The use of routing under the Laravel framework (source code analysis)
本篇文章给大家带来的内容是关于Laravel框架下路由的使用(源码解析),有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对你有所帮助。
前言
我的解析文章并非深层次多领域的解析攻略。但是参考着开发文档看此类文章会让你在日常开发中更上一层楼。
废话不多说,我们开始本章的讲解。
入口
Laravel启动后,会先加载服务提供者、中间件等组件,在查找路由之前因为我们使用的是门面,所以先要查到Route的实体类。
注册
第一步当然还是通过服务提供者,因为这是laravel启动的关键,在 RouteServiceProvider 内加载路由文件。
protected function mapApiRoutes()
{
Route::prefix('api')
->middleware('api')
->namespace($this->namespace) // 设置所处命名空间
->group(base_path('routes/api.php')); //所得路由文件绝对路径
}首先require是不可缺少的。因路由文件中没有命名空间。 Illuminate\Routing\Router 下方法
protected function loadRoutes($routes)
{
if ($routes instanceof Closure) {
$routes($this);
} else {
$router = $this;
require $routes;
}
}随后通过路由找到指定方法,依旧是 Illuminate\Routing\Router 内有你所使用的所有路由相关方法,例如get、post、put、patch等等,他们都调用了统一的方法 addRoute
public function addRoute($methods, $uri, $action)
{
return $this->routes->add($this->createRoute($methods, $uri, $action));
}之后通过 Illuminate\Routing\RouteCollection addToCollections 方法添加到集合中
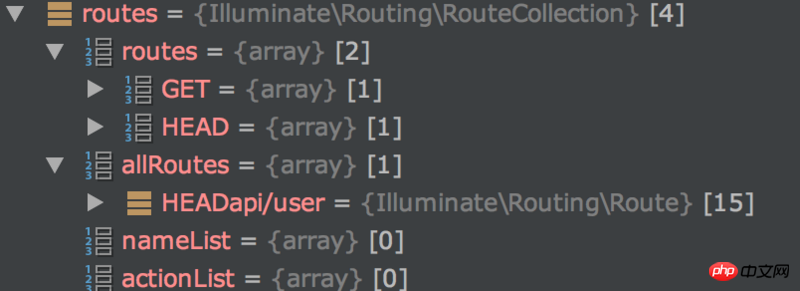
protected function addToCollections($route)
{
$domainAndUri = $route->getDomain().$route->uri();
foreach ($route->methods() as $method) {
$this->routes[$method][$domainAndUri] = $route;
}
$this->allRoutes[$method.$domainAndUri] = $route;
}添加后的结果如下图所示
调用
通过 Illuminate\Routing\Router 方法开始运行路由实例化的逻辑
protected function runRoute(Request $request, Route $route)
{
$request->setRouteResolver(function () use ($route) {
return $route;
});
$this->events->dispatch(new Events\RouteMatched($route, $request));
return $this->prepareResponse($request,
$this->runRouteWithinStack($route, $request)
);
}
....
protected function runRouteWithinStack(Route $route, Request $request)
{
$shouldSkipMiddleware = $this->container->bound('middleware.disable') &&
$this->container->make('middleware.disable') === true;
$middleware = $shouldSkipMiddleware ? [] : $this->gatherRouteMiddleware($route);
return (new Pipeline($this->container))
->send($request)
->through($middleware)
->then(function ($request) use ($route) {
return $this->prepareResponse(
$request, $route->run() // 此处调用run方法
);
});
}在 Illuminate\Routing\Route 下 run 方用于执行控制器的方法
public function run()
{
$this->container = $this->container ?: new Container;
try {
if ($this->isControllerAction()) {
return $this->runController(); //运行一个路由并作出响应
}
return $this->runCallable();
} catch (HttpResponseException $e) {
return $e->getResponse();
}
}从上述方法内可以看出 runController 是运行路由的关键,方法内运行了一个调度程序,将控制器 $this->getController() 和控制器方法 $this->getControllerMethod() 传入到 dispatch 调度方法内
protected function runController()
{
return $this->controllerDispatcher()->dispatch(
$this, $this->getController(), $this->getControllerMethod()
);
}这里注意 getController() 才是真正的将控制器实例化的方法
public function getController()
{
if (! $this->controller) {
$class = $this->parseControllerCallback()[0]; // 0=>控制器 xxController 1=>方法名 index
$this->controller = $this->container->make(ltrim($class, '\\')); // 交给容器进行反射
}
return $this->controller;
}实例化
依旧通过反射加载路由指定的控制器,这个时候build的参数$concrete = App\Api\Controllers\XxxController
public function build($concrete)
{
// If the concrete type is actually a Closure, we will just execute it and
// hand back the results of the functions, which allows functions to be
// used as resolvers for more fine-tuned resolution of these objects.
