %(name))
time.sleep(3)
print("执行结束")
if __name__=="__main__":
p1 = multiprocessing.Process(target=deamon,name='hello')
p1.daemon = True
p1.start()
time.sleep(2)
print("整个程序执行结束")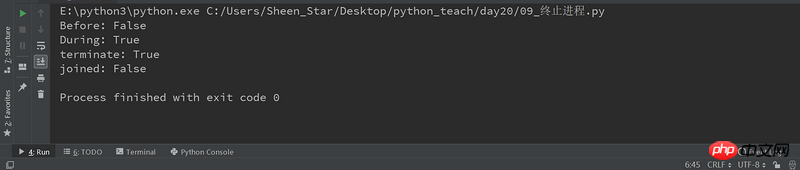
多线程模式通常比多进程快一点, 但是也快不到哪去, 而且, 多线程模式致命的缺点就是任何一个线程挂掉都可能直接造成整个进程崩溃, 因为所有线程共享进程的内存。 在Windows上, 如果一个线程执行的代码出了问题, 你经常可以看到这样的提示:“该程序执行了非法操作, 即将关闭”, 其实往往是某个线程出了问题, 但是操作系统会强制结束整个进程。
这里通过一个计算密集型任务,来测试多进程和多线程的执行效率。
import multiprocessing
import threading
from mytimeit import timeit
class JobProcess(multiprocessing.Process):
def __init__(self,li):
super(JobProcess, self).__init__()
self.li = li
def run(self):
for i in self.li:
sum(i)
class JobThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self,li):
super(JobThread, self).__init__()
self.li = li
def run(self):
for i in self.li:
sum(i)
@timeit
def many_processs():
li = [[24892,23892348,239293,233],[2382394,49230,2321234],[48294,28420,29489]]*10
processes = []
for i in li :
p = JobProcess(li)
processes.append(p)
p.start()
[pro.join() for pro in processes]
print("多进程执行任务结束,✌")
@timeit
def many_thread():
#创建进程和销毁进程是时间的,如果li长度不够,会造成多线程快过多进程
li = [[24892,23892348,239293,233],[2382394,49230,2321234],[48294,28420,29489]]*1000
threads = []
for i in li :
t = JobThread(li)
threads.append(t)
t.start()
[thread.join() for thread in threads]
print("多线程执行任务结束,✌")
if __name__ =="__main__":
many_processs()
many_thread()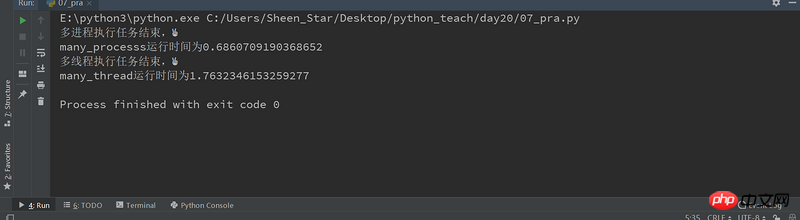
进程间通信-生产者消费者模型与队列
演示了生产者和消费者的场景。生产者生产货物,然后把货物放到一个队列之类的数据结构中,生产货物所要花费的时间无法预先确定。消费者消耗生产者生产的货物的时间也是不确定的。
通过队列来实现进程间的通信
import multiprocessing
import threading
from multiprocessing import Queue
class Producer(multiprocessing.Process):
def __init__(self,queue):
super(Producer, self).__init__()
self.queue = queue
def run(self):
for i in range(13):
#往队列添加内容
self.queue.put(i)
print("生产者传递的消息为%s" %(i))
return self.queue
class Consumer(multiprocessing.Process):
def __init__(self,queue):
super(Consumer, self).__init__()
self.queue = queue
def run(self):
#获取队列内容
#get会自动判断队列是否为空,如果是空, 跳出循环, 不会再去从队列获取数据;
while True:
print("进程获取消息为:%s" %(self.queue.get()))
if __name__=="__main__":
queue = Queue(maxsize=100)
p = Producer(queue)
p.start()
c = Consumer(queue)
c.start()
p.join()
c.join(2)
c.terminate() #终止进程
print("进程间通信结束,( •̀ ω •́ )y")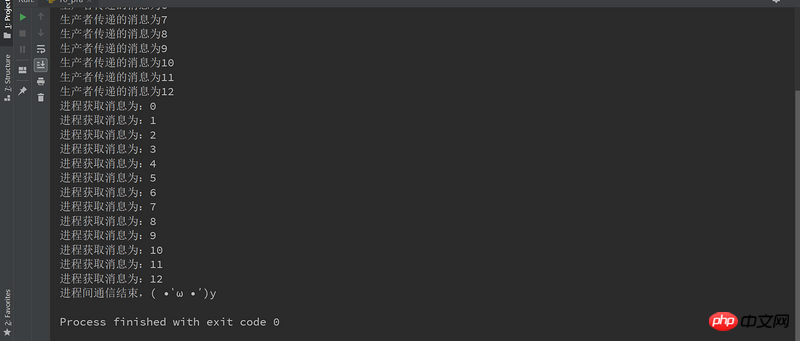
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to python multi-process (with examples). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
VS Code is the full name Visual Studio Code, which is a free and open source cross-platform code editor and development environment developed by Microsoft. It supports a wide range of programming languages and provides syntax highlighting, code automatic completion, code snippets and smart prompts to improve development efficiency. Through a rich extension ecosystem, users can add extensions to specific needs and languages, such as debuggers, code formatting tools, and Git integrations. VS Code also includes an intuitive debugger that helps quickly find and resolve bugs in your code.
 Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang is more suitable for high concurrency tasks, while Python has more advantages in flexibility. 1.Golang efficiently handles concurrency through goroutine and channel. 2. Python relies on threading and asyncio, which is affected by GIL, but provides multiple concurrency methods. The choice should be based on specific needs.
 Can visual studio code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Can visual studio code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
VS Code not only can run Python, but also provides powerful functions, including: automatically identifying Python files after installing Python extensions, providing functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Relying on the installed Python environment, extensions act as bridge connection editing and Python environment. The debugging functions include setting breakpoints, step-by-step debugging, viewing variable values, and improving debugging efficiency. The integrated terminal supports running complex commands such as unit testing and package management. Supports extended configuration and enhances features such as code formatting, analysis and version control.