if ($concrete instanceof Closure) {
return $concrete($this, $this->getLastParameterOverride());
}
$reflector = new ReflectionClass($concrete);
// If the type is not instantiable, the developer is attempting to resolve
// an abstract type such as an Interface of Abstract Class and there is
// no binding registered for the abstractions so we need to bail out.
if (! $reflector->isInstantiable()) {
return $this->notInstantiable($concrete);
}
$this->buildStack[] = $concrete;
$constructor = $reflector->getConstructor();
// If there are no constructors, that means there are no dependencies then
// we can just resolve the instances of the objects right away, without
// resolving any other types or dependencies out of these containers.
if (is_null($constructor)) {
array_pop($this->buildStack);
return new $concrete;
}
$dependencies = $constructor->getParameters();
// Once we have all the constructor's parameters we can create each of the
// dependency instances and then use the reflection instances to make a
// new instance of this class, injecting the created dependencies in.
$instances = $this->resolveDependencies(
$dependencies
);
array_pop($this->buildStack);
return $reflector->newInstanceArgs($instances);
}这时将返回控制器的实例,下面将通过url访问指定方法,一般控制器都会继承父类 Illuminate\Routing\Controller ,laravel为其设置了别名 BaseController
public function dispatch(Route $route, $controller, $method)
{
$parameters = $this->resolveClassMethodDependencies(
$route->parametersWithoutNulls(), $controller, $method
);
if (method_exists($controller, 'callAction')) {
return $controller->callAction($method, $parameters);
}
return $controller->{$method}(...array_values($parameters));
}Laravel通过controller继承的callAction去调用子类的指定方法,也就是我们希望调用的自定义方法。
public function callAction($method, $parameters)
{
return call_user_func_array([$this, $method], $parameters);
}The above is the detailed content of The use of routing under the Laravel framework (source code analysis). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Laravel Eloquent ORM in Bangla partial model search)
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
Laravel Eloquent ORM in Bangla partial model search)
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
LaravelEloquent Model Retrieval: Easily obtaining database data EloquentORM provides a concise and easy-to-understand way to operate the database. This article will introduce various Eloquent model search techniques in detail to help you obtain data from the database efficiently. 1. Get all records. Use the all() method to get all records in the database table: useApp\Models\Post;$posts=Post::all(); This will return a collection. You can access data using foreach loop or other collection methods: foreach($postsas$post){echo$post->
 The Future of PHP: Adaptations and Innovations
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Future of PHP: Adaptations and Innovations
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The future of PHP will be achieved by adapting to new technology trends and introducing innovative features: 1) Adapting to cloud computing, containerization and microservice architectures, supporting Docker and Kubernetes; 2) introducing JIT compilers and enumeration types to improve performance and data processing efficiency; 3) Continuously optimize performance and promote best practices.
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 Laravel's geospatial: Optimization of interactive maps and large amounts of data
Apr 08, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
Laravel's geospatial: Optimization of interactive maps and large amounts of data
Apr 08, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
Efficiently process 7 million records and create interactive maps with geospatial technology. This article explores how to efficiently process over 7 million records using Laravel and MySQL and convert them into interactive map visualizations. Initial challenge project requirements: Extract valuable insights using 7 million records in MySQL database. Many people first consider programming languages, but ignore the database itself: Can it meet the needs? Is data migration or structural adjustment required? Can MySQL withstand such a large data load? Preliminary analysis: Key filters and properties need to be identified. After analysis, it was found that only a few attributes were related to the solution. We verified the feasibility of the filter and set some restrictions to optimize the search. Map search based on city
 PHP's Current Status: A Look at Web Development Trends
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
PHP's Current Status: A Look at Web Development Trends
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
PHP remains important in modern web development, especially in content management and e-commerce platforms. 1) PHP has a rich ecosystem and strong framework support, such as Laravel and Symfony. 2) Performance optimization can be achieved through OPcache and Nginx. 3) PHP8.0 introduces JIT compiler to improve performance. 4) Cloud-native applications are deployed through Docker and Kubernetes to improve flexibility and scalability.
 Laravel and the Backend: Powering Web Application Logic
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Laravel and the Backend: Powering Web Application Logic
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:29 AM
How does Laravel play a role in backend logic? It simplifies and enhances backend development through routing systems, EloquentORM, authentication and authorization, event and listeners, and performance optimization. 1. The routing system allows the definition of URL structure and request processing logic. 2.EloquentORM simplifies database interaction. 3. The authentication and authorization system is convenient for user management. 4. The event and listener implement loosely coupled code structure. 5. Performance optimization improves application efficiency through caching and queueing.
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.




